Chapter 3 Syndicating Content
advertisement

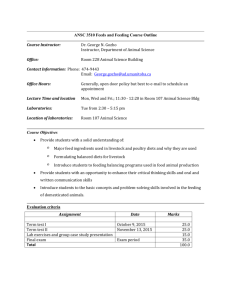
3 Syndicating Content Web 2.0: Concepts and Applications Overview Syndication is the process of making a summary of a Web site’s information available to other Web sites and applications A Web feed represents the list of items that are being shared Feed reader applications and devices access the Web feed of each of the subscribed sites and deliver any new content Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 2 Overview Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 3 Exploring Web Feeds RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is one of the first and most popular types of Web feeds Web sites providing feeds usually display an orange Web feed icon – Feed icon – RSS icon – XML icon Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 4 Publish / Subscribe Model Q: Do you read any subscription-based web content? What is it? Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 5 Exploring Web Feeds Many bloggers syndicate their blogs’ content as Web feeds News sites syndicate news headlines Monster provides an RSS feed with job postings eBay alerts users of daily deals Amazon keeps users informed about bestsellers Flickr notifies users of new photos Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 6 Subscribing to and Reading Feeds Internet Explorer Embedding feeds in a blog Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 7 Subscribing to and Reading Feeds The ability to subscribe to a feed is standard in many Web browsers The method by which you subscribe to feeds varies with each Web browser Every browser presents Web feeds differently – even though feeds are syndicated the same • using XML (Extensible Markup Language) Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 8 Subscribing to and Reading Feeds (Firefox) Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 9 Group Activity Explore some interesting web feeds: – – – – On Windows, use Internet Explorer/Firefox On Mac OS, use Firefox On iOS (iPhone/iPad), install Free RSS Reader or Feedly On Android, install Feedly or gReader Share among your group. Pick an interesting/useful one and introduce to the class. Time:10 minutes (including break) Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 10 Video: Feedly Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 11 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 12 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers Web-based feed readers – Google Reader (2005-2013) • Contains feed searching capability – Bloglines (2003-2015) – Feedly (2008-) Client (standalone) feed readers – FeedDemon – FeedReader – Microsoft Outlook Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 13 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers (MS Outlook) Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 14 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers Blogs can contain gadgets to display Web feeds in sidebar gadgets – Gadgets update when blog is loaded or refreshed Blogger defaults to automatically create feeds for its hosted blogs – Also syndicates full content Professional bloggers manage their feeds and collect information about how users interact with them – Feed managing services, e.g. feedburner – Metrics – Reach Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 15 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 16 Features of Web-Based and Client Feed Readers Web-based applications incorporate data from Web feeds to present it visually Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 17 Formats for Web Feeds RSS 2.0 is the most widely used version of RSS – RSS is closed to further modifications Atom is a newer, evolving alternative to RSS – Not as simple as RSS, but is becoming popular Differences between RSS and Atom are transparent to the user Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 18 Formats for Web Feeds XML (Extensible Markup Language) is the underlying technology used for describing content syndicated using RSS and Atom feeds – Tags describe information • Opening tags • Closing tags – RSS and Atom feeds are the most common types of content represented in XML Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 19 Formats for Web Feeds Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 20 Formats for Web Feeds Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 21 Exploring Podcasts A podcast is a series of audio or video files that are broadcast to a computer or personal media player over the Internet by a publication in an RSS feed – Podcast reader • iTunes – You can download and watch podcast episodes directly on a Web site, or with a Web-based application Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 22 Exploring Podcasts Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 23 Exploring Podcasts Web-based podcast services contain directory listings of audio and video podcasts – Podnova manages podcast selections Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 24 Group Activity 2 Explore some interesting podcasts on iTunes – – – – On Windows, use iTunes On Mac OS, use iTunes On iOS (iPhone/iPad), use Podcasts app On Android, use Podbean app Share among your group. Pick an interesting/useful podcast and introduce to the class. Time:10 minutes (including break) Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 25 Group Activity 2 What’s the content type? Audio or video? What’s it about? How long is each episode? How’s the sound/video quality of the production? What’s the publication frequency? How can users provide feedback? Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 26 Features of Podcast Readers Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 27 Anatomy of a Podcast Feed Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 28 Creating Podcasts Requires basic equipment for recording and editing digital audio and video – Most laptops have built-in Webcams and microphones, as well as recording software Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 29 Creating Podcasts Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 30 Summary Syndication is a way to distribute and share Web content – Web feeds Users can subscribe to Web feeds using a Web browser or a feed reader application Content publishers syndicate their content as feeds using either the RSS or Atom formats, represented in XML Podcasts are RSS feeds with an enclosed multimedia file Chapter 3: Syndicating Content 31