Monocot vs Dicot: Seed & Plant Structure Presentation
advertisement

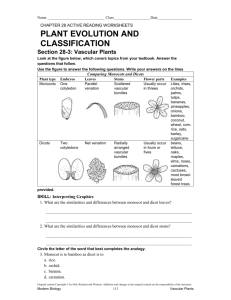
Seeds The seed is a stage in the life cycle of a flowering plant (angiosperms) Seed types • Monocot seeds and Dicot seeds • Example of a monocot seed is a corn seed • Example of a Dicot seed is an apple seed Dicot Monocot Parts of a monocot seed Corn seed Seed coat - protects the seed Endosperm - surrounds the embryo and stores food. Cotyledon - absorb nutrients from the endosperm and transport it to the plant. Dicot Bean Seed and Monocot Corn Seed Roots of Angiosperms Dicots have one long thick root called a taproot with secondary small roots growing from it. Monocot Roots The monocot root is made up of small branching fibers Stems • Stems contain tubes with veins that carry food down to the plant’s roots and water and minerals upward to the leaves. The bundles of veins within a monocot stem are scattered. The bundle of veins of a dicot stem are arranged in a neat circle Leaves • Leaves of a Monocot plant have parallel veins • Leaves of a Dicot plant have intersecting veins that form a branching pattern. Monocot leaf Dicot leaf Flowers • Monocot flowers have parts that are in three petals • Dicot flowers have four or five petals. Dicot flower Monocot flower Dicot angiosperms