Sound Review Answers
advertisement

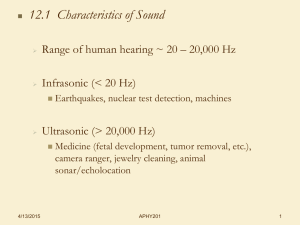
Physical Science II Sound Review Name ____________________ Period____________________ Conceptual Questions 1. What type of wave is sound? Sound is a mechanical, longitudinal wave. 2. Why can’t sound travel through space? Sound is a mechanical wave, so it needs a medium in order to travel. In space there is no medium. 3. Explain how sound waves travel through air. A sound wave is created by a vibration that causes compressions and rarefactions in a medium. The air for example is compressed and then allowed to expand again by the passing sound wave. 4. During lightning storms you will sometimes see the lightning several seconds before hearing any thunder. Why does this happen? Light travels much faster than sound, so the light from the lightning will reach your eyes before the sound reaches your ears. 5. What is the accepted value for the speed of sound in air? 343m/s 6. How is the speed of sound through a medium related to the density of the medium? As the medium becomes more dense, the speed of sound increases. 7. What is the approximate hearing range of humans? 20Hz – 20,000Hz 8. What is the main reason why an elderly person is unable to hear the same frequency sounds as a teenager? As you get older your ears start to naturally deteriorate making it difficult to detect all frequencies between 20Hz and 20,000Hz. 9. Why is it important for companies like Sony, Panasonic, Microsoft and Apple to limit the volume levels on their portable media devices? Loud sounds have been proven to cause hearing loss, since the portable music devices are so close to your ears, they can do more damage than normal. Thus, companies limit the volume level of their devices to protect consumers against hearing loss. 10. How does a hearing aid help someone to detect sounds? Hearing aids amplify sound, increasing its volume. Hearing aids cannot help you hear a frequency that your ears can’t normally detect. 11. What two factors determine the intensity level of a sound? 1) Your distance from the sound source. 2) The amplitude of the sound wave. 12. Why is it possible for a whisper to sound louder than a person shouting across a field? If you are very close to the source of the sound it can still be very intense. Thus being very close to the whisper will make it sound louder than someone shouting from very far away. 13. What are the units used to measure sound intensity? Decibels (dB) 14. On the decibel scale, what is the level of the threshold of hearing? 0 dB 15. On the decibel scale, what is the level given to the threshold of pain? 125 dB 16. If a sound level intensity level increases by 10dB, how do your ears perceive that sound? Your ears perceive the sound as being twice as loud. 17. If you turn the volume level up on your iPod from 30dB to 60dB, how much louder do your ears perceive the sound volume? Your ears perceive the sound as being twice as loud for every 10 dB, so the sound would appear to be 8 times louder. 18. How are pitch and frequency related? Pitch is the perceived highness or lowness of a sound frequency. If frequency is high than the pitch is high. If the frequency is low, than the pitch is low. 19. As a police car approaches you with its siren on, how does the perceived frequency of the sound compare with the actual frequency of the sound? While the police car is approaching, you perceive the sound to be at a higher frequency than normal. 20. After the police car passes, how does the detected frequency of the siren compare with the actual frequency of the siren? While the police car is traveling away, you perceive the sound to be at a lower frequency than normal. 21. Who invented the first recording device that was able to playback the recording? Thomas Edison 22. What company introduced the first long playing (LP) record? Columbia 23. How did the tape recorder change the way we listened to music? The tape recorder allowed people to have an affordable and easily transportable music playing device. You could now record music or listen to music anywhere and at any time. 24. Until the invention of the CD in the 1980’s, what were the main media formats available to the public? Available for purchase were either cassette tapes or vinyl records. Problems 1. An ambulance is driving to a hospital at a speed of 25m/s with its 225Hz siren turned on. a) What is the detected frequency by a stationary observer when the ambulance is approaching? 𝒗+𝒗 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟐𝟓𝑯𝒛 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟐𝟓𝒎/𝒔) 𝒔 𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟐𝟓𝑯𝒛 𝟑𝟏𝟖𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟒𝟐. 𝟕𝑯𝒛 b) What is the detected frequency by that observer after the ambulance has passed? 𝒗+𝒗 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒔 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟐𝟓𝑯𝒛 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟐𝟓𝒎/𝒔) 𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟐𝟓𝑯𝒛 𝟑𝟔𝟖𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟐𝟎𝟗. 𝟕𝑯𝒛 2. If an ambulance is traveling at a speed of 20 m/s with its siren sounding at 350 Hz. An observer is traveling in the opposite direction at 15 m/s. What is the detected frequency in each of the following cases? a) When the police car and observer are approaching one another. 𝒗+𝒗 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟏𝟓𝒎/𝒔) 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟐𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝒔 𝟑𝟓𝟖𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 𝟑𝟐𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟖𝟕. 𝟗𝑯𝒛 b) When the police car and the observer are moving away one another. 𝒗+𝒗 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟏𝟓𝒎/𝒔) 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟐𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝒔 𝟑𝟐𝟖𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 𝟑𝟔𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟏𝟔. 𝟑𝑯𝒛 3. A person is riding a bus that is traveling at 10m/s. A car approaching at 15m/s blows its horn, which is heard as 350Hz by the person on the bus. What was the actual frequency of the car horn? 𝒗+𝒗 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒔 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟏𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 = 𝒇𝒔 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟏𝟓𝒎/𝒔) 𝟑𝟓𝟎𝑯𝒛 = 𝒇𝒔 (𝟏. 𝟎𝟕𝟔) 𝟑𝟓𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝟑𝟓𝟎 = 𝒇𝒔 𝟑𝟐𝟖𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟑𝟐𝟓. 𝟑𝑯𝒛 4. During the summer a person is driving by Hershey Park Stadium at a speed of 20m/s. They hear a sound coming from a concert that appears to be at 475Hz. What was the actual frequency of this sound? 𝒗+𝒗 𝒇𝒅 = 𝒇𝒔 𝒗−𝒗𝒅 𝒔 𝟒𝟕𝟓𝑯𝒛 = 𝒇𝒔 (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔+𝟐𝟎𝒎/𝒔) (𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔−𝟎𝒎/𝒔) 𝟒𝟕𝟓𝑯𝒛 = 𝒇𝒔 (𝟏. 𝟎𝟓𝟖) 𝟑𝟔𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝟑𝟓𝟎 = 𝒇𝒔 𝟑𝟒𝟑𝒎/𝒔 𝒇𝒅 = 𝟒𝟒𝟗. 𝟎𝑯𝒛