Chapter 16 Study Guide Answers Habeas corpus – right of accused
advertisement

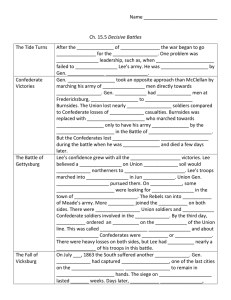
Chapter 16 Study Guide Answers Habeas corpus – right of accused person to a hearing before being jailed – Lincoln suspended this in many states during the war Blockade runner – Confederate ships that broke through the Union blockade Peace Democrat – became known as “copperheads” because of copper pennies they wore on their shirts – were in favor of negotiating peace with the Confederacy Bull Run- first major battle – at Manassas, VA – both sides realized this will be a long and costly fight Hampton Roads – (Virginia) Battle between USS Monitor and CSS Virginia (Merrimack) Shiloh – First Union victory in the west – April 6 & 7, 1862 – bloodiest battle up to that point Antietam – bloodiest single day – used by Lincoln to take a stand against slavery Gettysburg – Lee’s second attempt at a Northern invasion - Began when Confederates were looking for shoes – July 1-3, 1863 Vicksburg – important Confederate strong hold on the Mississippi Rv. – after a month long siege it fell to the Union on July 4, 1863 Petersburg – Nine month siege – resulted in Union being able to capture Richmond Appomattox Court House – sight of Lee’s surrender to General Grant on April 9, 1865 William Tecumseh Sherman – Union General who led famous “March to the Sea” from Atlanta to Savannah Ulysses S. Grant – General for Union forces in the west then later given command of entire Union army – sometimes called “unconditional surrender Grant” – secured Mississippi Rv for the Union – favored by Lincoln who said “I need that man, he fights” George Meade – Union commander at Gettysburg Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson – Confederate hero at the First Battle of Bull Run – wounded at Chancellorsville and later died from infection George B. McClellan – appointed commanding general of the Union forces after the first Battle of Bull Run Robert E. Lee – Confederate general of the Army of Northern Virginia Clara Barton – served as a nurse and founded the American Red Cross Emancipation Proclamation - signed and went into effect on Jan. 1, 1863 – freed slaves in the Confederate states only Question answers: See your study guide for the original questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. South was fighting on their own land Reunite the Union Leave slavery alone were it already existed but do not let it spread to new territories Union – Washington D.C.; Confederate – Richmond, VA 48 counties in western VA organized themselves and voted to secede from VA in 1861 . Gain control of the Tennessee and Mississippi River 7. Served as spies, nurses, cooks, worked in factories, and some disguised themselves as men to fight 8. Felt that is was a rich man’s war and a poor man’s fight – there was a riot in NY City 9. Lee realized that further fighting would not accomplish anything and would lead to heavy losses Numerous Union victories in late 1863 and 1 Gettysburg – short answer Day 1 – The Union and Confederacy met by accident to Gettysburg, PA. Confederates pushed the Union forces back through the town until they secured a defensive position to the south of the town on Cemetery Ridge Day 2 – The two flanks ends (Culps Hill to the north and Little Round Top to the south) were areas of intense fighting and the Confederates tried to outflank the Union Day 3 – Lee decided to try to bust through the center of the Union line by an all out assault (known as Pickett’s charge). This was a failure and resulted in heavy casualties. Lee retreated but Meade did not pursue Essay – This is not a complete answer and you need to expand on this information to write a complete paragraph essay. These are key ideas only! Rewriting these bullet points will not get you full credit for an essay question! • • • • • • • all slaves are freed (with 13th Amendment) Southern economy was destroyed and billions of dollars in damage Boom in Northern industry Saved the Union Over 620,000 casualties Women took on new roles Federal government is strengthened, state governments loose power