無投影片標題
advertisement

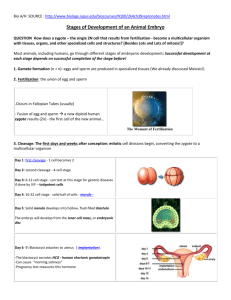
Hello,I am Francis. I will introduce the morphology of Molluscs Echinoderms and Chordates to you !! Mammal Bird Fish Reptile Amphibian Echinodermata Molluscs Starfish Tapering arm Mouth Closed picture of starfish •Has many short,hard and blunt spines •Has eyespot for sensation of light Structure of starfish Adaptive features Organisation Gaseous exchange Radial symmetry, triploblastic, unsegmented Gill (papulae) between spines Nutrition Mouth stomach digest externally Support Water vascular system, madreporite Fertilization External fertilization Embryo develop External Movement Tube feet link to w.v.s. Special features Tentacle and eyespot, pedicellariae Morphology of the starfish Molusca Bivalve Shell Morphology • Bilateral symmetrical • Have gill • With hard shell • With foot Internal structure of Oyster Chiton Cuttlefish Snail Adaptive features Gaseous exchange Mantle or gill Nutrition Support Filter feeding or mouth or radula or sucker on tentacle Shell or water Fertilization Internal or external Embryo develop external Movement Adductor muscle or tentacle Special features Cuttlefish with modern eye More… Adaptive features Gaseous exchange Gill Nutrition Mouth with teeth Support Cartilage or bone Fertilization External Embryo develop External Movement Fins Special features Lateral line, wet mucus scales gills on this great white shark can be seen as vertical slits on the shark's side. Gill of fish Fishes undergo gaseous exchange by respiration with gills Swimming bladder Function?? - assist to supply extra oxygen to fish living stagnant water Function: Serves as a “distance touch”in water for detecting and locating objects and moving animals Morphology of fish GiantMonkeyTree Frog Salamander Web hand digit Function??? • Provide large surface Then? • Help to push against water when swimming • Streamlined body • Skin with mucus • With webs • Lung,skin and buccal surface for respiration Skeleton of amphibians • both bony and cartilaginous components in different ratio (depends on strength required for locomotion) Adaptive features Gaseous exchange Skin lung gill and buccal cavity Nutrition Mouth Support Bone Fertilization External Embryo develop External Movement Tail or leg Special features Metamorphoses, 3 chambers heart, Naked wet skin • have • more a largely cartilaginous skeleton rigid and bony to withstand the impact of jumping and landing Generalized Anatomy of a Reptile • Nearly all reptiles have threechambered hearts • Crocodilians have fourchambered hearts. Morganucodon Characteristics of reptile • most lack external ears • breathe with lungs • Dry and tough skin • have backbones or spinal columns. Except for snakes • covered with scales Skeletal Features All reptiles have backbones or spinal columns. Except for snakes, reptiles have paired limbs that typically end in fiveclawed fingers or toes. Most reptiles have a pelvis that is associated with at least two spinal bones. Heat Location With Pit Organs Adaptive features Gaseous exchange Lung Nutrition Mouth Support Bone Fertilization Internal Embryo develop External - lay egg Movement Tail, leg Special features Dry scale, 3,4 chambers heart • sight is important for hunting • Some organisms like bat,eyes have been lost or have become greatly reduced • Amphibians are very susceptible to temperature and pressure change Different styles of foot Adaptive features Gaseous exchange Lung and air sac Nutrition Beak Support Hollow bone Fertilization internal Embryo develop Egg external Movement Wing with feather to fly, walk Special features Wing, beak, feather, scale on leg • with feathers and wings • have four-chambered hearts • warm-blooded • feathers are waterproof Adaptive features Gaseous exchange lung Nutrition Mouth with incisor, canine, molar Support bone Fertilization internal Embryo develop internal Movement Wing in bat, legs Special features Fur, hair, parental care Characteristics of mammal –Large brain Characteristics of mammal • Covered with hair • Respiration by lung • Usually with 4 limbs • Internal fertilization classification Game