PowerPoint slides - Food, Farming and Community
advertisement

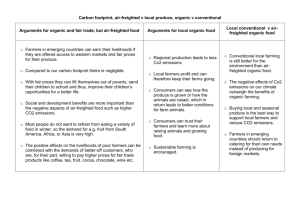
Strategies for Supporting Sustainable Food Systems Session 6 Local Farmers’ Markets Positives Challenges • Healthy and fresh food. • Strengthens local economy. • Direct profit for farmers • Community interaction; grows trust. • Seasonal eating follows a natural ecological cycle. • Zoning regulations: can effect growing or selling of food. • Seasonality: markets may operate only part of the year. • Real estate development: Farmland sold for developments. • Economics: Policy that favors large commodity farming. Urban Gardening Positives • Access to fresh food for people living in urban areas. • Strengthens local economy. • Physical exercise. • Intergenerational knowledge exchange and learning. • Strengthens community; grows trust and interdependence based on relationships. • Recovery of healthy soils. Challenges • Contaminated soil • Zonings regulations: can effect growing/selling of food. • Access to equipment. • Knowledge: gardening, farming experience, soil revitalization. • Water is expensive. Community Supported Agriculture (CSAs) Positives • Supports local farms; economic partnership. • Direct ties between producer and consumer; knowledge of how food was grown. • Management is done collectively. • Distribution style can vary to serve the local community. Challenges • Consumer adjustment to eating seasonally; knowledge of how to cook with new produce. • Risks of poor weather and other factors that can impact harvest. • Prices may be higher than grocery stores. • Farm capacity to maintain records/management. Farm to Schools programs Positives Challenges • Supports local economy. • Healthy food for schools. • Students have an opportunity to learn from the farmer and farm. • Schools and local farmers build relationships. • Distribution: Food and safety regulations differ state to state. • Preparation: Produce comes uncut and not portioned out. • Government subsidies for pre-existing lunch programs can impact a schools ability to purchase and the need. ? • Large quantities of produce can be hard to acquire at one time from local farms. Fair Trade Positives • No use of pesticides, child labor, genetically modified organisms, and exploitive working conditions. • Supports small farmers and cooperatives; a fair wage is paid for what is purchased. • Direct relationship between importer and grower or cooperative. • Products are available all year round. Challenges • Consumer awareness. • Access: many mainstream food suppliers do not supply Fair Trade products. • Fair Trade can be costly • Packaging is necessary. • Fair Trade can require miles of transportation. Organic Positives Challenges • No use of genetically modified organism. • Access is becoming more widely available. • Greatly decreases the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. • Can help to conserve healthy farmland. • Seasonal and regional. • Large organic productions can threaten smaller more localized organic productions. • Large scale distribution uses heavy fuels. • Transitioning into organic farming practices can take years and pose high economic risk for farmers. • Price and availability. Pasture Raised Animals Positives • Better quality of life for animals. • Often from a local farm. • Can support the health of surrounding ecosystems. • Quality of meat and dairy can be improved. • No use of hormones and antibiotics can help improve water systems around farmland. Challenges • Overgrazing can degrade the natural habitat and stress the ecosystem. • Deforestation: Forests are cleared for grazing. • Consumer expectation: Consumption of pasture raised meat can mean a decrease in the amount of meat in diets.