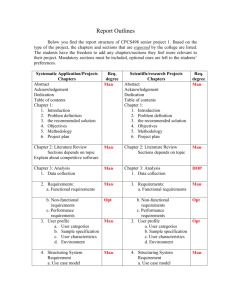
Outline of dissertation
advertisement

Reasons the Middle-Class is Opting Out of State Standardized Testing Martin K. Greene I. Chapter One: Background Information A. Introduction 1. CCS and RttT have created a bevy of HST 2. Parents around the nation, especially in NY, are opting out B. Problem Statement 1. Why are middle-class parents in specific school districts choosing to opt out? a. What are the social, educational, economical, and political factors influencing their decision? b. How are these factors representative of the middle class? 2. How will this research help school districts? a. Administrators can use information to work with parents b. Districts can share information with state to affect change C. Rationale 1. Opting out is not consistent between districts with similar demographics 2. Middle-class phenomenon D. Research Questions 1. What are the social factors that influence parents to opt out of state standardized testing? 2. What are the political factors that influence parents to opt out of state standardized testing? 3. What are the educational factors that influence parents to opt out of state standardized testing? E. Definitions 1. Business Roundtable 2. Common Core Standards 3. English Language Arts, or ELA 4. Elementary and Secondary Act, or ESEA 5. High Stakes Testing, or HST 6. Human Capital 7. No Child Left Behind, or NCLB 8. Opt out 9. Opt Out Movement 10.Race to the Top Initiative, or RttT 11. Socioeconomic, or SES 12. Standardized Testing F. Significance 1. The Opt Out movement continues to increase a. Fewer students taking the tests b. Less data to evaluate teachers c. States have threatened to cut funding 2. Understanding the movement might curtail expansion a. Schools and parents can work together towards a common goal b. Schools can clearly communicate local concerns to the state G. Limitations 1. There is no control over how many people will respond. 2. There is no control over personal agendas of the people who do respond. 3. There is no control over the number of people who will respond during the two-month collection period 4. To be added as research is complete H. Summary 1. CCS mandate comprehensive and extensive testing 2. Parents do not want their child/children to participate II. Chapter 2: Literature Review A. Opponent of HST believe it is shifting the focus of education from learning to testing B. Parents are having their children opt out of testing C. History 1. President George W. Bush signed NCLB into law in 2002 a. to improve math and reading skills b. annual standardized testing i. grades three – eight ii. last test in tenth grade 2. Spending on standardized testing increased 160% in six years 3. Arne Duncan admitted 82% of schools could fail to meet NCLB’s 2014 goal 4. Janet Napolitano wrote initiative for National Governors Association a. focused on improving math and science education b. she concluded America couldn’t lead the world in innovation if we didn’t have an internationally competitive education system 5. Napolitano’s standards combined with NCLB a. President Obama renewed NCLB b. He added the Race to the Top Initiative in 2009 6. Opposition to CCS a. educators and parents felt they could work within the NCLB framework b. CCS were introduced with less flexibility and greater stakes D. Testing Mandates and the CCS 1. CCS does not mandate testing a. NY’s implementation of CCS and testing caused controversy b. CA’s implementation of CCS without testing did not cause controversy 2. Alternate assessments a. States do not have to use multiple choice or short, open-ended questions b. Some states use projects, portfolios, or performance 3. Race to the Top a. did not add new testing mandates b. required test scores to be used in teacher evaluations E. Impact of CCS on classroom practice 1. Criticism of standards a. not developmentally appropriate b. gaps in learning from grade to grade c. overlaps in learning from grade to grade 2. Classroom practice a. focus on test-taking strategies b. loss of creative and critical thinking activities 3. Teachers are afraid of evaluation process a. too many variables for it to be an accurate assessment of teacher b. poverty is leading indicator of student success or failure, not testing c. big business, not educators, are driving the tests i. Bill and Melinda Gates, Pearson run Education Development Center ii. EDC study proved no connection between evaluation system and student performance d. HST creates anxiety that undermines performance F. Political Jockeying 1. Politicians have flipped a. Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker, R b. New Jersey Governor Chris Christie, R c. Washington State’s Central Committee of the Democratic Party condemned the CCS 2. Democratic presidential candidate Hillary Clinton a. tries to stay neutral b. when pressed by media, supported CCS G. Opt Out Movement 1. US Secretary of Education Arne Duncan a. in 2013, criticized parents who questioned RttT b. inspired the many grassroots movements to opt out 2. Should not have been a surprise a. no educator review b. no community opinion H. United Opt Out National 1. supports parents across the country 2. focuses on big business end of CCS a. non-educators making educational decisions b. tremendous profits for business, not for schools I. Parents who are against big business taking over our schools 1. Morna McNulty a. claims billions of dollars are at stake b. sees ending testing as the way to make education revolution possible 2. Frank Breslin a. former teacher who agrees big business is in it for the money b. also believes big business is looking to take over the public school system J. Parents who worry about children 1. Children are developing anxiety over tests 2. Children are not enjoying school 3. Jeanette Deutermann a. child was becoming physically ill and didn’t want to go to school b. she started “Long Island Opt Out” K. Parents who fear loss of privacy 1. fear collection of student data a. govnerment use of data b. big business use of data 2. believe parents need more information about data collection a. what is being collected? b. who will have access? c. how will it be used? L. Parents against CCS as a pathway to government takeover 1. Afraid the government is trying to create a national curriculum 2. Afraid the federal government is trying to usurp state and local governments M. Growth of Opt Out Movement 1. First boycott was in 2001 2. Growth has been huge between 2013-2015 3. Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights a. against Opt Out movement i. believes it is necessary for data collection in poor and minority districts ii. believe opting out is undermining efforts to improve all schools b. group consists of 12 minority organizations N. Theoretical Framework 1. Middle class as a construct a. variables i. income ii. assets iii. aspirations iv. social values v. political alignment b. emerging and middle class have similar values 2. Determining the motivation of the middle class in local school districts O. Conclusion 1. Opt out movement is not going away 2. It is driven by white, middle class parents 3. School districts need to understand the reasons compelling parents to opt out III. Chapter Three: Methodology A. Purpose was to examine perceptions of a select group of parents to understand the factors that led to opting out 1. New York State school report card 2. interviews 3. surveys B. Data was used to support research 1. Hypothesis One: Middle-class parents opt out of state standardized testing to avoid political intrusion on local education systems 2. Hypothesis Two: Parents hope to reduce high stakes pressure placed on children by opting out of state standardized testing. 3. Hypothesis Three: A correlation can be identified between local social pressure and opting out. C. Instrumentation 1. Survey items a. section one focused on existing social implications b. section two focused on emotional component of HST c. section three focused on the educational relationship to the opt out decision 2. Survey items were developed from an analysis of previous survey items D. Method of Analysis 1. examined the surveys 2. keyed and coded data into database in SPSS software 3. analysis of descriptive responses E. Summary 1. described research methodology 2. explained the sample selection 3. described the procedure used to design the instrument