Physics Fall Semester Prep The following problems represent the
advertisement
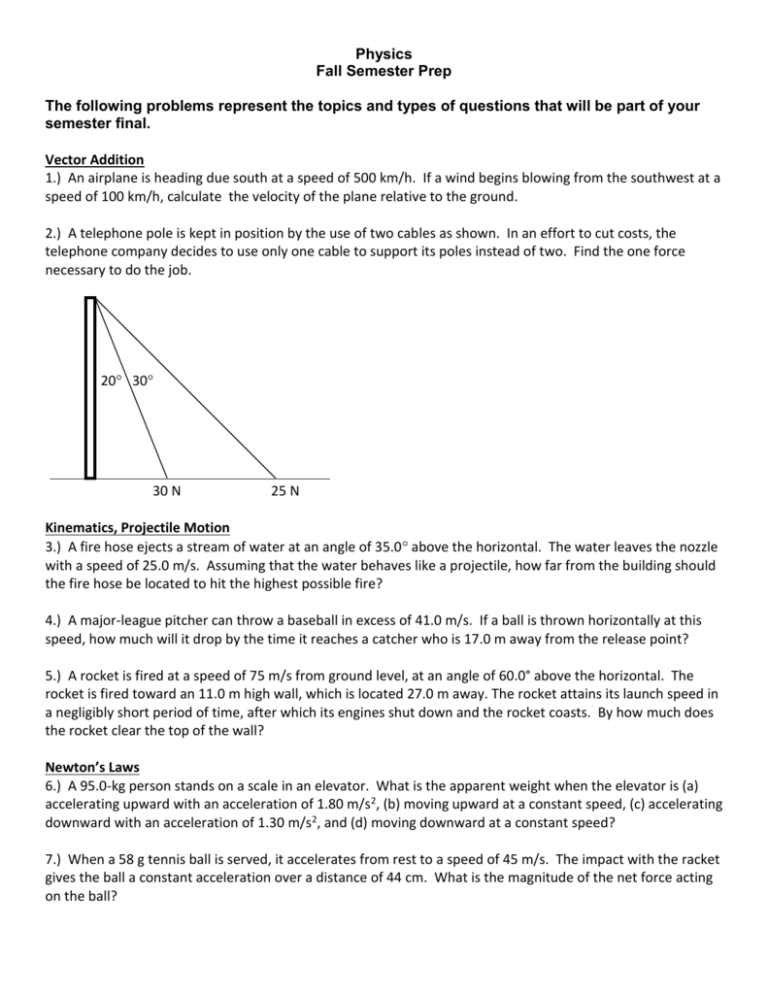
Physics Fall Semester Prep The following problems represent the topics and types of questions that will be part of your semester final. Vector Addition 1.) An airplane is heading due south at a speed of 500 km/h. If a wind begins blowing from the southwest at a speed of 100 km/h, calculate the velocity of the plane relative to the ground. 2.) A telephone pole is kept in position by the use of two cables as shown. In an effort to cut costs, the telephone company decides to use only one cable to support its poles instead of two. Find the one force necessary to do the job. 20 30 30 N 25 N Kinematics, Projectile Motion 3.) A fire hose ejects a stream of water at an angle of 35.0 above the horizontal. The water leaves the nozzle with a speed of 25.0 m/s. Assuming that the water behaves like a projectile, how far from the building should the fire hose be located to hit the highest possible fire? 4.) A major-league pitcher can throw a baseball in excess of 41.0 m/s. If a ball is thrown horizontally at this speed, how much will it drop by the time it reaches a catcher who is 17.0 m away from the release point? 5.) A rocket is fired at a speed of 75 m/s from ground level, at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal. The rocket is fired toward an 11.0 m high wall, which is located 27.0 m away. The rocket attains its launch speed in a negligibly short period of time, after which its engines shut down and the rocket coasts. By how much does the rocket clear the top of the wall? Newton’s Laws 6.) A 95.0-kg person stands on a scale in an elevator. What is the apparent weight when the elevator is (a) accelerating upward with an acceleration of 1.80 m/s2, (b) moving upward at a constant speed, (c) accelerating downward with an acceleration of 1.30 m/s2, and (d) moving downward at a constant speed? 7.) When a 58 g tennis ball is served, it accelerates from rest to a speed of 45 m/s. The impact with the racket gives the ball a constant acceleration over a distance of 44 cm. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on the ball? 8.) A 1380 kg car is moving due east with an initial speed of 27.o m/s. After 8.00 s the car has slowed down to 17.0 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the net force that produces the deceleration. 9.) A car is towing a boat on a trailer. The driver starts from rest and accelerates to a velocity of 11 m/s in a time of 28 s. The combined mass of the boat and trailer is 410 kg. The frictional force acting on the trailer can be ignored. What is the tension in the hitch that connects the trailer to the car? 10.) The following pulley system contains 3 masses. All of the pulleys surfaces are frictionless. m2 T1 T2 m1 m3 (a) Draw the appropriate free-body diagrams. If the mass of each block is m1=8 kg, m2=2 kg, Find the tension in each cable. (c) Find the acceleration of the system. m3=4 kg (b) Momentum 11.) Two friends, Al and Jo, have a combined mass of 168 kg. At an ice skating rink they stand close together on skates, at rest and facing each other, with a compressed spring between them. The spring is kept from pushing them apart because they are folding each other. When they release their arms, Al moves off in one direction at a speed of 0.90 m/s, while Jo moves off in the opposite direction at a speed of 1.2 m/s. Assuming no friction, find Al’s mass. 12.) Batman (m = 91 kg) jumps straight down from a bridge into a boat (m = 510 kg) in which a criminal is fleeing. The velocity of the boat is initially 11 m/s. What is the velocity of the boat after Batman lands in it? Work & Energy 13.) A 0.075 kg arrow is fired horizontally. The bowstring exerts an average force of 65 N on the arrow over a distance of 0.90 m. With what speed does the arrow leave the bow? 14.) A 2.00 kg rock is released from rest at a height of 20.0 m. Ignore air resistance and determine the kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, and total mechanical energy at each of the following heights: 20.0 m, 10.0 m, and 0 m. 15.) A 47.0 kg golf ball is driven from the tee with an initial speed of 52.0 m/s and rises to a height of 24.6 m. (a) Neglect air resistance and determine the kinetic energy of the ball at its highest point. (b) What is its speed when it is 8.0 m below its highest point?