Stage 9 Review Note to all of you: This review is just that: a review
advertisement

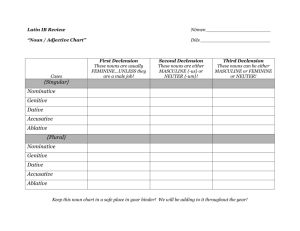
Stage 9 Review Note to all of you: This review is just that: a review. The questions here might be on the test as they are here or in a different form (as in, what might be in multiple choice here could be in true or false on the test). Use this as practice test. But of course, a practice test with your notes and a book… Reading Comprehension In this section of the test, you’re given a short story to read in Latin. Feel free to translate sentences on the test but you will not be asked to translate. Instead, you will be asked questions regarding the events of the story and then a few questions on grammar. Keep in mind that on the test, the questions will be multiple choice. This story is taken from the previous stage’s test. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 pugnax erat gladiator notissimus. mercator Graecus iuvenem cepit et eum in foro Pompeiano vendidit. Pugnax tamen de vita non desperabat quod erat fortis. lanista, qui multos gladiators habebat, Pugnacem emit. cotidie ille homo insanus eum verberabat, postquam alius gladiator Pugnacem superavit. pugnax tamen non erat perterritus. tandem magnus dies advenit hodie dives senator magnum spectaculum in amphitheatre edebat. omnes Pompeiani errant otiosi, et cives caveam complebant multi Pompeiani aderant – senatores, senes, iuvenes, feminae, puellae et pueri. postquam tuba sonuit, murmillones pugnam commiserunt tum nuntius aliam pugnam nuntiavit, et Pugnax arenam fortiter intravit. duos retiarios facile superavit, et turba commota mortem poscebat. Pugnax erat laetissimus, et retiarios facile interfecit. sed leonem ingentem in amphitheatro non vidit. leo rudivit. subito leo impetum fecit. eheu! victor pugnax erat mortuus. saepe nunc Pompeiani umbram mirabilem in via et in arena vident. Words and Phrases eum – him de vita … desperabat – was desperate about his life lanista – gladiator trainer qui – who cotidie – every day ille homo – that man insanus – insane verberabat – was beating alius – another tandem – at last magnus dies – big day advenit – arrived dives – rich edebat – was presenting otiosi – at leisure cives – citizens caveam – seating area complebant – were filling up pugnam commiserunt – began the fight fortiter – bravely commota – moved poscebat – was demanding interfecit – killed rudivit – roared impetum fecit - attacked 1. Who was Pugnax? Why was his name a good descriptor of his character? (think of its Latin definition) Pugnax was a gladiator and his name was a good descriptor because his name means “fight”, which is essentially what he does. 2. Who seized Pugnax? What did that person do to Pugnax afterwards? A Greek merchant took Pugnax and sold him afterwords. 3. Pugnax wasn’t worry about what was happening because he was…. a. an optimist b. too dumb to worry c. brave 4. Circle whether or not this sentence is true or false. If it is false, change it so that it would become true. Verum / Falsum The Nucerians were putting on a great show in the amphitheater. 5. What type of fighters did Pugnax go up against? What did the crowd want at their defeat? He went up against the Retiarii (net-fighters). The crowd wanted their death at their defeat. 6. Who killed Pugnax? Where do Pompeians sometimes see the ghost of Pugnax? Puganx was killed by a lion. Pompeians sometimes see his ghost in the arena. Grammar Identify the following grammar/structure items based on the content of the above story. 7. In line 1, the declension of gladiator is 3rd declension. 8. In line 1, notissimus is a superlative adjective. 9. In line 1, the tense of cepit is perfect. 10. In line 2, the subject of vendidit is Greek merchant (Mercator Graecus). 11. In line 3, the tense of erat is imperfect. 12. In line 4, insanus is a positive adjective. 13. In line 5, the declension of Pugnacem is 3rd declension. 14. In line 7, the declension of Pompeiani is 2nd declension. 15. In line 9, the declension of feminae is 1st declension. 16. In line 12, the part of speech of facile is adverb. Nouns – Cases Identify the case and number (singular/plural) of the underlined nouns and then translate. Remember: case = nominative, dative, accusative 17. agricola gladiatores laudavit. Accusative plural The farmer praised the gladiators. 18. agricola gladiatores laudavit. Nominative singular The farmer praised the gladiators. 19. venalicius servos in foro vendidit. Accusative plural The slave dealer sells/sold servants in the forum. 20. senes spectaculum spectant. Nominative plural The old men are watching the spectacle/show. 21. puella gladiatoribus tunicas dedit. Dative plural The girl gave togas to the gladiators. 22. servi feminae stolas ostendebant. Dative singular The servants/slaves were showing the stolas to the woman. 23. centurio venalicio gladium offerebat. Nominative singular The centurion (Roman soldier) was offering a sword to the slave dealer. 24. canis servis signum dedit. Accusative singular The dog gave a sign to the servants. Datives v. Accusatives Translate the underlined word into its correct Latin form. Hint: the underlined words are either the direct or the indirect object of the sentence. 25. poeta to the spectators fabulam narravit. (spectator) spectatoribus 26. dominus to Melissa pecuniam dat. (Melissa) Melissae 27. coquus tibi food dedit. (cibus) cibum 28. mercator gladiatori tunics vendit. (tunica) tunicas 29. ancilla to Quintus vinum dat. (Quintus) Quinto 30. Marcellus to the women tunicas vendit. (femina) feminis 31. servus pueris discus tradidit. (discus) discum 32. coquus for the youths cenam coquit. (iuvenis) iuvenibus 33. Melissa for the girl donum emit. (puella) puellae 34. athleta mihi money dedit. (pecunia) pecuniam What do these cases do? nominative dative accusative Match the correct purpose to its case name. c b a a. direct object of the sentence b. indirect object of the sentence – “to”, “for” c. subject of the sentence English Identification Can you identify what the nominative, dative, and accusative cases are in English? Not all nouns will have cases at the moment. You currently only know 3 out of the 5 cases. Example: James gave a rose to Hannah from the garden of his mother. nominative accusative dative Luke fed cheese puffs of his brother to Palm from his highchair. N A D Jack kicked Palm’s soccer ball to Luke with his left foot. N Endings A D Fill in the chart as best as you can. 1f 2m 2n 3mf 3n nominative a us um ** ** dative ae o o i i accusative am um um em ** nominative ae i a es a dative is is is ibus ibus accusative as os a es a For the following words, decline each in the dative case. Make sure you make both the singular and plural forms. Dative singular Dative plural Declension # 1. scaena, scaenae scaenae scaenis 1 2. dominus, domini domino dominis 2 3. mendax, mendacis mendaci mendacem 3 4. civis, civis civi civibus 3 5. toga, togae togae togis 1