Cells Review for Quiz
advertisement

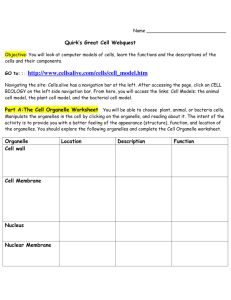
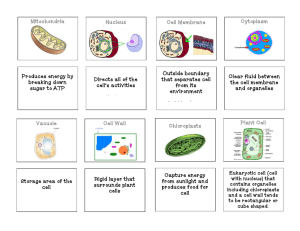
AP Biology Ch. 6 Tour of the Cell Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. A cell has the following molecules and structures: enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, plasma membrane, and mitochondria. It could be a cell from A. a plant or an animal C. a plant, but not an animal. B. an animal, but not a plant. D. a bacterium. 2. Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell? A. rough ER B. lysosome C. vacuole D. Golgi vesicles 3. Which of the following is a compartment that often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell? A. lysosome B. vacuole C. mitochondrion D. Golgi apparatus 4. When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure of cells, they most likely would use A. a light microscope. D. A and B B. a scanning electron microscope. E. B and C C. a transmission electronic microscope. 5. Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large and complex lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition? A. The ER B. the Golgi C. the lysosome D. mitochondria 6. The liver is involved in detoxification of many poisons and drugs. Which of the following structures is primarily involved in this process and therefore abundant in liver cells? A. rough ER B. smooth ER C. Golgi D. ribosomes 7. Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to which of the following structures in animal cells? A. peroxisomes B. desmosomes C. gap junctions D. extracellular matrix 8. Cyanide binds with at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide would be found within the A. mitochondria. B. ribosomes. C. peroxisomes. D. lysosomes. 9. Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell? A. rough ER B. ribosome C. nuclear envelope D. chloroplast 10. The peroxisome gets its name from its interaction with hydrogen peroxide. If a liver cell is detoxifying alcohol and some other poisons, it does so by removal of hydrogen from the molecules. What, then, do the enzymes of the peroxisome do? A. combine the hydrogen with ATP C. transfer the harmful substances to the mitochondria B. use the hydrogen to break down hydrogen D. transfer the hydrogens to oxygen molecules peroxide 11. Which of the following makes it necessary for animal cells, although they have no cell walls, to have intercellular junctions? A. Cell membranes do not distinguish the types of ions and molecules passing through them. B. Large molecules, especially proteins, do not readily get through one, much less two adjacent cell membranes. C. Cell-to-cell communication requires physical attachment of one cell to another. D. Maintenance of connective tissue shape requires cells to adhere to one another. 12. If an individual has abnormal microtubules, due to a hereditary condition, in which organs or tissues would you expect dysfunction? A. sperm, larynx, and trachea B. microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli C. all ducts, such as those from salivary or sebaceous glands D. limbs, hearts, areas with a good deal of contraction Which type of organelle is primarily involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids? A. ribosome B. lysosome C. smooth ER D. nucleolus Cells of the pancreas will incorporate radioactively labeled amino acids into proteins. This "tagging" of newly synthesized proteins enables a researcher to track their location. In this case, we are tracking an enzyme secreted by pancreatic cells. What is its most likely pathway? A. ER --> Golgi--> nucleus B. Golgi--> ER -->lysosome C. nucleus--> ER --> Golgi D. ER --> Golgi --> vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane Which of the following relationships between cell structures and their respective functions is correct? A. cell wall: support, protection C. chromosomes: cytoskeleton of the nucleus B. chloroplasts: chief sites of cellular respiration D. ribosomes: secretion Which of the following is a major cause of the size limits for certain types of cells? A. the evolution of larger cells after the evolution of smaller cells B. the difference in plasma membranes between prokaryotes and eukaryotes C. the evolution of eukaryotes after the evolution of prokaryotes D. the need for a surface area of sufficient area to allow the cell's function A primary objective of cell fractionation is to A. view the structure of cell membranes. B. identify the enzymes outside the organelles. C. determine the size of various organelles. D. separate the major organelles so that their particular functions can be determined. Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through A. desmosomes B. gap junctions C. tight junctions. D. intermediate filaments Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules? A. lipids B. starches C. proteins D. steroids A cell lacking the ability to make and secrete glycoproteins would most likely be deficient in its A. nuclear DNA. B. extracellular matrix. C. Golgi apparatus. D. B and C only Which is one of the main energy transformers of cells? A. mitochondria B. vacuole C. lysosome D. Golgi apparatus Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules? A. cilia B. centrioles C. flagella D. A and C only Which of the following contains its own DNA and ribosomes? A. lysosome B. vacuole C. mitochondrion D. Golgi apparatus Microfilaments are well known for their role in which of the following? A. ameboid movement D. A and B only B. formation of cleavage furrows E. A, B, and C C. contracting of muscle cells ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. ____ 20. ____ 21. ____ 22. ____ 23. ____ 24. ____ 25. Under which of the following conditions would you expect to find a cell with a predominance of free ribosomes? A. a cell that is secreting proteins B. a cell that is producing cytoplasmic enzymes C. a cell that is constructing its cell wall or extracellular matrix D. a cell that is digesting food particles ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 26. The nuclear lamina is an array of filaments on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. If a method were found that could cause the lamina to fall into disarray, what would you expect to be the most likely consequence? A. the loss of all nuclear function B. the inability of the cell to withstand enzymatic digestion C. a change in the shape of the nucleus D. failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information 27. In the fractionation of homogenized cells using centrifugation, the primary factor that determines whether a specific cellular component ends up in the supernatant or the pellet is A. the relative solubility of the component. B. the size and weight of the component. C. the percentage of carbohydrates in the component. D. the number of enzymes in the fraction. 28. Which of the following possesses a microtubular structure similar to a basal body? A. centriole B. lysosome C. nucleolus D. peroxisome 29. In animal cells, hydrolytic enzymes are packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles functions in this compartmentalization? A. chloroplast B. lysosome C. vesicle D. peroxisome 30. Which cell would be best for studying lysosomes? A. muscle cell C. phagocytic white blood cell B. nerve cell D. leaf cell of a plant 31. Which of the following contains hydrolytic enzymes? A. lysosome B. vacuole C. centriole D. Golgi apparatus 32. A biologist ground up some plant leaf cells and then centrifuged the mixture to fractionate the organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, while organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, A. mitochondria and chloroplasts. C. peroxisomes and chloroplasts. B. chloroplasts and peroxisomes. D. chloroplasts and mitochondria 33. Which of the following are capable of converting light energy to chemical energy? A. chloroplasts B. mitochondria C. leucoplasts D. peroxisomes 34. Which structure is common to plant and animal cells? A. chloroplast C. central vacuole B. mitochondria D. cell wall of cellulose 35. Which of the following modifies proteins that will be secreted? A. Golgi apparatus B. vacuole C. ribosome D. lysosome 36. Organelles other than the nucleus that contain DNA include A. ribosomes. C. chloroplasts. B. mitochondria. D. B and C only 37. Which of the following contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen? A. peroxisome B. vacuole C. mitochondrion D. Golgi apparatus 38. The advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that A. light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy. B. light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy. C. light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells. D. light microscopy can be used to view the smallest organelles, while electron microscopy cannot. 39. All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell except A. DNA B. a cell wall. C. a plasma D. rough ER. ____ 40. ____ 41. ____ 42. ____ 43. ____ 44. membrane. Which structure is not part of the endomembrane system? A. nuclear envelope C. Golgi apparatus B. chloroplast D. plasma membrane Cells can be described as having a cytoskeleton of internal structures that contribute to the shape, organization, and movement of the cell. Which of the following are part of the cytoskeleton? A. the nuclear envelope C. microfilaments B. mitochondria D. lysosomes Which structure-function pair is mismatched? A. nucleolus; production of ribosomes C. ribosome; protein synthesis B. lysosome; intracellular digestion D. smooth ER; cell division Why isn't the mitochondrion classified as part of the endomembrane system? A. It only has two membrane layers. C. Its structure is not derived from the ER B. It has too many vesicles. D. It is not involved in protein synthesis. A biologist is studying kidney tubules in small mammals. She wants specifically to examine the position of different types of cells in these structures. The cells in question can be distinguished by external shape, size, and 3-dimensional characteristics. Which would be the optimum method for her study? A. transmission electron microscopy B. scanning electron microscopy C. light microscopy using stains specific to kidney function D. light microscopy using living unstained material Essay 45. ORQ#1 Cellular Organelles Eukaryotic cells contain several membrane-bound organelles that serve particular functions for the cell. For two of the organelle pairs below, describe the structure and function of each organelle in the pair. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) and smooth ER Lysosomes and vacuoles Nucleus and nucleolus Ribosomes and Golgi apparatus . 46. ORQ#2 Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Mitochondria and chloroplasts are two organelles that convert energy for cells. They have unique characteristics that set them apart from other cellular organelles. A) Compare and contrast mitochondria and chloroplasts in terms of structure and function. B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought by scientists to have once been prokaryotes that became incorporated into larger cells (endosymbiotic theory). What evidence suggests this possibility?