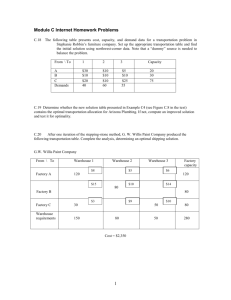
Locate Plants and Warehouses Simultaneously
advertisement

第 十三單元(2) : Facility Decisions Network Design in a Supply Chain
Facility Decisions
Network Design in a Supply
Chain
蔣明晃教授
【本著作除另有註明外,採取創用CC「姓名標示
-非商業性-相同方式分享」台灣3.0版授權釋出】
1
Conventional Network
Vendor
DC
Materials
DC
Finished
Goods DC
Customer
DC
Customer
Store
Codigofonte.net
Vendor
DC
Customer
Store
Component
Manufacturing
Plant
Warehouse
Customer
DC
Customer
Store
Components
DC
Vendor
DC
Finished
Goods DC
Final
Assembly
2
Customer
Store
Codigofonte.net
Customer
DC
Codigofonte.net
Customer
Store
Network Design Decisions
► Facility role and processes needed to be performed
► Facility location: strategic view
》Lower cost, flexibility: Toyota
》Responsiveness, cost-effective: Amazon
► Capacity allocation
► Market and supply allocation
Microsoft。
3
Factors Influencing Network
Design Decisions
► Strategic roles:
》 Off-shore facility: low-cost for export production
》 Source facility: low-cost facility for global production
(involve manufacture through oversea)
》 Server facility: regional market supporting
》 Contributor facility: regional with development skills
》 Outpost facility: regional build to gain local skills
》 Lead facility: lead in development and process
technologies
Microsoft。
4
Factors Influencing Network
Design Decisions
► Technological: availability, cost and flexibility
》 examples: computer chips v.s. Coke
► Macroeconomic:
》 tariffs and tax incentives (WTO, regional agreements,
free trade zone, local content & limits)
》 Exchange rate and demand risk
► Political:
》 stability; legal system
► Infrastructure:
》 available sites, labor availability, proximity to
transportation channels, local utilities
Microsoft。
5
Factors Influencing Network
Design Decisions
► Competitive:
》 Positive externalities: company tend to locate close to each
other, develop appropriate infrastructure
》 Locating to split the market: capture the largest market share
a
1-b
0
1
》 Customer response time and local presence
Microsoft。
6
The Cost-Response Time
Frontier
Hi
Local FG
Mix
Regional FG
Local WIP
Cost
Central FG
Central WIP
Central Raw Material and
Custom production
Custom production with raw
material at suppliers
Low
Low
7
Response Time
Hi
Factors Influencing Network
Design Decisions
► Logistics and facility costs:
》Inventory costs
》Transportation costs: weight or volume
》Facility setup and operating costs
8
Cost Build-up as a function of
facilities
Cost of Operations
Total Costs
Percent Service
Level Within
Promised Time
Facilities
Inventory
Transportation
Labor
Number of Facilities
9
A Framework for Global Site
Location
Competitive STRATEGY
INTERNAL CONSTRAINTS
Capital, growth strategy,
existing network
PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGIES
Cost, Scale/Scope impact, support
required, flexibility
PHASE I
Supply Chain
Strategy
PHASE II
Regional Facility
Configuration
TARIFFS AND TAX
INCENTIVES
REGIONAL DEMAND
Size, growth, homogeneity,
local specifications
POLITICAL, EXCHANGE
RATE AND DEMAND RISK
COMPETITIVE
ENVIRONMENT
10
GLOBAL COMPETITION
PRODUCTION METHODS
Skill needs, response time
PHASE III
Desirable Sites
FACTOR COSTS
Labor, materials, site specific
PHASE IV
Location Choices
AVAILABLE
INFRASTRUCTURE
LOGISTICS COSTS
Transport, inventory, coordination
Tailored Network: Multi - Echelon
Finished Goods Network
Regional
Finished
Goods DC
National
Finished
Goods DC
Local DC
Cross-Dock
Store 1
Customer 1
DC
Local DC
Cross-Dock
Customer 2
DC
Regional
Finished
Goods DC
Local DC
Cross-Dock
Store 1
Store 2
Store 2
Store 3
Codigofonte.net
Store
3
11
Information Needed for Design
Decision
► Location of supply sources and markets
► Location of potential facility site
► Demand forecasts by market
► Facility, labor, and materials cost by site
► Transportation costs between each pair of sites
► Inventory costs by site as well as a function of quantity
► Sales price of product in different regions
► Taxes and tariffs as product is moved between locations
► Desired response time and other service factors
Microsoft。
12
Phase II: Network Optimization
Models
► Decide the regions where facilities to be located by
considering regional demand, tariffs, economies of
scale, and aggregate factor costs
► Two possible alternatives:
》Setup facility in each region
》Consolidate plants in few regions
13
Phase II: Network Optimization
Models
► Decide the regions where facilities to be located by
considering regional demand, tariffs, economies of
scale, and aggregate factor costs
► Two possible alternatives:
》Setup facility in each region
》Consolidate plants in few regions
14
The Capacitated Plant
Location Problem
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
15
n =number of potential
locations/capacity
m = number of markets
Dj = annual demand of market j
Ki = capacity of plant i
fi = annualized fixed cost of
keeping factory i opened
Cij = cost of producing and
shipping 1 unit from factory i to
market j
yi = 1 if plant is located at site i, 0
otherwise
xij = Quantity shipped from plant
site i to customer j
n
n
m
Min f i y cij xij
i
i1
i1 j1
s.t.
n
x D
i1
ij
j
n
x K y
j1
ij
y {0,1}
i
i
i
Phase III: Gravity Location Models
► Identify potential locations in each region
► Geographical locations:
》 Plainer: Gravity location models
》 Network: median models, center models
16
Gravity Methods for Location
► Ton Mile-Center Solution
》 x,y: Warehouse
Coordinates
》 xn, yn : Coordinates of
delivery location n
》 dn : Distance to delivery
location n
d
n
k
x
k
Min TC dnDnFn
n 1
17
Dn Fn xn
n
D F /d
k
y
dn
n 1
i1
》 Fn : cost of shipping one
unit for one mile
》 Dn : Annual tonnage to
delivery location n
(x xn) (y yn)
2
n n
DnFn y n
n 1
n
n
dn
D F /d
i1
n n
n
2
Gravity Methods for Location
k
Dn
X=
Fn Xn
n1
k
Dn
Fn
n1
k
Dn
Y=
n1
k
Dn
n1
18
Fn Yn
Fn
Gravity Methods for Location
► Ton Mile-Center Solution
》 x,y: Warehouse
Coordinates
》 xn, yn : Coordinates of
delivery location n
》 dn : Distance to delivery
location n
d
n
k
x
k
Min TC dnDnFn
n 1
19
Dn Fn xn
n
D F /d
k
y
dn
n 1
i1
》 Fn : cost of shipping one
unit for one mile
》 Dn : Annual tonnage to
delivery location n
(x xn) (y yn)
2
n n
DnFn y n
n 1
n
n
dn
D F /d
i1
n n
n
2
Phase IV: Network
Optimization Models
► Decide how market will be allocated to facilities
► Must consider customer service constraints in term of response
time
► Decision should be altered on a regular basis as cost change
and market evolve.
20
Demand Allocation Model
◈
Which market is served by which plant?
◈
Which supply sources are used by a plant?
》 n =number of potential
locations/capacity
m
》 m = number of markets
Min c ij xij
》 Dj = annual demand of market j
s.t.
》 Ki = capacity of plant i
》 Cij = cost of producing and shipping
1 unit from factory i to market j
》 xij = Quantity shipped from plant
site i to customer j
21
n
i 1 j 1
n
x D
ij
j
x K
i
i 1
m
j 1
x
ij
ij
0
The Capacitated Plant Location
Problem
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
22
n =number of potential
locations/capacity
m = number of markets
Dj = annual demand of market j
Ki = capacity of plant i
fi = annualized fixed cost of keeping
factory i opened
Cij = cost of producing and shipping
1 unit from factory i to market j
yi = 1 if plant is located at site i, 0
otherwise
xij = Quantity shipped from plant site
i to customer j
n
n
m
Min f i y cij xij
i
i1
i1 j1
s.t.
n
x D
i1
ij
j
n
x K y
j1
ij
i
m
i
y k; y {0,1}
i1
i
i
Capacitated Plant Location with
Single Sourcing
◈
◈
yi = 1 if plant is located at site i, 0 otherwise
xij = 1 if market j is supplied from plant site i, 0 otherwise
n
n
m
Min f i y D j
i
i 1
i 1 j 1
c x
s.t.
n
x
i1
ij
1
n
x D K y
j 1
ij
j
i
n
i
y k; x , y {0,1}
i 1
23
i
ij
i
ij
ij
Location Allocation Decisions
Plants
Warehouses
Markets
1
2
Which plants to establish? Which warehouses to establish?
How to configure the network?
24
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
25
n =number of potential locations/capacity
m = number of markets or demand points
l = number of suppliers
t = number of potential warehouse locations
DJ = annual demand of market j
Ki = capacity of plant i
Sh = supply capacity at supplier h
We = potential warehouse capacity at site e
Fi = annualized fixed cost of keeping factory i opened
fe = annualized fixed cost of keeping warehouse e opened
Chi = cost of shipping 1 unit from supply source h to factory i
Cie = cost of producing and shipping 1 unit from factory i to
warehouse e
Cej = cost of shipping 1 unit from warehouse e to market j
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
supplier
manufactory
plant
warehouse
customer
market
(l)
(n)
(t)
(m)
Sh
Ki
We
Dj
◈
26
l =hiJ=number
m
tn
D
K
S
W
=
number
=capacity
number
supply
annual
potential
of
capacity
demand
of
of
suppliers
potential
warehouse
markets
plant at
of
i warehouse
locations/capacity
supplier
market
or capacity
demand
j h locations
at
points
site e
e=
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
supplier
manufactory
plant
warehouse
customer
market
(l)
(n)
(t)
(m)
Chi
Sh
◈
◈
27
Cie
Ki
Fi
Cej
We
fe
Dj
fFeiej
C
cost of shipping
producing
fixed
cost
1 and
unit
ofshipping
from
keeping
supply
warehouse
1warehouse
unit
source
from
e toheito
==annualized
annualized
fixed
cost
of keeping
factory
hi=
ie
opened
factory
market
openedij to warehouse e
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
28
◈
yi = 1 if factory is located at side i
◈
ye = 1 if warehouse is located at side e
◈
xej = quantity shipped from warehouse e to market j per year
◈
xie = quantity shipped from factory i to warehouse e per year
◈
xhi = quantity shipped from supplier h to factory i per year
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
supplier
manufactory
plant
warehouse
customer
market
(l)
(n)
(t)
(m)
xhj
yi
Chi
Sh
◈
◈
◈
◈
◈
29
xie
ye
Cie
Ki
Fi
xej
Cej
We
fe
Dj
yi = 1 if factory is located at side i
ye = 1 if warehouse is located at side e
xej = quantity shipped from warehouse e to market j per year
xie = quantity shipped from factory i to warehouse e per year
xhi = quantity shipped from supplier h to factory i per year
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
n
t
i 1
e 1
l
n
n
t
t
m
Min Fi y i fe y e c hi x hi c ie x ie c ej x ej
h 1 i 1
e 1 j 1
supplier
manufactory
plant
warehouse
customer
market
(l)
(n)
(t)
(m)
xhj
yi
Chi
Sh
30
i 1 e 1
xie
ye
Cie
Ki
Fi
xej
Cej
We
fe
Dj
Locate Plants and Warehouses
Simultaneously
n
x
hi
Sh
for h 1,, l
i1
t
l
x x
hi
0 for i 1,, n
e 1
h 1
t
x
ie
ie
for i 1,, n
K i yi
e 1
m
n
x x
ie
0 for e 1,, t
j1
i1
m
x
ej
ej
We y e
ej
Dj
for e 1,, t
j1
t
x
e 1
31
for
j 1,, m
Accounting for Taxes, Tariffs, and
Customer Requirements
◈
If rj is the revenue form selling one unit in market j, the objective
function of the capacitated plant location model can be modified
as
m
n
n
j 1
i 1
i 1
n
m
Max rj x ij f i y c ij x ij
◈
i
i 1 j 1
Also the constraint related to demand is modified as
n
x D
i1
◈
32
ij
j
Customer preferences and requirements can be modeled in
terms of modes of transportation.
Making Network Design
Decisions in Practice
► Do not underestimate the life span of facilities
► Do not gloss over the cultural implications
► Do not ignore quality of life issues
► Focus on tariffs and tax incentives when locating facilities
Microsoft。
33
版權聲明
頁碼
34
作品
授權條件
作者/來源
2, 11
本作品轉載自Codigofonte.net網站(http://www.codigofonte.net/galeria-deimagens/cliparts/visualizar/LOJA.jpg),瀏覽日期2012/2/18。依據著作權法第46、52、
65條合理使用。
2, 11
國立臺灣大學 蔣明晃
2
本作品轉載自Codigofonte.net網站(http://www.codigofonte.net/galeria-deimagens/cliparts/visualizar/FABRICA2.gif),瀏覽日期2012/2/18。依據著作權法第46、
52、65條合理使用。
3
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據Microsoft 服務合約及著作權
法第46、52、65條合理使用。
4
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據Microsoft 服務合約及著作權
法第46、52、65條合理使用。
5
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據Microsoft 服務合約及著作權
法第46、52、65條合理使用。
6
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據Microsoft 服務合約及著作權
法第46、52、65條合理使用。
12
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據Microsoft 服務合約及著作權
法第46、52、65條合理使用。
版權聲明
頁碼
33
35
作品
授權條件
作者/來源
本作品轉載自Microsoft Office 2007多媒體藝廊,依據
Microsoft 服務合約及著作權法第46、52、65條合理使用。