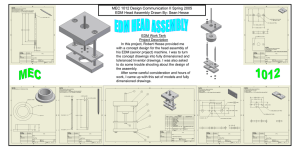
enterprise data model(edm)
advertisement

PLANNING THE ENTERPRISE DATABASE Chandra S. Amaravadi IN THIS PRESENTATION.. Introduction Enterprise Analysis Methodology Enterprise Data Model Planning process Resource requirements THE DEVELOPMENT CYCLE The database development cycle starts with planning: Planning Analysis (Requirements definition) Design (Logical & Physical) Implementation Maintenance INTRODUCTION PLANNING IN GENERAL What are some situations that require planning? What happens if you don’t plan? What information do you need to know in order to build a library? WITHOUT ADEQUATE PLANNING Problems caused by inadequate planning: Inaccurate estimation of resources Project cannot be completed on schedule Schedule changes Organizational changes impact planning Rework Project may be halted DATABASE PLANNING ABOUT DATABASE PLANNING Database planning is carried out before the rest of the development cycle, to get an overview of the data, scope of the project and resource requirements. Typical issues addressed are: What areas of the organization? How large will the database be? How many analysts will it require? What are the HW/SW needs? ENTERPRISE PLANNING METHODOLOGY (also called Business Systems Planning) ENTERPRISE PLANNING METHODOLOGY A method of planning that covers the entire organization. philosophy: processes easier to identify than data study processes and then data (information classes) map processes with data (EA matrix) develop Enterprise Data Model (EDM) develop a preliminary idea of requirements An information class is a collection of information/data NOTION OF A BUSINESS PROCESS Examples of business processes are: Registration Order raw materials Production planning job set up A process is a group of related activities PROCESSES ARE PART OF FUNCTIONS Function: a broad grouping of related processes Process: a broad grouping of related activities Activity: a step in a process; an individual action Function Process1 Activity1 Activity2 Process2 Activity3 Process3 FUNCTIONS PROCESSES & ACTIVITIES PRODUCTION ? ? ? ? ? ? ACTIVITY—DATA RELATIONSHIP FN./PROCESS/ACTIVITY CAN Create data (C) Update/Use data (U) Delete data (D) WHAT DATA DO THESE CREATE/UPDATE? Registration Order raw materials Maintaining an equipment Quality control AN ENTERPRISE ANALYSIS MATRIX Info. classes Emp. list Processes Producti Raw on plan Matls. list production planning C U order raw matls. m/c set up quality control Quality specs U U U CREATING AN EA MATRIX draw a table with a large top row and as many rows as there are processes. Create columns in the table. used to list information classes (see below) identify all processes list all processes in the first column, rowwise (skip heading row) identify all information classes E.g. course schedule, student list them in the heading row, after the first column Whenever a process uses an information class use “C” or “U” to denote creates and uses. FOR DISCUSSION Create an Enterprise Analysis matrix for a university ENTERPRISE DATA MODEL (also called Planning Model) ENTERPRISE DATA MODEL(EDM) An Enterprise Data Model (EDM) is a preliminary data model created during planning to understand ??? needs. ENTERPRISE DATA MODEL.. Depicts eclasses & relationships [Name written on relationship] Does not show ??? Use only horizontal and vertical lines A B 1:1 A B 1:M A B M:N DEVELOPING AN EDM has PRODUCT PLANT PRODUCT WARRANTY has has *Assume a complex product SHIFTS DEFECTS ENTERPRISE DATA MODEL(EDM) LEASE BUILDING Leased to Signed by TENANT Has an OWNER Associated with PARCEL FOR DISCUSSION Draw an Enterprise Data model for a university THE PLANNING PROCESS PLANNING PRE-REQUISITES Requirements to be fulfilled before planning starts: 1. Top management commitment green signal public acknowledgement 2. Project team team co-ordinators database analysts THE PLANNING META MODEL.. Organization descr. of information gathered during planning. Functions CSFs Processes E class Application CSF: Critical Success Factor; a business variable that is very important to success CRITICAL SUCCESS FACTORS Factors critical to success of organization Key resources – e.g. specialists Key processes – e.g. patient care Key activities – e.g. MRI PLANNING STEPS 1. Identify organizational background e.g. functions, processes, strategies, # of employees 2. Identify information used/created by functions/processes 3. Develop planning matrices e.g. function vs CSF, process vs eclass etc. 4. Develop Enterprise Data Model 5.Define scope of the development, project teams. 6. Develop planning report ELEMENTS OF A DATABASE PLAN (REPORT) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Exec Summary Organizational background Enterprise Analysis results/Data Models Hardware/Software recommendations Implementation plan PLANNING OUTCOMES Outcomes of database planning are: Understanding of the organization’s requirements. Planning matrices Preliminary data model (Enterprise model) Project planning scope, priorities, team assignment Resource requirements for database development hardware, software, personnel 29 RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS AND PITFALLS RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS FOR ENTERPRISE PLANNING FROM A STUDY OF NINE ORGANIZATIONS: Cost from $450,000 - $2 m Team size 10-15 Duration 31/2 months - one year 31 PLANNING PITFALLS Planning fails because: insufficient management support organizational direction not clearly known strategic IS plan not available or up-to-date lack of co-ordination among planning sub-units DISCUSSION What stage in the development process is planning carried out? What do we accomplish in database planning? What would be the essential elements of a database plan? Why do we need to study org. functions? What does the Enterprise Data Model show? What are CSFs, apart from expansion of definition? How can we identify critical processes? How can we prioritize database development? What are the common causes of failure in the planning process? THAT’S ALL FOLKS!