Notes-14-Doppler EffectwEq
advertisement

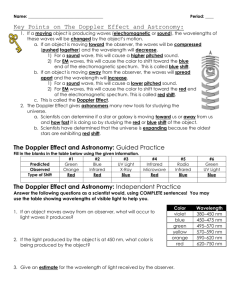
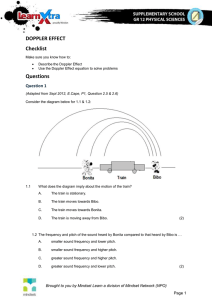
Section 14.6 The Doppler Effect: A change in frequency (pitch) due to relative motion between a source of sound and its observer The Doppler Effect can be produced by either the source moving or by the observer moving. Doppler Effect for a Moving Observer Actual Wave Large wavelength Small frequency (low pitch ) Small wavelength Large frequency (high pitch) Observed Wave For a sound source moving towards a stationary observer with speed vs , the perceived wavelength decreases and velocity remains constant ◦ Therefore observed frequency will increase from f to f’ For a sound source moving away from a stationary observer with speed vs , the perceived wavelength increases and velocity remains constant ◦ Therefore observed frequency will decrease from f to f’ For an observer moving towards a stationary sound source with speed v0 , the perceived velocity increases and wavelength remains constant ◦ Therefore observed frequency will increase from f to f’ For an observer moving away from a stationary sound source with speed v0 , the perceived velocity decreases and wavelength remains constant ◦ Therefore observed frequency will decrease from f to f’ (new) observed frequency speed of observer (old) actual frequency speed of sound (usually 343 m/s) speed of sound source Use the top set of signs (+ in numerator & - in denominator) when the objects are moving towards each other Use the bottom set of signs (- in numerator & + in denominator) when the objects are moving away from each other Some everyday examples are: ◦ Radar detectors Waves that strike an approaching car will bound back with a higher frequency Waves that strike a car moving away will bounce back with a lower frequency ◦ Loud fire engines/sirens moving past you As the fire engine/siren approaches, the pitch of the siren sound (a measure of the siren's frequency) is high As the fire engine/siren passes by, the pitch of the siren sound is low. Virtual Physic Lab Simulation ◦ Animals (bats) A) Stationary object: Waves will reflect off surface with same spacing as when they arrived; no shift in frequency between cry and echo B) Insect flying away: Echo waves will have wider spacing (lower frequency) than cry waves because insect moves farther from bat between waves C) Insect approaching: Echo waves will be more compressed (higher frequency) than cry waves because insect moves closer to bat between waves How fast are the following aircrafts moving with respect to the speed of sound? (slower than, at, or faster than…?) Aircraft moving at the speed of sound Aircraft moving faster than the speed of sound What is the “V” shape that forms behind an aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound? High pressure regions result from the overlapping of compressions What causes the “V” shape? ◦ Compressions interfere (overlap) ◦ Superposition of compressions ◦ One BIG compression all at once What do you hear as the result of this big compression? When do you hear a sonic boom? ◦ As the high pressure region hits your ears all at once! ◦ NOT as a plane crosses the threshold of sound Where else in the real world do you see the “V” shape occur? ◦ Water behind a duck ◦ Boats ◦ Wakeboarding/Waterskiing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yWIMWqk cRDU&feature=related