The Colonies
advertisement

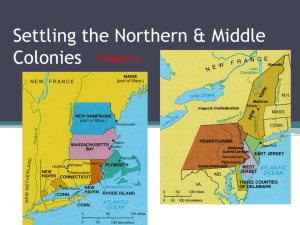
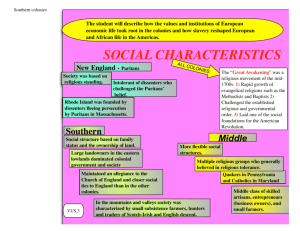
The Colonies What do we know? ► What problems did the new settlers face in the new world? ► What colonist saved the colonists from starvation? ► What crop saved the Virginia Company? Who introduced it? ► What were the big farms called? Who worked on the farms? ► 1st legislative body in English colonies? Southern Colonies ► Virginia, Maryland, Carolina’s, Georgia ► Reason=economic opportunity ► Maintained an allegiance to the Church of England and closer social ties to England then other colonies. Maryland ► Proprietary Colony: Private land grant ► Founded: Lord Baltimore Maryland ► Purpose: Safe place for Catholics (haven) ► Significance: Toleration Act Protected religious freedom for all Christians A Haven for Catholics Maryland Toleration Act of 1649 Supported by the Catholics in MD. Guaranteed toleration to all CHRISTIANS. Decreed death to those who denied the divinity of Jesus [like Jews, atheists, etc.]. In one way, it was less tolerant than before the law was passed!! Virginia ► Some of Virginia’s early settlers are called Cavaliers- English nobility who received large land grants from the king. ► Poor English immigrants came seeking better lives as small farmers or artisans in the Shenandoah Valley. Carolinas ► Royal Colony: King Controlled ► Purpose: Grow food for the West Indies ► Major City: Charleston (Charles Town) South Carolina grows rich through trade North Carolina lacks a good port ► Outer Banks: Sink Ships Georgia ► Last of the original colonies ► Founded: James Oglethorpe ► Purpose: Buffer Colony: Protect S.C. from Spanish Florida Debtor Colony: Place to start over Life in the South ► Political: ► Government run by the rich plantation owner (representative colonial legislatures) White males who owned land allowed to vote ► Virginia’s House of Burgesses Life in the South ► Economic: Plantation (cash-crops) economy Tobacco, Rice, Indigo ► Few towns ► Charleston: Major city Indentured Servitude Headright System: Each Virginian got 50 acres for each person whose passage they paid. Indenture Contract: 5-7 years. Promised “freedom dues” [land, £] Forbidden to marry. 1610-1614: only 1 in 10 outlived their indentured contracts! English Tobacco Label First Africans arrived in Jamestown in 1619. Their status was not clear perhaps slaves, perhaps indentured servants. Slavery not that important until the end of the 17c. Slavery ► Slaves replace indentured servants ► Middle Passage: Journey from Africa to America Part of the Triangular Trade ► Slave Codes: Harsh laws against slaves ► Slave Response: Suicide, vandalism, revolts Middle Colonies ►Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, Delaware ►Colonial Breadbasket ► Rich Economy: Farming & Industry (shipbuilding) Middle Colonies ► Settled mainly by English, Dutch, and German speaking immigrants seeking religious freedom and economic opportunity. ► Cities like New York & Philadelphia began to grow as seaports and commercial centers. Middle Colonies ► Pennsylvania: Proprietary Colony ► Founded By: William Penn ► Purpose: Home for Quakers Pacifist religious group ► Philadelphia: “City of Brotherly Love” Middle Colonies = religious toleration? ► The middle colonies were home to multiple religious groups- Quakers in Pennsylvania, Huguenots & Jews in NY, Presbyterians in NJ that generally believed in more religious tolerance. ► Middle Colonies had a more flexible social structure and began to develop a middle class of skilled artisans, entrepreneurs, and small farmers. New England ► Northern area of English colonies. ► Made up of people seeking religious freedom (sort of!!!) ► Plymouth Bay Colony (PBC), Massachusetts Bay Colony (MBC), Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire Massachusetts Created for religious purposes Two groups of settlers: Pilgrims Puritans Puritanism Calvinism Institutes of the Christian Religion Predestination. • Good works could not save those predestined for hell. • No one could be certain of their spiritual status. • Gnawing doubts led to constantly seeking signs of “conversion.” Puritans: Want to totally reform [purify] the Church of England. Grew impatient with the slow process of Protestant Reformation back in England. Pilgrims 1620: Arrive @ Plymouth William Bradford: Pilgrim leader Separatists: Believed Church of England was corrupt. Never to return to England. Separatists Separatist Beliefs: Puritans who believed only “visible saints” [those who could demonstrate in front of their fellow Puritans their elect status] should be admitted to church membership. Because the Church of England enrolled all the king’s subjects, Separatists felt they had to share churches with the “damned.” Therefore, they believed in a total break from the Church of England. Pilgrims Mayflower Compact: Legal document that established democracy in Plymouth Bay Colony Governor William Bradford The Mayflower Compact November 11, 1620 Written and signed before the Pilgrims disembarked from the ship. Not a constitution, but an agreement to form a crude govt. and submit to majority rule. Signed by 41 adult males. Led to adult male settlers meeting in assemblies to make laws in town meetings. Puritans Established the Massachusetts Bay Colony Non-Separatist: Goal is to be an example for all to follow and reform the church Puritans John Winthrop: Puritan leader Goal: create a “City on the hill” Covenant Community- Based on the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. Covenant Theology “Covenant of Grace”: between Puritan communities and God. “Social Covenant”: Between members of Puritan communities with each other. Required mutual watchfulness. No toleration of deviance or disorder. No privacy. Religious Freedom Puritans did not allow other faiths in Massachusetts Dissenters: People who opposed Puritan control Dissenters Roger Williams: Founder of Rhode Island. Kicked out of Massachusetts for preaching “liberty of conscience” Liberty of conscience = separation of: Church State Rhode Island 1636 Roger Williams fled there. Remarkable political freedom in Providence, RI • Universal manhood suffrage later restricted by a property qualification. • Opposed to special privilege of any kind freedom of opportunity for all. RI becomes known as the “Sewer” because it is seen by the Puritans as a dumping ground for unbelievers and religious dissenters More liberal than any other colony! Anne Hutchinson Kicked out of MBC for disagreeing with ministers Moved to Rhode Island Connecticut Founded by Puritans seeking greater freedoms and land Fundamental Orders: 1st written Constitution in colonies Life in the North New England: “Cod and God” Rocky soil and long winters: Bad for farming Practiced “Direct Democracy” at town meetings (remember Athens, Greece) New England Economy Shipbuilding: Fishing: Cod Lumbering: Subsistence Farming: you farm to sustain your life Life in the North Religion dominated all aspects of life All people must learn how to read the Bible. Life in the North Education: Elementary schools required to be built in all towns > 50 families Harvard College (1636): 1st college in America Life in the North As MBC grows religious faith begins to decline. Salem Witch Trials (1692): An attempt to scare people back to church by claiming Satan was corrupting society. Life in the North Great Awakening: A revival in the church Brings passion and energy to church services. Led by two men: Jonathan Edwards and George Whitefield Fire and Brimstone sermons Life in the North ► Effects of the Great Awakening: More people go to church New churches created ►Baptist ►Methodist New Colleges created People question authority Enlightenment ► Challenges the authority of the church in science and philosophy while elevating the power of human reasoning. ► Locke- natural rights (life, liberty, and property) ► Montesquieu- 3 branches of government ► Enlightened thinkers greatly influence our Founding Fathers on the road to revolution. REVIEW QUESTIONS ► What was the 1st English group to arrive in New England? ► John Winthrop was the leader of this group of people? What kind of city did he hope to create? ► What is the difference between a separatist & a non-separatist? ► How did the geography of New England affect the lives of the people there?