chap 10 hw ( 11)
advertisement

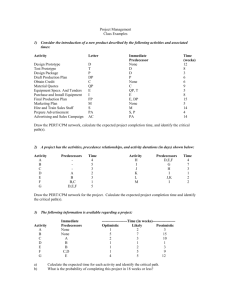
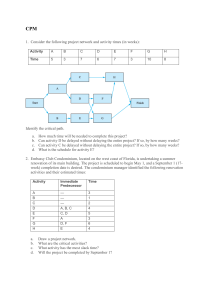
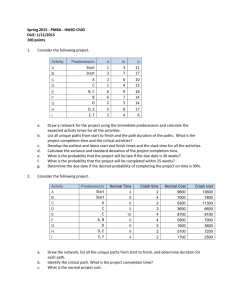
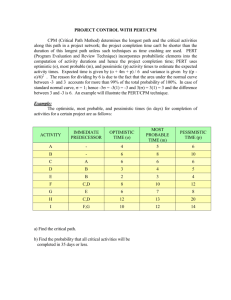
Question 1 A GANTT chart represents mainly Answer an immediate identification of predecessor task. a record-keeping device used in scheduling activities. a general identifier. the number of workers directly involved in the project. 1 points Question 2 A PERT/CPM activity has an optimistic time estimate of 3 days, a most likely time estimate of 8 days, and a pessimistic time estimate of 10 days. The expected time (in days) of this activity is: Answer 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 1 points Question 3 A PERT/CPM activity has an optimistic time estimate of 4 days, a most likely time estimate of 6 days, and a pessimistic time estimate of 10 days. The standard deviation of this activity is: Answer 7/6 1/3 2/3 1.0 1 points Question 4 A list of the tasks, broken down into modules, components, and individual tasks, is called a Answer work breakdown structure (WBS). PERT. planning matrix. critical path. 1 points Question 5 A work breakdown structure breaks down a project into Answer weeks. areas. arcs. modules. 1 points Question 6 Consider the following project. What is the critical path? Answer ACFG ADFG BEG ACDFG 1 points Question 7 Consider the following project. What is the minimum possible time for completing this project? Answer 15 days 16 days 18 days 20 days 1 points Question 8 Consider the following project. Compute the slack time for activity C. Answer 0 4 2 3 1 points Question 9 Consider the following project. What is the latest possible time that Activity E can be started without delaying the completion of the project? Answer 8 3 7 9 1 points Question 10 Consider the following project. What is the latest time that activity B can start without delaying the project? Answer 0 8 4 7 1 points Question 11 Consider the following project. What is the latest time that activity B can finish without delaying any other activities? Answer 0 8 9 4 1 points Question 12 Consider the following project. Determine the critical path. Answer ACEH BCEH BDFH BDGH 1 points Question 13 Consider the following project. Determine the estimated completion time of the project. Answer 23 days 22 days 25 days 20 days 1 points Question 14 Consider the following project. Determine the slack for activity D. Answer 2 days 4 days 6 days 5 days 1 points Question 15 Consider the following project. Determine the slack for activity F. Answer 2 days 3 days 4 days 5 days 1 points Question 16 Consider the following project. How much can activity F be delayed without delaying the project completion? Answer 1 day 2 days 3 days 4 days 1 points Question 17 Elements of project planning include Answer defining project objectives. identifying activities to crash. calculating expected times and standard deviations. conducting a "lessons learned" session. 1 points Question 18 If an activity cannot be delayed without affecting the entire project, then it is a ________ activity. Answer completed critical crashed normal 1 points Question 19 If t is the expected completion time for a given activity, then: Answer LF = LS - t EF = ES - t EF = ES + t EF = LS - t 1 points Question 20 In a CPM/PERT network the critical path is the Answer lowest path through the network. highest path through the network. shortest path through the network. longest path through the network. 1 points Question 21 Joe used a project management software package and has determined the following results for a given project: What is the probability of completing the project within 20 days? Answer 0.3849 0.8849 0.1151 0.7642 1 points Question 22 Joe used a project management software package and has determined the following results for a given project.: What is the probability of completing the project over 20 days? Answer 0.3849 0.8849 0.1151 0.7642 1 points Question 23 Once a project is underway, the project manager is responsible for the Answer people. cost. time. All of these 1 points Question 24 Project control involves Answer crashing. three time estimates. a backward or forward pass. earned value analysis. 1 points Question 25 Project management differs from management of more traditional day-to-day activities because Answer it has limited time frame. it has an unlimited budget. it is more expensive. it involves more of the workforce. 1 points Question 26 The LS and LF are calculated using the Answer backward pass through the network. forward pass through the network. values for ES and EF. backward and forward pass through the network. 1 points Question 27 The activities that must be completed prior to the start of an activity in question are called the immediate ________ of the activity in question. Answer successors predecessors successors and predecessors followers 1 points Question 28 The critical path is the ________ path through the network. Answer longest shortest straightest most expensive 1 points Question 29 The normal cost for an activity is $7,000 and the crash cost is $12,000. The normal time to complete this activity is 8 days and crash time is 4 days. If this activity is crashed by 2 days it will cost an additional: Answer $1000 $1250 $2000 $2500 1 points Question 30 Which of these statements regarding project crashing is true? Answer Crashing is not possible unless there are multiple critical paths. Activities not on the critical path cannot become critical after crashing. Crashing shortens the project duration by assigning more resources to one or more of the critical tasks. Crashing a project often reduces the time it takes for lengthy or complex, but noncritical activities. 1 points Save and Submit Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers. Click Close Window to close window. Save and Submit