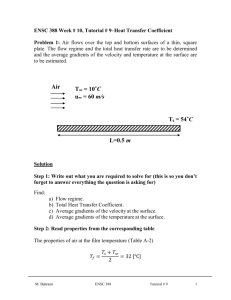
Overview on Scalable Video Coding - II
advertisement

Scalable Video Coding with
Wavelet-Based Approaches
Presenter: Mahin Torki
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
1
Paper Title: “State-of-the-Art and Trends in Scalable Video
Compression With Wavelet-Based Approaches”
Authors: Nicola Adami, Alberto Signoroni, Ricardo Leonardi
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,
Vol. 17, No. 9, September 2007
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
2
Outline
Motivation
Wavelet SVC (WSVC) Fundamentals
Coding Architectures for WSVC Systems
WSVC Reference Platform in MPEG
Comparison between WSVC and SVC
Conclusion
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
3
Motivation
Several working points corresponding to different
quality, picture size and frame rate in a unique bit
stream
Two types of SVC systems:
Hybrid schemes (used in all MPEG-x or H.26x
standards)
Spatio-temporal wavelet technologies
Main difference of SVC and transcoding systems
Low complexity
Do not require coding/decoding operations
Simple parsing operation on the coded bitstream
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
4
Motivation
Decode according to
required QoS or
available hardware resources.
Encode
once
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
5
A Typical SVC System
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
6
A possible structure of an SVC bitstream
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
7
Extracting a scaled bitstream
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
8
Tools Enabling Scalability
A multi-resolution signal decomposition inherently enables a low to high
resolution scalability by representing the signal in transformed domain
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
9
Tools Enabling Scalability
Inter-Scale Prediction (ISP)
The simplest way to represent a signal with two
resolutions
The signal x can be seen as a coarse resolution c and a
~
detailed signal d
Not critically sampled
Laplacian Pyramid
An iterated version of ISP
Results in a coarsest resolution signal c and a set of
~
details d (l ), l 1,..., n
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
10
Laplacian Pyramid
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
11
Spatial Scalability
Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT)
Projects the signal in a set of multi-resolution
(MR) subspaces
Critically sampled
Generates a coarse signal and a set of details
For multi-dimensional signals like images
Separable pyramidal and DWT decompositions
July 2008
Separate filtering on rows and columns
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
12
DWT Filter Bank
Implementing DWT by a two-channel filter
bank iterated on a dyadic tree path
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
13
2D-DWT Transform
2D Wavelet decomposition inherently provides spatial
scalability
Bit-plane
Coder
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
14
Spatial Scalability
Lifting scheme
July 2008
Alternative spatial domain processing
introduced by Sweldens
Generates a critically sampled (c,d)
representation of the signal x
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
15
Lifting Scheme
Signal x is split in two polyphase components, even
and odd samples(each one half the original resolution)
Two components are correlated
A prediction can be performed
The subsampled signal x2i could contain a lot of
aliased components, so, it should be updated
Perfect reconstruction is guaranteed
Every DWT can be factorized in a chain of lifting steps
Has a fundamental role in MC Temporal Filtering
(MCTF)
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
16
Temporal Scalability
Motion Compensating Temporal Filter (MCTF)
July 2008
A key tool enabling temporal scalability while
exploiting temporal correlation
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
17
MCTF implementation by Lifting steps
Index i has now a temporal meaning
P and U can be guided by motion information
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
18
MCTF implementation by Lifting steps
ME/MC implemented according to a certain motion
model
ME/MC usually generate a set of motion vector fields
mv(l,k)
mv(l,k) is estimation of the trajectory of the blocks
between the temporal frames, at spatial level l, involved
in the kth MCTF temporal decomposition level
With lifting structure, non-dyadic temporal decomposition
is possible
July 2008
Temporal scalability factors different from a power of two
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
19
Some benefits of MCTF
By exploiting local adaptability of P and U
operators and using mv(l,k) information, MCTF
can handle:
July 2008
Handle occlusion and uncovered area problems
Blocking effects can be reduced by considering
adjacent blocks
When fractional pixel MVs are provided, the lifting
structure can be modified to implement the
necessary pixel interpolation
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
20
MCTF
L0
L0
L0
L0
L0
L1
H1 L1
H1
1
L1 H
H2
L2
H3
July 2008
L0
H2
L0
L0
L0
L0
L0
L0
1
L1 H
L1
H1 L1
H1
H2
L2
L2
L3
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
H3
21
Hybrid temporal and spatial scalability
video sequence
1st temporal level
H
2nd temporal level
LH
3rd temporal level
LLL
July 2008
LLH
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
22
Quality Scalability
Wavelet-based image compression schemes, provide high R-D
performance with limited computational complexity
They do not interfere with spatial scalability requirements
High degree of quality scalability
Truncating the coded bitstream at arbitrary points
Most techniques are inspired from zero tree idea
Embedded Zero Tree Wavelet (EZTW) by Shapiro
SPIHT, reformulated EZTW by Said and Pearlman
Embedded Zero Block Coding (EZBC), with higher performance
Embedded Block Coding with Optimized Truncation (EBCOT)
Do not use zero tree idea
Adopted in JPEG2000
Combines layered block coding, block-based R-D optimizations,
and Context-based arithmetic coding
Good scalability and high coding efficiency
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
23
WSVC Notation
xS(n) (xT(m)): the original signal undergoes an n-level (m-
level) multi-resolutional spatial (temporal) Transform
S(n) (T(n))
The spatially transformed signal consist of the subband
set:
xS ( n) {xSc ( n) , xSd((nn)) ,..., xSd((1n)) }
l
k
xˆ
is the decoded version of the original signal x, at
given temporal resolution k and spatial resolution l at
reduced quality rate
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
24
Basic WSVC Architectures
T+2D
2D+T
Adaptive Architectures
Multiscale Pyramids
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
25
Basic WSVC Architectures
T+2D
Temporal transform is applied before spatial
Guarantees critically sampled subbands
Low spatial scalability performance
Full resolution motion vectors
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
26
Basic WSVC Architectures
2D+T
Spatial transform is applied before temporal
Often called In-band MCTF (IBMCTF)
Estimation of mv(l,k) is made independently on each spatial level
Leading to a structurally scalable motion representation
Spatial and temporal scalability are more decoupled
Lower coding efficiency especially at higher temporal resolutions
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
27
Basic WSVC Architectures
Adaptive Architectures
Combine the positive aspects of T+2D and 2D+T structures
Adaptive spatio-temporal decompositions optimized with
respect to suitable criteria
Content-adaptive 2D+T versus T+2D improves coding
performance
Multiscale Pyramids
Also called 2D+T+2D
Compensates the T+2D versus 2D+T drawbacks
Uses ISP to exploit the multiscale representation
redundancy
Disadvantage: over-complete transforms, which result in a
full size residual image
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
28
Pyramidal WSVC with pyramidal
decomposition before MCTF
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
29
Pyramidal WSVC with pyramidal
decomposition after MCTF
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
30
Spatio-Temporal prediction (STP)Tool Scheme
Promising WSVC architecture which presents
some similarities to the SVC standard
Adopted as a possible configuration of the
MPEG VidWav (Video Wavelet) reference
software
Based on a multiscale pyramid but differs in
the ISP mechanism
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
31
STP-Tool Scheme
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
32
Advantages of STP-Tool Scheme
Prediction is performed between two signals
which are likely to bear similar pattern in the
spatio-temporal domain
No need to perform any interpolation
Instead of full resolution residuals, the spatiotemporal subbands and residues are
produced for different resolutions
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
33
WSVC Reference Platform in MPEG
In 2004, the ISO/MPEG set up a formal evaluation of
SVC
Performance of H.264/AVC pyramid appeared the most
competitive
Later, MPEG and IEC/ITU-T jointly adopted JSVM (Joint
Scalable Video Coding)
As scalable reference model and software platform
Microsoft Research Asia (MRA) was selected as the
reference for wavelet technologies
The MPEG WSVC reference model and software
(RM/RS) is indicated as VidWav (Video Wavelet)
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
34
VidWav: General framework
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
35
VidWav: Main modules
Spatial Transform
with pre- and post-spatial decomposition, different SVC
configurations (T+2D, 2D+T, STP-Tool) can be implemented.
Temporal Transform
Framewise MC wavelet transform on a lifting structure
ME and Coding
MB-based motion model with H.264/AVC like partition patterns
Forward, backward or bidirectional motion model for each block
Entropy coding
3D extension of the EBCOT algorithm is used for entropy coding of
the resulted coeficients
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
36
VidWav STP-Tool Configuration
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
37
Comparison between WSVC and SVC
Single layer coding tools
Scalable coding tools
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
38
Comparison between WSVC and SVC
Single layer coding tools
VidWav uses a block-based motion model
Block mode types are similar to JSVM but no Intra-mode is
supported by VidWav
JSVM operates in a local manner
Divides frames into MB and treats MB separately in all
coding phases
VidWav operates with a global approach
Spatio-temporal transform applied to a group of frames
Unlike JSVM, single layer VidWav only supports open loop
encoding/decoding
In-loop deblocking filter in JSVM due to closed loop
encoding
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
39
Comparison between WSVC and SVC
Scalable coding tools
Spatial scalability in JSVM compared to VidWav in
STP-Tool configuration
July 2008
Block-based versus frame-based
Similar to JSVC, STP-Tool can use both closed and
open loop inter layer encoding
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
40
Objective and Visual Result Comparisons
Fair objective comparison is impaired due to
Visually, the ref. seq. generated by wavelet
filters are more detailed, but sometimes have
spatial aliasing effects due to different down
sampling filters
Depending on the spatial down-sampling filter
used, reduced spatial resolution decoded seq.
differ even at full quality
PSNR is used as the performance criterion at
intermediate spatio-temporal resolution levels
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
41
Objective Comparison Results
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
42
Subjective Comparison Results
Visual tests conducted by ISO/MPEG
included 12 expert viewers
July 2008
On average JSVM 4.0 is superior
Marginal gains in SNR conditions
Superior gains in combined scalability settings
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
43
Applications of WSVC
Based on a series of experiments:
July 2008
DCT-based technologies outperform waveletbased ones for relatively smooth signals and vice
versa
Eligible applications for WSVC are those that
produce or use High Definition/High Resolution
content
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
44
Home distribution of HD video using
WSVC
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
45
New Application Potentials for WSVC
HD material storage and distribution
Use nondyadic wavelet decomposition to
support multiple HD formats to be used in
video surveillance and mobile video
efficient similarity search in large video
databases
Multiple descriptions coding
Space variant resolution adaptive decoding
July 2008
Only a certain region of the image is decoded
at high resolution
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
46
Conclusion
Brief review of different tools used in WSVC
WSVC architectures are introduced
Comparison of WSVC with SVC
Potential applications for WSVC
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
47
Any questions?
Thank you!
July 2008
ENSC 820 - Simon Fraser University
48