Functions Based Behavior Intervention Planning From FBA to BIP
advertisement

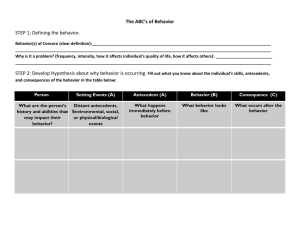
Functions Based Behavior Intervention Planning From FBA to BIP Day Two Vermont PBiS Team Tiffany Cassano, Ken Kramberg, Richard Boltax Welcome Back!! COMPETING PATHWAYS CHART STUDENT: DATE: SCHOOL: GRADE: Related Events (Setting Events) TEACHER: Desired Behavior Maintaining Consequences Problem Behavior Maintaining Consequences Antecedent Events Acceptable Alternative INTERVENTION PLAN Related Events/Strategies Antecedent Strategies Behavior Problem Adapted from Sugai, Lewis-Palmer, & Hagan, 1999 Desired Consequences/Strategies Problem Desired Review of Functions Based Assessment • D.A.S.H • Use team process • Use Competing Behavior Pathway to build behavior intervention plan What do we do with This Information? If the team has confidence in the hypothesis Develop/I mplement a Behavior Support Plan Simple FBA If the team does not have confidence in the hypothesis Gather More Informatio n: Do at Full FBA Competing Behavior Pathways Desired Behavior 3 Literacy Class 2 Independent Work 5 Remains on Task, complete work tasks independently 1 Makes noises, taps pencil Receives positive reinforcement for staying on task and completing work. 4 Teacher assists student Attention Fundamental Rule! “You should not propose to reduce a problem behavior without also identifying alternative, desired behaviors person should perform instead of problem behavior” (O’Neill et al., 1997, p. 71). Competing Behavior Pathways 5 Remains on Task, complete work tasks independently 3 Literacy Class 2 Independent Work 1 Makes noises, taps pencil 6 Raises hand when he needs assistance Receives positive reinforcement for staying on task and completing work. 4 Teacher assists student Attention Activity 1 Using the post its on your table, write the setting event, antecedent, behavior, maintaining consequence, replacement behavior, desired behavior and new maintaining consequence for your team’s student in one of the blank Competing Behavior Pathways. Group Share Tell us about your student. What is the… Observable behavior you chose? Antecedent? Setting Event? Consequences? Hypothesis of Function of Behavior Selected Desire Behavior Replacement Behavior Activity 2 With your team, discuss and modify the Competing Behavior Pathway for your student. (Upper Portion Only) Group Share Which Strategy did you choose to try? How did it go? Setting Event Strategies Antecedent Strategies Teaching Strategies Consequence Strategies Eliminate/ neutralize setting events Modify or remove triggers to prevent problem behavior Teach alternative that is more efficient Add effective reinforcers for alternative and desired behavior Teach desired skills Minimize reinforcement (“payoff”) for problem behavior Prompt alternative and/or desired behavior Behavior Intervention Program (BIP) •Two Goals: Reduce problem behaviors Increase appropriate behaviors •Make behaviors: Irrelevant Inefficient ineffective Function Based Strategies • The team will consider the FUNCTION of the problem behavior when identifying: Setting Event Strategies Antecedent Strategies Teaching Strategies Consequence Strategies Eliminate/ neutralize setting events Modify or remove triggers to prevent problem behavior Teach alternative that is more efficient Add effective reinforcers for alternative and desired behavior Teach desired skills Minimize reinforcement (“payoff”) for problem behavior Prompt alternative and/or desired behavior Setting Event Strategies These are structural changes made to the students day or classroom Alternative Schedule Sitting Near the Teacher Lunch in the support room Student Check In Early or late entry to class/activity T Cassano 2011 Antecedent Strategies Antecedent Strategies Antecedent strategies are designed to make problem behavior irrelevant by: 1. Eliminating or Modifying antecedents that “trigger” the behavior Setting Event Strategies Eliminate or Neutralize Setting Events Manipulate Antecedent Prevent/Modify “Triggers” Teach Behavior Alter Consequences Teach Alternate Behavior Reinforce Alt/Des Behavior Teach Desired Behavior/ Academic/ Social Skills Response to Problem Behavior/ Corrective Feedback AND 2. Prompting alternative/Desired behavior (precorrection) Prompts for Alt/Des Behavior Identifying Antecedent Strategies • When asked to read independently at his seat, Ronnie makes inappropriate noises and makes faces at peers. Based on the FBA data collected, the team agreed that the function of Ronnie’s behavior is to obtain peer attention. Addresses: 1.Antecedent? Function? • Which is the best antecedent modifying strategy? • • • • • Provide student with an easier reading assignment Remind student of expectations related to respectful behavior Allow student to wear headphones during independent reading Ask student to work quietly 1:1 with a ‘reading buddy’ Have student check in with the teacher at the beginning of class Identifying Antecedent Strategies • When Pam is asked to work on long-division problems in math class, she argues, refuses to work, and uses profanity to avoid/escape the difficult task. • Which is the best antecedent modifying strategy to prevent problem behavior? Why or Why Not? • Move student’s seat closer to the teacher • Give student more time to complete the difficult tasks • Give student an easier math assignment she can be successful with • Warn student she will be sent to office for using profanity • Allow student to practice long-division on the computer Consequence Strategies Consequence strategies help make problem behavior ineffective by: Setting Event Strategies Manipulate Antecedent Prevent problem & prompt alternate/desired behavior Eliminate or Neutralize Setting Events Modify/Prevent “Triggers” Teach Behavior Explicitly Teach Alternative & Desired Behaviors Teach Alternate Behavior Alter Consequences Reinforce alternate & desired behavior & extinguish negative behavior Reinforce Alt/Des Behavior Reinforcing appropriate behaviors AND… Minimizing reinforcement for problem behavior Prompt Alt/Desired Behavior Teach Desired Behavior/ Academic/ Social Skills Response to Problem Behavior - Redirection -Extinction Reinforcing Alternative and Desired Behavior Behavior Intervention Program (BIP) •Two Goals: Reduce problem behaviors Increase appropriate behaviors •Make behaviors: Irrelevant Inefficient ineffective Consequences: Reinforcing the Alternative Behavior • It is extremely important that the alternative behavior is reinforced: – Immediately – Consistently and… – Results in the same type of reinforcement as the problem behavior • This is necessary for the alternative behavior to successfully compete with the problem behavior. • In other words, the problem behavior cannot happen if the student is exhibiting the desired behavior…they can’t happen at the same time! Identifying Consequence Strategies: Reinforcing Alternative/Desired Behavior • During independent seatwork, Ronnie makes inappropriate noises and makes faces at peers. The function of Ronnie’s behavior is to obtain peer attention. Function? Which are the best reinforcement strategies? Reasonable expectations? • Student is allowed to sit by a preferred peer for 15 minutes, if he is quiet and on task during seatwork every day for a week • Student will receive a “free homework pass” if he has no problem behavior during independent seatwork • When student is on task with no problem behavior for 15 minutes, he will be allowed to sit at back table and read with a peer • Student receives frequent teacher praise for staying on task • Student is allowed to work with a peer when asks appropriately Identifying Consequence Strategies: Reinforcing Alternative/Desired Behavior • During independent reading time in language arts, Audrey makes noises, talks out, and walks around the room. The FBA has shown that this behavior is maintained by adult attention. Which are the best reinforcement strategies? Why or Why Not? • Student can play a game with the teacher if she works quietly (no more than 2 talk-outs) during independent reading • Student is allowed to work with a peer when she has been quiet for 15 minutes • Student receives help from teacher if asks appropriately • Student can eat lunch with the teacher if no talk-outs for one month • Student earns a homework pass for on-task behavior Consequences: Responding to Problem Behavior • Responses to Problem Behavior should focus on two things: #1. Redirecting to the Alternative Behavior #2. Extinction of the Problem Behavior Responding to Problem Behavior: Redirection • At the earliest signs of problem behavior, quickly redirect to the alternative behavior Example: • During independent work, Annie often talks out to get teacher attention. If ignored, Annie will begin yelling and knocking materials off her desk. – When Annie first starts talking out, her teacher will immediately remind her how to appropriately get adult attention and will praise Annie’s use of the alternative behavior. Responding to Problem Behavior: Extinction • Do NOT allow the problem behavior to “work” or “pay off” for the student. • Eliminate/minimize the amount of missed instructional time or work provided to a student for engaging in problem behavior • • But… make sure student is capable of doing work… or provide support/instruction so student can complete the work Eliminate/minimize the amount of attention for engaging in problem behavior • • Limit verbal interactions/explanations Create a signal to cue the student to use the alternative behavior instead Responding to Problem Behavior: Extinction ** Note: extinction should ALWAYS be combined with frequent reinforcers for alternative/desired behavior. Example: • Darci engages in problem behavior that results in peer attention. – Darci’s peers will receive “Panther Paws” for ignoring her inappropriate behavior. • Darci will also be learning how to interact (and provided frequent opportunities to practice interacting) with peers appropriately and will earn time with peers for alternative/desired behavior. Teaching Strategies These are the skills the student will need to be taught to do *How to ask for a break using break card *How to monitor his/her progress with a point sheet *How to engage in appropriate conversations with peers during small group counseling T Cassano 2011 Activity 3 Use the post its on your table to come up with 1 setting strategy, 1 antecedent strategy, 1 behavior teaching strategy and 1 consequence strategy and place them on the appropriate chart paper. ACTIVITY 4 In your packet, complete the lower portion (initial intervention plan) for your student. Leaving Thoughts Keep the Simple FBA Simple Save Full FBA for more complex cases COMPETING PATHWAYS CHART STUDENT: DATE: SCHOOL: GRADE: Related Events (Setting Events) TEACHER: Desired Behavior Maintaining Consequences Problem Behavior Maintaining Consequences Antecedent Events Acceptable Alternative INTERVENTION PLAN Related Events/Strategies Antecedent Strategies Behavior Problem Adapted from Sugai, Lewis-Palmer, & Hagan, 1999 Desired Consequences/Strategies Problem Desired Full FBA Required more data collection -Teacher/Parent/Student Interviews -More Behavior Observations -File Review -Office Discipline Referrals -Grades -Test Scores Building Behavior Support Plans • Step 1: Develop Competing Behavior Pathway • Step 2: Identify and Select Behavior Support Strategies • Step 3: Develop Implementation Plan • Step 4: Develop Evaluation Plan STEP 7: SELECT INITIAL INTERVENTION STRATEGIES Tasks Person Responsible By When Review Date Evaluation Decision · Monitor · Modify · Discontinue *If emergency behavior management procedures are necessary, attach crisis plan as separate sheet Progress Monitoring in Data collection systems • Identify the skills to be addressed within the specialized instruction and choose an appropriate program/approach • Either select or develop a data collection tool which aligns with the focus of the goals/objectives - develop a file of templates for data collection for future use • Use a data sheet that is set up to take data efficiently and clearly - checklists/tallies- with correct measurement that aligns with the language of the goal/objectives STEP 8: EVALUATE PLAN Behavioral Goal (Use specific, observable, measurable descriptions of goal) What is the short-term behavioral goal? _________ Expected date What is the long-term behavioral goal? _________ Expected date Evaluation Procedures Data to be Collected Procedures for Data Collection Person Responsible Timeline Plan review date:_________________ We agree to the conditions of this plan: _______________________________ Student (date) ______________________________ Parent or guardian (date) _______________________________ Teacher (date) ___________________________ ___ Teacher (date) _______________________________ Action Team member (date) ______________________________ Action Team member (date) ! "#$$%&'( )*$'+, , %,, - %. $' ' ! $/0%. $'1 #- %2'33333333333333333333333333333'''''! $#&$4. 5'6 #$%2'333333333333333333333333333333' ' 7* #)2'333333'8 4))'9%', * "4#)): '%. 5#5%0'8 4$; '<%%&, '0/&4. 5', - #))'5&* /<'#"$4=4$4%,'#. 0' /. , $&/"$/&%0'$4- %,'>? @'* A'$; %'$4- %'9: '1 * =%- 9%&'B, $'#. 0'C? @'* A'$; %'$4- %'9: 'D #&"; ' B, $E'#, '0* "/- %. $%0'* . '; 4, F; %&', * "4#)'%. 5#5%- %. $', "#$$%&'<)* $'9: '%4$; %&'#'<#&#' <&* A%,, 4* . #)'* &'")#, , &* * - '$%#"; %&G' '''! * "4#)): 'H. 5#5%0' ' ' I * 8 'J #$%,'* A'! *"4#)'H. 5#5%- %. $' '''' ''''1 * $'! * "4#)): 'H. 5#5%0' K9, %&=%&2'3333333333333333333333333333333333333333333333333' ' LFB' LFM' LFN' LFL' LFO' LFC' C2? ? ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2? L' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2B? ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2BL' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2M? ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2ML' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2N? ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' C2NL' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' B? 2? ? ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' LFB? ' LFBB' LFBB' LFBM' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' Name __________________________ Behavior Goals Followed Directions Without talking Back Math Reading Date __________________ Phonics Writing Social Studies Science Asked for help Accepted help appropriately When _____________ demonstrates any of his/her goal behaviors, immediately praise him/her and tell him/her that he/she did a good job working on his goals and name the specific behavior so he/she knows he/she is getting a tally mark. After 10 tally marks across each subject, ______________ may “cash in” for a prize. ! Name______________ Date________ Activity I Followed Directions Check One: Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Check One: Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) Not There Yet (try again) Getting There (1 point) I’ve Got It (2 points) I Followed Directions Not There Yet – Try Again I ignored directions I did something different than what I was asked I refused to follow directions I did not correct my behavior when reminded of the rules I wandered around during work time ! Getting There – 1 point I complied when reminded of the direction(s) I followed group directions when individualized follow-up was provided I complied when reminded of learning center rules I returned to my space when reminded I’ve Got It! – 2 point When any adult told me to do something, I did it right away When group directions were given, I followed them along with peers I followed learning center rules without being told I was where I was supposed to be when I was supposed to be there Daily Behavior Sheet Date !=Fantastic Expected Behaviors Completed assigned work Talked nicely to students Talked nicely to staff Remained calm, even when mad Was a good helper Staff signature Arrival "=Not so good X= Okay 1st 2nd 3rd Lunch 4th 5th 6th Advisory ACTIVITY 5 Discuss with your team a plan for progress monitoring your student/case study FBA and Check In Check Out • CICO generally used as first intervention prior to FBA • FBA is done if CICO student DPR goals are not being met • School-wide expectation should be referenced when desired behavior is named and taught i.e. Desired Behavior – raise hand and ask for help School-wide expectation - Responsibility/Respect for others • CICO daily progress reports can be used for teaching and reinforcement and can be modified as a result of a FBA Thanks and • Think about coaching needs back home and try to arrange for at least one on-site coaching visit with one of us with your team back home during an actual FBA/BIP