Product Development Cycle in Modern Manufacturing
advertisement

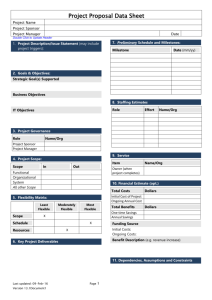
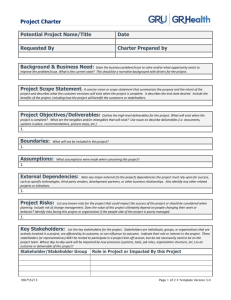
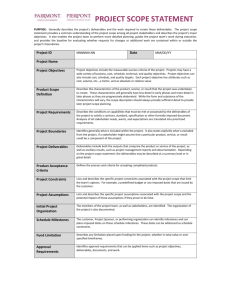
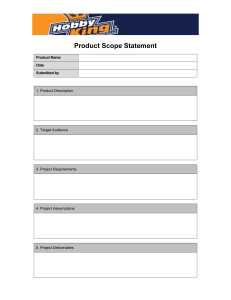
The Product Development Cycle in Today’s Manufacturing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. OVERVIEW Explain the product development cycle Define project management processes Relate #1 and #2 Discuss the tasks behind each process Suggest simple communication tools Bob Carson March 11, 2004 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process Expected Outcomes Individuals will understand: product development in today’s industry processes of project management value of simple communication Individuals will recognize the value of effective project management skills in today’s product development cycle 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 2 Common Definitions Product Development Cycle: the period of time needed to complete the set of events that develops an idea into a quality product Process: the ordered set of events required to achieve a quality result and ensure robust, repeatable results Project: the organization of the team’s commitment to deliver a product Project Management: the control of team behaviors across the Product Development Cycle 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 3 Motivation • Engineers should learn about today’s development practices • An engineer’s skill set should parallel industry’s expectations • Efficient individuals develop effective project management skills 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management 4 Phases of the Product Development Cycle Phase 0 - Generate Idea Phase 1 - Plan Phase 2 - Develop Phase 3 - Validate Phase 4 - Qualify Phase 5 - Produce 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 5 Product Development Phases Phase Goal 0 Sell Ideas Generate many ideas 1 Plan Develop Plan 2 Develop Advance idea to product 3 Validate 4 Qualify 5 Produce Proof of specs Proof of build Robust process Process Develop Plan the Engineer work for Functional the Team Models Test Proto units Build & Test Pilot units Release Product to Sell Main Initial Artifact Project Gantt Chart Solid System Proto Working Product Quality Product Ideas into Proposal Summary Owner Project Core Champion Team 11MARCH04 Working Modules & Prototypes Extended or Core Team Member Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 6 Project Management Process Steps 1. Present an idea 2. Plan the work 3. Work the plan Learn from experiences 4. 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 7 Process–Phase Relationship Project Phase 0 Phase 1 Ideas Plan Mgmt Process Steps 1 Develop Ideas 2 3 4 11MARCH04 Phase 2 Phase 3 Develop Validate Phase 4 Phase 5 Qualify Produce Plan the work Work the Plan Learn from positive and negative events Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 8 Process Step 1. Present an Idea Phase 0 • Collect ideas • Consider customers • Know stakeholders • Write proposal (Initial Project Summary) QUICK 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 9 Ideas come from Many Sources • • • • • • • STEP 1 Customer wants Customer needs Competitor products Competitor plans Marketing/sales logs Organizational strategies Society attitudes and opinions Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 10 Consider All Customers • External customers buy products that provide the lifeblood for the organization • Internal customers have objectives linked to products that meet organizational goals • Business partners help develop products to further everyone’s organizational goals • Carefully consider each customer need STEP 1 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 11 Know all Stakeholder Agendas • Understand all external customer plans • Check alignment of the idea with the current organizational strategies • Solicit input from all internal customers and provide continuous feedback • Uncover any hidden agendas through open conversations and discussions STEP 1 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 12 Develop the Initial Project Summary (IPS) Goal Product Roadmap Key Selling Points Key Customers Proposed Team Business Case Recommendation to decision-makers STEP 1 Quick Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 13 Process Step 2. Plan the work Phase 1 Incorporate new organizational input Select the team Identify tasks Link deliverables to milestones Anticipate showstoppers Define tradeoffs Freeze the plan 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 14 Consider new input Decision-makers typically set direction for the project at the Phase 0 exit review (quality, performance, schedule and cost) Meld those inputs into the IPS as you develop the project plan Oversight or ignoring organizational direction can be costly down the road STEP 2 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 15 Select the teams The core team may include 8 members The extended team contains as many members as needed to complete the work – BUT time, humans and money are never infinite resources STEP 2 CORE TEAM – – – – – – – – Research Quality Hardware Software Mechanical Manufacturing Marketing/Sales Finance Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 16 Identify the tasks Break down the work into tasks for each project phase Assign owners Assign proposed due dates Set milestones and review dates Iterate to a potential plan STEP 2 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 17 Link deliverables Match deliverables to milestones by phase. Plan for deliverables that are not tied to key milestones. What are some examples of key deliverables? – – – – – – STEP 2 New parts or components Module prototypes System prototypes Marketing collateral New test equipment and rework systems New manufacturing equipment or machines Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 18 Define tradeoffs Showstoppers need defined before finalizing the plan Establish tradeoffs to give the team clear direction should known risks develop This task avoids wasted time later in the project. It shows the decision-makers a team’s due diligence to project success STEP 2 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 19 Freeze the plan Establish reporting structure Define project metrics - QPSC Set firm values – Phase Schedules – Cost – Qualification date – Production date Recommend a final plan for approval STEP 2 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 20 Process Step 3. Work the plan Phases2-5 • The team must report on progress and address any issues as the project unfolds. The concepts for Work the Plan include: – – – – – Commit and deliver to plan Monitor and report metrics with data Discuss obstacles and engage stakeholders Communicate change Recommit and deliver to change 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 21 Commit and Deliver • “Can do” attitudes ensure project success • Cohesive teams produce a synergy STEP 3 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 22 Report routinely • Report project progress using data • Communicate project status to all decisionmakers and stakeholders with Quality, Performance, Cost and Schedule metrics • Suggest recommendations when negative data identifies a need for change. Never report a problem without a recommended solution STEP 3 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 23 Date: 11MAR04 GREEN RED Status Report: 04-123 Project Manager: Carson Year-to-Date Project Figures Quality Performance Schedule Cost Project Budget: $_____ % Under Budget _____ Project Start Date:10DEC04 Current Phase: Validation Original End Date: 2APR04 Current End Date: 27APR04 5MAY04 Upcoming Activities UACT 1 UACT 2 UACT n Start Date Completed Activities CACT 1 CACT 2 CACT n Completion Date Expected $$ Overrun ___ % Over Budget _____ Team Member Summary of current week’s activities Due Date Andersen Finalized the test fixtures for Proto3A Modified the test code for UL testing platform 20MAR04 24MAR04 Green Green Zeller Modified test fixtures for Proto4A Build self locking fixturing for Mfg Qualification tests 15MAR04 10MAR04 Green Issue Summary Action Schedule Beryllium Copper late in arriving – due 12MAR Will work OT on 13-14MAR Comments: Low risk item: Mfg Engr has high confidence that Production tests will still meet schedule WEEKLY STATUS REPORT Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process Owner HILL Status RED Due Date 15MAR 24 Discuss obstacles with stakeholders • Discuss the effects of any obstacle with every stakeholder and ensure understanding • Engage all stakeholders to meet each one’s needs. Over-communicate to ensure concurrence with change plans • Submit recommendations to decision-makers and stakeholders. Welcome comments and feedback on any change plans STEP 3 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 25 Cost of Changes Cost $1,000,000 1,000,000 900,000 800,000 700,000 600,000 $500,000 500,000 400,000 300,000 $250,000 200,000 100,000 0 $50,000 $5,000 $500 Phase 0 Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 HYPOTHETICAL Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 26 Communicate change Never surprise anyone • Over-communicate when change happens • Ensure all decision-makers and stakeholders agree with any new tasks or plan changes STEP 3 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 27 Recommit and Deliver • Change plans get the scrutiny of many • Recognize there may be lots of emotion around any change in plans. It’s the team’s responsibility to plan accordingly • Emphasize commitment and delivery to the change plan. It may be more important than achieving the original plan. STEP 3 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 28 Process Step 4. Learn from experience Phases 0-5 Professionals use well-documented events to reinforce good behaviors and discourage bad ones. Continuous improvement discipline demands everyone to learn from past experiences – shed the bad and share the good. 11MARCH04 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 29 Learn from experience Document events Train the positive Toss the negative Teach your world STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 30 Document events Every project experiences both positive and negative events Record all events using accurate data STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 31 Toss the negative Every event during a project is an opportunity for improvement. Eliminate these events from practice by modifying processes and work instructions to prevent recurrence. Live the NMI discipline STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 32 NMI Discipline NameIt: If a process is not defined the you do NOT know what to do MeasureIt: You cannot measure a process unless you have defined it ImproveIt: A process cannot be improved unless you can measure it STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 33 Train the positive Every event during a project is an opportunity for improvement. Incorporate these events into practice by modifying processes and work instructions to ensure recurrence. Live the NMI discipline STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 34 Teach your organization Both positive and negative experiences provide valuable insight to others. Proactively share the “Lessons Learned” across the organization. Educate others of possible benefits in other areas of the organization. STEP 4 Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 35 Conclusions Process Phase 0 Ideas Steps 1 Phase 1 Plan Phase 2 Phase 3 Develop Validate Phase 4 Qualify Phase 5 Produce Develop Ideas 2 Plan the work 3 4 11MARCH04 Work the Plan Learn from positive and negative events Product Development Cycle and Project Management Process 36