1.2. Industrial relations in the market mechanism in Vietnam
advertisement

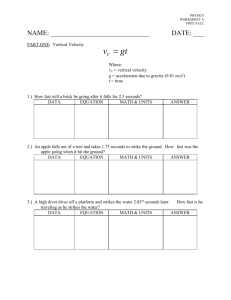
INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS AND STRIKES IN VIETNAM Dr. Tran Ngoc Dien Ministry of Labor - Invalids and Social Affairs Nurenberg, 08-09/10/2012 I. INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS IN VIETNAM DURING THE REFORM PERIOD 1.1. Industrial relations in the centralized planning mechanism Economy operating under the targets goverment, including target of jobs (centralized planning) Only two types of enterprise: state-owned (ownership of the entire population) and co-operative (collective ownership) Labor status is always distribute and controlled from central to locality Simple labor relations, consent to the assignment by the competent authorities of the State Passive labor, does not promote creativity, dynamism and efficiency. 1.2. Industrial relations in the market mechanism in Vietnam The economy is operating under the market mechanism under the State management (compliance with the rules of value, supply and demand, competition, efficiency) Economic development policies have been issued, the enterprises under different forms of ownership have been strongly developed: State enterprises are the majority (entire people’ ownership); Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) are encouraged; Non-state enterprises (Equity shares or private) Cooperatives (collective ownership) are of interest. 1.2. Industrial relations in the mechanism of conversion market in Vietnam Labor and jobs are considered to be one of the key policies. Employees are entitled to freely find legitimate appropriate jobs, which are protected by the State. Industrial relation has developed by several forms: In the State and administrative agencies (Officials - Civil servants and Specific Contract), employees are employed/salaried according to the State regulations); In other enterprises, the employees are recruited on a voluntary application and equality with the employer through negotiation, agreement and labor contract. 1.2. Industrial relations in the mechanism of conversion market in Vietnam Industrial relations between enterprises and employees: In the State enterprises (the Leader who are representative of the state-owned enterprise will be the employer) In the foreign-invested enterprises (FDI) (owner directly or through a hired representative will be the employer) In private enterprises (Direct owner will be the employer), In Limited Liability or Joint Stock Company (Direct owner or the hired representative indirectly will be the employer) In cooperative (direct owner is the employee or the employer) II. DISPUTES AND STRIKE IN THE INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS 2.1. Labor disputes, strikes - The problems of market economy Labor disputes is a natural phenomenon in the market economy. Labor disputes often arise when a conflict of rights and interests between the employee and the employer to appear in the process of implementation of labor relations; Labor dispute with the protesting activities are the spontaneus and passive self-defense as the employeers simply protect their right and interest; When conflict of rights and interests between the employees and the employers is not resolved promptly and satisfactorily, the climax of the labor disputes will be the strikes. 2.1. Labor disputes, strikes - Problems of market economy Vietnam is a country in transition economy following the market mechanism, the problems arising in the labor relations on the imperfect labor market are indispensable. In labor relations, conflict between personal capacity, labor productivity, wage income and the owner’s interests is constantly increasing, bringing negative impact on labor relations; To overcome the shortcomings mentioned above, Vietnam has issued a number of policies and laws to regulate and manage the social relations in the field of labor especially labor relations. However, in comparison with the practical requirements, such policies still contain limitations that do not meet demand on social development, of which, labor disputes leading to strikes are becoming pressing issues. Strike at Phong Phu Textile Company (Da Nang) on 02/07/2012 (Viet Nam Law Newspaper). 2.2. Strike situation in Vietnam for the period of 1995-2011 2.2.1. Strike in labor disputes in Vietnam Labor disputes and strikes in Vietnam for the period of 1995-2011 complicated and expanded widely. Total number of strikes in16 year is 4170. 245 strikes a year. In 1995 were 60 strikes, in 2003 were142, in 2008 were 720 and in 2011 were 885 (see Table 1, Figure 2). The number of strikes increased, more frequently, with spatial scope expanded not only in the south localities but also in the northern provinces and the whole country. In 2011 in Binh Duong and Hochiminh City were 400 strickes, Hanoi were 41, Hai Phong & Hai Duong were 21). The strike prolonged, the forms, content and nature of which have changed, mixing disputes & struggles for the rights and economic interests with socio-cultural benefits. Total number of strikes occurred in period of 1995 - 2011 (Source: Ministry of Labour - Invalids and Social Affairs) Year Total by year Type of Enterprise State Enterprise FDI Private Enterprise 1995 60 11 28 21 1996 59 6 39 14 1997 59 10 35 14 1998 62 11 30 21 1999 67 4 42 21 2000 70 15 38 17 2001 90 9 55 26 2002 99 5 65 29 2003 142 3 104 35 2004 124 2 92 30 2005 152 8 105 39 2006 390 4 287 99 2007 551 1 438 112 2008 720 0 584 136 2009 218 0 158 60 2010 422 0 360 62 2011 885 3 676 206 4170 92 3136 942 Total State Enterprise Percentage (%) FDI Private Enterprise 18,33 46,67 35 10,17 66,10 23,73 16,95 59,32 23,73 17,74 48,39 33,87 5,97 62,69 31,34 21,43 54,29 24,29 10,00 61,11 28,89 5,05 65,66 29,29 2,11 73,24 24,65 1,61 74,19 24,19 5,26 69,08 25,66 1,03 73,59 25,38 0,18 79,49 20,33 0,00 81,11 18,89 0,00 72,48 27,52 0,00 85,31 14,69 0,34 76,38 23,28 2,21 75,20 22,59 Chart 2: Percentage of strikes by type of business 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 DN NN DN FDI DN DD 2.2.2. Some of the major reasons of labor disputes and strikes in Vietnam In different stages, labor disputes have different contents and characteristics. In the 90s of the 20th century, the cause of this phenomenon is mainly due to "cultural differences, points of view and perceptions." From 2001 up to now, economic benefits and right to work have become major reasons. Strikes took place in different types of businesses (Strike in FDI sector more common (up 75.2%), in the private enterprises (22.59%) and State Enterprises (2.21%)). Strikes in FDI sector are varied by different owners of capital (Taiwan 37.8%; Korea 30.09; Singapore and the United States 1.18%). Strike at Hung Nghiep Co., Ltd. (Pouchen Vietnam) – Dong Nai on 05/4/2010 (Source: Tuoi Tre Online) Chart 3: Percentage of strikes in the FDI by origin of capital investment 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 DN có vốn đầuTaiwan tư Đài Loan FDI from FDI from DN có vốnfrom đầuTaiwan tưKorea Hàn Quốc FDI DN khác FDI from others FDI from Korea Strike at Matrix Co., Ltd. – (Vinh - Nghe An) on 26/12/2009 (Source: Dan tri Online) Four main reasons lead to labor disputes and strikes in Vietnam The cause of the labor management agencies The cause of the workers The cause of the business owners The cause of the representations for the employees’ rights and interests First, the cause of the labor management agencies Policies on labor relations have not been completed, there were leaks in legal framework and weakness in labor management; Legal system on labor relations have not enough specific details; Content of the labor legal system still contains some provisions that are not enough comprehensive and flexible as requested by the market economy; In the process of implementation there are many limitations, lack of clear regulations on powers and responsibilities of the competent agencies (State Representative, enterprises’ representatives, employees’ representatives); Capacity of the policy enforcement system have not meet the demand of a transformed, dynamic, diverse and complicated labor market. Second, the cause of the workers A large number of employees in Vietnam lack of understanding of labor law; Due to lack of knowledge on labor laws, the employees do not have the sense of labor discipline, when stressed into an industrial production machinery they felt to be so confined that lead to the psychological inhibition (60% of employees consider that the strike is to relieve psychological pressing for strict, restrictive labor regulations; Due to the lack of understanding, the employees do not pay attention to the commitments on their obligations and responsibilities for the enterprises when entering into labor contract, the conflicts, therefore, arise during the implementation of the contract. Increasing inflation, decreasing real income of the employees affects their material and spiritual life, causing psychological stress, depression…, leading to the strikes with request on increase of salary, bonuses and welfare activities. Third, the cause of the business owners Business owners seriously pay attention to the exploitation of cheap labor force instead of development of long-term human resource. Business owners exploit labor force through maximize equipment performance and work time; Businesses often split wages into two parts: basic salary and additional amounts in order to avoid or minimize the contribution of obligations such as social insurance, health care insurance, unemployment insurance... This type of salary structure causes stress and totally exploits the workers’ force. Hard working conditions and pressing working time but inadequate wages of workers leads to difficult life and deprivation; Business owners do not pay attention to the laborers’ cultural, mental & emotional lifes. Fourth, cause by the representations for the laborers’ rights and interests The trade unions in enterprises operate under the movement and inefficient. Trade union officials do not often work closely with the labor collective, not really pay attention to the workers’ aspirations, often compromise in order to protect their own interests. The representation of trade union is faint due to lack of the power in the laborers’ trust. The trade unions agencies is insufficient and weak in consulting activities to support the workers when the labor dispute occurred. When strikes occurred, 90% of the trade unions do not capture the information on the case and do not forecast the arising situations. III. SOME SOLUTIONS Promoting harmonious labor relation and mitigating strike 3.1. Enhance the State management over labor relations State with a subjective role in promulgating policies, laws, guiding the implementation, monitoring and supervising the compliance with labor laws, strictly handling the violations of labor laws, promoting harmonious labor relations, should carry out the following tasks:: Complete the general, comprehensive, and flecxibe labor law system in order to protect the legitimate rights and interests of the parties in labor relations; Perform the function of State management, supervise, inspect and strictly handle violations. Strickly and efficiently implement the new Labor Code (adopted in 2012, effective as of May 01, 2013) Tăng cường chỉ đạo hoạt động cơ chế đối thoại 3 bên, minh bạch linh hoạt và hiệu quả c. Form and equip the agencies and organizations supporting the labor relations with operational capacity d. Consistently direct the implementation of 3-party dialog mechanism, transparency, flexibility and efficiency. 3.2. Improve the social responsibility of business and the employer For the Company: - Promoting propaganda on labor law towards corporate social responsibility is a commitment to human behavior, ethically and contribution to the sustainable development of society; - Organize activities to honor and promote the typical example of effective implementation in the field. For the employer: - Raise the awareness of the laws; - Execute transparent remuneration for the employees; - Enhance dialogue at work, resolve promptly the recommendations of the workers ... 3.3. Improve the employees’ understanding of the laws Enhance legal awareness through dissemination of labor rights, benefits, responsibilities and obligations of employees in the legally binding labor relations; Immediately bring program on disseminating laws to the programs of general education and vocational training; Create conditions for employees to learn labor laws through the mass media, books, documents, consulting; Organize the movements to learn labor laws, especially for sensitive issues such as the rights, interests, and negotiate disputes in labor relations. 3.4. Enhancing the role of trade unions Need to continue to improve regulations on the functions of the trade union organizations. Should equip the union leaders with legal knowledge to participate in mediation, negotiation, protect the legitimate rights and interests of labor collectives. Ensure credibility and accountability of the executive committee of the trade union through activities based on real trust of workers, operating according to the requirements and duties as a bridge to protect the legitimate rights and interests of workers. Strictly and effectively implement the provisions of the new Trade Union Law (adopted in 2012, effective as of Jan 01, 2013). THANK FOR YOUR ATTENTION!