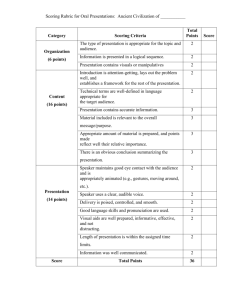
project selelction
advertisement
Project Selection Models 1 Strategic Management and Project Selection Maturity of Project Management Criteria for PS Models Nature of PS Models Types of PS Models Uncertainty Analysis and Risk Management Information Base for PS Models Project Portfolio Process (PPP) Project Proposal 2 Overview of PS Process Project Management Office (PMO): Aligning corporate needs and project goals Project selection: Choose candidate projects using evaluation criteria Dealing with uncertainty: Risk analysis Strategically selecting best projects: Project Portfolio Process (PPP) Locking up the deal: Writing a project proposal 3 Project Management Maturity Levels Ad-hoc (essentially disorganized) Abbreviated (some processes exist) Organized (standardized processes) Managed (measured processes) Adaptive (continuous improvement) 4 PS Models Idealized view of reality Representing the STRUCTURE of the problem, not the detail Deterministic or stochastic 5 Criteria for Project Selection Models (Soulder) Realism (technical-, resource-, market-risk) Capability (adequately sophisticated) Flexibility (valid results over large domain) Ease of Use (no expert needed to run model) Cost (much less than project benefit) Easy Computerization (use standard software) 6 Nature of PS models: Caveats Project decisions are made by PM --NOT by PS model! A PS model APPROXIMATES, but does NOT DUPLICATE reality! 7 Nature of PS Models: Methodology Start with detailed list of firm’s goals Create list of project evaluation factors (PEF’s) Weigh every element in PEF list Compute an overall score for project based on weighted PEF’s Select project that has the closest alignment with firm’s goals 8 Project Evaluation Factors (PEFs) Production Factors Marketing Factors Financial Factors Personnel Factors Administrative and Misc. Factors 9 Types of PS Models: Nonnumeric Sacred Cow Operating Necessity Competitive Necessity Product Line Extension Comparative Benefit Model 10 Numeric PS Models: Profit/Profitability Payback Period (PB) Average Rate of Return Discounted Cash Flow (NPV) Internal Rate of Return Profitability Index Other Profitability Models 11 Numeric PS Models: Scoring Unweighted 0-1 Factor Model Unweighted Factor Scoring Model Weighted Factor Scoring Model Constrained Weighted Factor Scoring Model S = ∑(x) S = ∑(s) S = ∑(s·w) S = ∑(s·w) ∏(c) 12 Choosing the PS Model Dependent on wishes and philosophy of management 80% of Fortune 500 firms choose “nonnumeric” PS models Firms with outside funding often choose scoring PS models Firms without outside funding often choose profit / profitability PS models 13 Management of Risk: Terminology Risk: Decision based on complete information about the probability of each possible outcome. Uncertainty: Decision based on incomplete or insufficient data. Game: Decision based under conditions of conflict. 14 Areas of Uncertainty Project timing & expected cash flow. Direct outcome of project, i.e. what exactly will the project accomplish Side effects and unforeseen consequences of project 15 Project Portfolio Process (PPP) Step Step Step Step Step Step Step Step 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: Establish a Project Council Identify project categories & criteria Collect project data Assess resource availability Reduce project and criteria Set Prioritize projects within categories Prioritize the projects within categories Implement the Process 16 Step 1: Establish a Project Council Includes: Senior Management Project Managers of major projects Relevant general managers Those who identify key risks Those who could derail PPP later 17 Step 2: Identify Project Categories and Criteria Derivative Projects Platform Projects Breakthrough Projects R & D Projects 18 Step 3: Collect Project Data Use “activity based costs” Verify all data Include timing for benefits and resource needs Document assumptions for future checking 19 Step 4: Access Resource Availability Access availability of Internal and External Resources by: Type Department Timing: can vary 100% over project life cycle 20 Step 5: Reduce the Project and Criteria Set Narrow down existing projects required competence exists in organization Market for offering Profitability Risk Potential partner to assist with project Right resources available at the right times Good technological fit with organization Uses organization’s strengths Synergetic with other important projects Slipped in desirability 21 Step 6: Prioritize Projects within Categories Rank projects within each category Measure by Risk Development of new knowledge Consider benefits first Consider cost second 22 Step 7: Select the projects to be Funded and Held in Reserve Determine the mix of projects across various categories and time periods Leave 10-15 % of organization’s resources free Focus on committing to FEWER projects 23 Step 8: Implement the Process Make results of the PPP widely known Senior management must fully fund Process will be repeated on a regular basis 24 Project Proposal: Content Cover letter Executive summary Description and past experience of project team Nature of technical problem to be solved How to approach solution of technical problem Plan for implementation of project Plan for logistic support and administration 25 Project Proposal: Cover Letter & Executive Summary Compose a cover letter as key marketing instrument Explain fundamental nature and general benefits of project Minimally technical language 26 Project Proposal: Past Experience of Project Team List all key project personnel with titles and qualifications Include full resume of each principal Provide all pertinent references 27 Project Proposal: Technical Approach General description of problem to be addressed or project to be undertaken Major subsystems of problem or project Methodology of solving the problem Special client requirements Test and inspection procedures 28 Project Proposal: Implementation Plan Estimates of time, cost and materials for each subsystem and the whole project Establish major milestones to break project into phases List equipment, overhead and administrative cost Develop contingency plans (including slack time) 29 Project Proposal: Plan for Administration and Logistic Support Control over subcontractors Nature and Timing of all reports (progress, budget, audits) Change management Termination Procedures “Touch of class” capabilities (artist’s renderings, meeting facilities, video conferencing, computer graphics) 30