japheth's descendants
advertisement

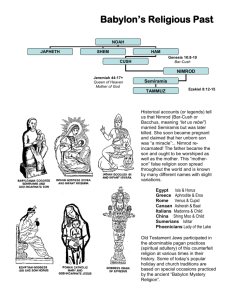
GENESIS • PART FIVE BOOK OF BEGINNINGS GOD AS CREATOR MAN MADE IN GOD’S IMAGE EDENTEMPTATIONSIN THE FALL AND ITS CONSEQUENCES GENESIS PART FIVE BOOK OF BEGINNINGS GOD AS CREATOR MAN MADE IN GOD’S IMAGE EDENTEMPTATIONSIN THE FALL AND ITS CONSEQUENCES GOD’S RESPONSE PROVIDES A COVERING (CLOTHING) FOR MAN’S SIN PROMISE OF A REDEEMER (ONE OF EVE’S DESCENDANTS) – TRACED IN ALL ANCIENT CULTURES CAIN and ABEL Biblical Principle: “First the natural, then the spiritual” (1 Cor. 15:46) CAIN KILLS ABEL, A TYPE OF CHRIST. SETH, THE SUBSTITUTE FOR ABEL. ADAM’S GENEALOGY ENOCH METHUSELAH NOAH “A man in God’s image, a substitute, mortal, an acquisition, none other than God, will descend, teaching, and will bring by his death, destruction, and rest to the weary.” NOAH ANTEDILUVIAN CLIMATE, LIFESPAN FALLEN ANGELS CORRUPTING MANKIND THE ARK THE FLOOD (ONE YEAR) ARGUMENTS FOR A WORLDWIDE FLOOD ARK SIGHTINGS NOAH – A TYPE OF CHRIST Noah is a shadow, a picture of the Messiah. What Noah did is symbolic of the work that the Messiah would do one day. JESUS NOAH • Name means “rest”. • Jesus brings us into God’s rest (Hebrews 4:1-9). • Was just, righteous and ‘perfect’. • Was just, righteous and perfect. • Walked with God (communed and communicated with God). • Walked with God (Luke 6:12). • Prepared the way of salvation for the world. • Prepared the way of salvation for the world (John 14:6) • Obeyed God. • Obeyed God (John 15:10, Phil 2:8). • Offered a sacrifice to God. • Offered a sacrifice to God (Eph 5:2). • God established a covenant with Noah. • God established a covenant with Christ (Heb 13:20). THE ARK – A TYPE OF CHRIST The Ark, similarly, is a picture of the redemptive work of Christ. THE ARK CHRIST • Divine provision, not Noah’s idea. • God chose to send His Son; man did not find a way to save himself from sin. • Made of wood. • The Cross was made of wood. • A refuge from divine judgement. • Christ saves us from God’s wrath. • Only one door. • Jesus is the only way of salvation (John 10:9, 14:6; Acts 4:12). GOD’S COVENANT WITH NOAH Noah’s first action upon leaving the Ark was to sacrifice to God a sacrifice of thanksgiving, which was a sweet smell and pleasing to God (Genesis 8:20-22). This was most likely fairly high up on the mountain where the Ark had rested. GOD’S COVENANT WITH NOAH God instituted a covenant “with all living creatures” (Genesis 9:9-10), which has 5 characteristics. 1. It was instituted solely by God (Genesis 9:9). 2. The covenant was eternal (Genesis 9:16). GOD’S COVENANT WITH NOAH 3. God made certain promises to Noah (Genesis 9:9-17). God will never again use a flood to destroy all life, and a flood will never again cover the whole earth. 4. The sign of the covenant was a rainbow (Genesis 9:13-16). It is possible that a rainbow had never been seen before if there had been no rain, and a thick, cloudy atmosphere through which the sun could not be seen. Alternatively, it is from this point on that the rainbow takes on the significance of the symbol of God’s covenant. 5. The unborn children were included in the covenant (Genesis 9:9). POST-FLOOD CONDITIONS Noah entered a very different world to the one he had left 375 days earlier. • Atmosphere had lost its watery covering. • Land changed dramatically because of volcanic activity (some probably still active for a while after the flood). • Higher sea level. • No cities or people or animals. • Vegetation re-growing – a fresh start. POST-FLOOD CONDITIONS God issued Noah with a set of instructions (similar to Adam). • Repopulate the earth (Genesis 9:1). • Animals would fear mankind from now on (Genesis 9:2). • Man given permission to eat meat for the first time (Genesis 9:3). • Blood must not be eaten/drunk (Genesis 9:4). Blood represented life and God used blood sacrifices as symbolic of the cost of sin (Leviticus 17:11). POST-FLOOD CONDITIONS • Capital punishment was instituted for the ultimate crime – killing a person: destroying God’s image (Genesis 9:6). To God, righteousness is more important than life – which is why Christ had to die. HAM’S SIN First mention of wine in scripture is associated with: Drunkenness Shame Curse HAM’S SIN Noah plants a vineyard, drinks of the wine it produces, gets drunk and “uncovers” himself – a Hebrew phrase which implies a deliberate act. Ham behaves in a manner which is either disrespectful, mocking or malicious – displeasing to God. HAM’S SIN After the effects of the wine had worn off, Noah (sober) pronounces a prophecy from God upon his 3 sons (Genesis 9:24-27). NB: This was not an angry father cursing one son and blessing the other two, but the first of many prophesies by a father over his sons. NOAH’S PROPHECY Ham was cursed in a manner which suited his sin – namely, he sinned as a disrespectful son, and so his son Canaan was cursed. Shem was blessed by a relationship with God (Genesis 9:26). Japheth was blessed by being promised an enlargement – a physical increase in lands and descendants. NOAH’S PROPHECY All 3 prophecies came true – indicative that Noah was speaking a word from God. All of Canaan’s descendants suffered as servants to the descendants of his uncle’s descendants in the years to come. Japheth was the father of by far the greatest number of “races” or “peoples” covering a large portion of the earth’s surface. Shem was an ancestor of the messiah, so he did indeed have a special covenant relationship with God. JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS Japheth means “extender” or “enlarger”. He is probably the Japetus whom the Greeks thought was the father of the human race. Also possible that the Roman “Jupitor” derives from Japheth. Japheth had 7 sons (Genesis 10:2-5). JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 1. GOMER (“completion”): Gauls, Celts, Cimmerians. Gomer had 3 sons (Ashkenaz, Riphath, Togarmah): it is generally believed that these 3 sons produced the Germans French Welsh Irish Britons Anglo Saxons JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 2. MAGOG (“increase”): Scythians, Tartars. Magog is the general name of the country north of the Caucasus mountains, which are between the Black and Caspian Seas. 3. MADAI (“middle”): Medes and Persians. JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 4. JAVAN (“supple”): Greeks, Syrians (Asia Minor). Javan had 4 sons: • Elishah • Tarshish (“hard”) • Dodanim – from whom came the Portuguese, Spanish and Italians. • Kittim – representing Cyprus and the Mediterranean coasts. JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 5. TUBAL (“production”): • • • • Iberians Georgians Cappadocians Other Asiatic and European races JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 6. MESCHECH (“drawing out”): Muscovites (Russia) 7. TIRAS (“desire of parents”): Thracians Etruscans (coast of Aegean Sea) JAPHETH’S DESCENDANTS 6. MESCHECH (“drawing out”): Muscovites (Russia) 7. TIRAS (“desire of parents”): Thracians Etruscans (coast of Aegean Sea) HAM’S DESCENDANTS Ham means “swarthy” or “dark”. He had 4 sons (Genesis 10:6-20). 1. CUSH (“black”): Ethiopia Cush had 6 sons: • Seba (“old man”) – produced the Sabeans in Yemen/Ethiopia • Havilah • Sabtah • Sabtecher • Raamah • Nimrod (“rebel”) HAM’S DESCENDANTS 2. MIZRAIM (“double”): Egypt Mizraim had 7 sons: • Ludim • Anamim • Lehabim • Naphtuhim • Pathrusim • Caphtorim • Casluhim (from whom came the Philistines) HAM’S DESCENDANTS 3. PHUT (“bow”): Lybia, North Arica 4. CANAAN (“low, flat”): Palestine, Phoenicia, Arabia Canaan had 11 sons: • Sidon (Ancient Phoenicia) • Heth (Hittites) • Jebus (Jerusalem) • Amorite • Girgashite • Hivite • Arkite • Sinite • Arvadite • Zemarite • Hamathite SHEM’S DESCENDANTS Shem means “name” or “renown”. From him all the Semitic (“shem etic”) people trace their line. Shem had 5 sons (Genesis 10:21-31). SHEM’S DESCENDANTS 1. ELAM (“youth”): East of Babylon and the Persian Gulf 2. ASSHUR (“level plain”): Assyrians 3. LUD (“bending”): Asia Minor SHEM’S DESCENDANTS 4. ARAM (“high” or “exalted”): Armenians (called Syrians) Aram had 4 children: • Uz (“firmness”) – Northern Arabia, where Job lived • Hul (“circle”) • Gether (“valley”) • Mach (“drawn”) SHEM’S DESCENDANTS 5. ARPHAXAD (“one that releases”): Arphaxad had 8 children: • Israelites • Arabians • Edomites • Moabites • Ammonites • Ishmaelites • Midianites • Other tribes of Asia SHEM’S DESCENDANTS ARPHAXAD’s line is the one that is followed through the rest of scripture: ARPHAXAD SELAH (“rock” or “cliff”) EBER (“shoot”) The word “Hebrew” probably comes from “Heber” (Eber). SHEM’S DESCENDANTS EBER had 2 sons: •Peleg (“division”) •Joktan (“little”) During Peleg’s time, the Earth was divided. The Hebrew meaning implies a physical division, as occurs during an earthquake. This is possibly some late shifting or resting of the Earth’s crust as a result of settling down after Noah’s flood, during which time the continents as we know them today were shaped. SHEM’S DESCENDANTS JOKTAN had 13 sons, of whom the most well-known are Sheba and Ophir. (Ophir famous for its gold – 1 Kings 9:28, 10:11). From Peleg we have a family tree (Genesis 11:10-26) leading up to Abram, upon which the rest of the book of Genesis hinges. Peleg Reu Serug Nahor Terah Abram THE TOWER OF BABEL BABYLON Records from this ancient city support the following biblical statements: • Story of 2 creations • Flood • Tower of Babel • Three men in a furnace • Cyrus’ decree to rebuild Jerusalem BABYLON Babylon was the product of civilized people. They had a complex society Highly developed school system Mathematics Astronomy Water systems Building programmes, etc. BABYLON The main centres of this empire were: UR: centre of Moon worship. BABYLON: centre of Baal worship. HARRAN (“road”): junction of all roads from Babylon, Egypt, Arabia and Palestine: also a centre of Moon worship. MESOPOTAMIA: Greek “between the rivers” Sumerians came from the east (or north-east) to settle here (Genesis 11:1-3). THE TOWER ZIGGURATS (“mountain of god”) were built as shrines to the Moon god and goddess. They were made of 7 stages of square bases. Around a central tower were a number of chapels or temples dedicated to principal gods, facing the cardinal points. ZIGGURATS Reasons for building them: • To get nearer to their god (the god of the heavens, and the god of the mountain). • Easier to get god’s attention from high up. • Halfway House for the god to whom it was dedicated. • Continuing the tradition of Noah who sacrificed on a mountain peak (“in a zikkurat sade”) when coming out of the Ark. ZIGGURATS Genesis 11:4 “Let us build a tower whose top … unto heaven” could mean: • “on whose top is the heavens” – various astrological signs have been found decorating the top walls of ziggurats • “whose top is dedicated to the heavens” BABEL “Gate of God” • It is uncertain as to which of the recently discovered ruins was the biblical tower. • This tower symbolises man’s religion – man’s efforts to reach God. • Men united to make a name for themselves, so God created confusion by changing their language. • Babylon, from Hebrew “balal”, means “confusion”. BABEL God commands mankind to fill the earth (Genesis 9:1). Man defies this command and builds a base from which to unify themselves (Genesis 11:4). God gives them all a different language (Genesis 11:7). The people scattered because they were confused (Genesis 11:8). THE CHURCH Note the New Testament parallel: • Jesus commands His disciples to preach the good news in Jerusalem, Judea, Samaria and all parts of the world (Acts 1:8). • The Holy Spirit is poured out on the church in Jerusalem, giving everyone a new language (Acts 2:4). • The church was scattered by God because of persecution (Acts 8:1). BABYLON Babylon symbolises an anti-Christ system and is often contrasted with Jerusalem. JERUSALEM BABYLON • Built by man (Nimrod). • Built by God (City of God). • Built on a plain. • Heavenly city, built above. • Bricks are mud/slime. • Bricks are “living stones” – Christians. • Prostitute/whore. • Bride of Christ. GODS OF BABYLON The early kings of Babylon and Assyria were deified because they were regarded as God’s representatives on earth. Two chief gods were: SIN (or NANNUR) – Moon god MARDUK (or MERODACH) – Sun god MOON GOD SIN (or NANNUR) and his wife, NINGAL. Moon goddess also known as ISHTAR or INNANNA. Main centres of Moon worship were Ur and Harran. Mountains of Sinai, and Desert of Sin were named after the Moon god. It was the most popular cult in Babylon. SUN GOD MARDUK (MERODACH), known as Lord of Babylon, “Lord par excellence”, or Bel (Lord). He was the chief god. Babylon was founded by Merodach. Merodach, from Hebrew “marad” (to rebel), became Nimarad or Nimrod. NIMROD • “Mighty hunter before the Lord” implies that he hunted men. • He was the first world/kingdom leader. • Ancient literature describes him as building a tower to ascend to heaven and make war with God. • Also claims the confusion of languages at Babel occurred during Merodach’s time. NIMROD Nimrod cast victims into his annual bonfires at the beginning of May (mid/late spring) – similar to Medieval English “May Day” burning of straw figures while dancing around the central pillar. This is the origin of Maypole dancing. NIMROD Two symbols used extensively: • “ankh” • Sun wheel Both were used as symbols of life, particularly in Egypt. NIMROD Marduk/Merodach/Nimrod had many other names in other cultures: • Osiris (Egypt) • Baal (Canaan) • Tammuz (Phoenicia) There are many legends and myths in ancient literature about Nimrod and his mother (Shammu-rammat, known as Semirami in the Greek version), the only woman to survive in the “king’s list” of ancient Babylon. NIMROD Nimrod’s mother is known as Ishtar or Ashteroth in the legends, and is purported to have had unnatural intercourse with her father. Years later she marries her son, Tammuz (a spring god of vegetation) who is slain one day while hunting wild boar. Ishtar collects pieces of his dead body and travels to the underworld to plead for her dead son to be restored to life and returned to her. She is successful and receives him back from the gods of the underworld – her dead son is restored to life! NIMROD In Egypt the story is the same with the names changed to Isis (mother) and Horus (son). A central feature of the religion that sprang up around these figures, was the annual lamentation for the death of Tammuz. Ezekial 8 describes the practices of these cults, with verse 14 dealing with the weeping for Tammuz. NIMROD The Ishtar/Tammuz fertility cult spread worldwide and became recognised under different names. Ishtar was served/worshipped and became more popular than her husband/son. In all the religions the Mother figure goddesses were all powerful, and had shadowy male consorts (lacking real power), who were “husbands of their mothers”. NIMROD Ishtar and Isis are often depicted suckling a babe. She was known as the “Queen of Heaven” (see Jeremiah 7:17,18 and 44:15-19). MYSTERY RELIGIONS The fertility cult of Nimrod and his mother spread in popularity and became widespread over the world. The names of the Mother/son changed in different regions but all the Mystery Religions had 7 things in common: • Mother and child symbol • Celibate priesthood • Temple virgins, married to their god • Intermediaries • Two major, annual festivals • Initiation ceremonies • Mysteries MYSTERY RELIGIONS 1. MOTHER AND CHILD SYMBOL Depicted in the case of: • Isis • Ishtar • Guadalupe • Juno • Venus • Cybele • Phyria In all cases, salvation was obtained from these goddesses through the sacrifice of a bull. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 2. CELIBATE PRIESTHOOD The priests of the Great Mother cults all espoused celibacy. Some, in the case of the Syrian goddess, were eunuchs who danced and cut their bodies with knives before her image. Others were well-organised and serene in their devotion. Sexual abstinence was an absolute requirement of those who celebrated the Great Mother’s holy mysteries. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 3. TEMPLE VIRGINS These sometimes lived chastely, and sometimes ended up as prostitutes in the temple – particularly those of Innanna/Ishtar – with no stigma attached. These “vestal virgins”/prostitutes were known as “Entu of the Lady” (Ishtar). The famous Vestal Virgins of ancient Rome were required to be celibate for at least 30 years of service. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 4. INTERMEDIARIES The father of each house became the High priest for his family. Each house had many gods (Hebrew – “teraphim”). The Great Gods were too remote and too great to be approached by ordinary mortals; thus the family needed the teraphim (little gods) as intercessors to carry the family’s prayers to the Great Gods. Sometimes the people applied to the gods for help through a priest other than the father of the household. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 5. MAJOR FESTIVALS There were 2 major annual festivals: Winter Solstice (21-25 December) This festival culminated on 25 December with complete sexual abandon. This day was celebrated because it was perceived that the Sun god was getting stronger again as the days began to lengthen from this time on. The Romans celebrated this time under the name of Saturnalia. MYSTERY RELIGIONS Easter (Spring) Festival Celebration of life, commemorating the fertility goddesses (Isis, Ishtar, Ashteroth). In the religion of Baal, Easter was preceded by 40 days of self denial. In Roman times important Isis festivals were celebrated on 25 December, 6 January and 5 March. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 6. INITIATION CEREMONIES In all mystery religions the candidates swore an oath of secrecy (oath of the Isis Mysteries is preserved on papyrus). Before initiation into the new religion the candidate had to tell, at length, the story of the faults of his life. Baptism was often part of the initiation ceremony, symbolising a clean start in the service of the god. Sometimes initiation ceremonies involved a “marriage” to the cult, with the priest often showing a nimbus (or halo) effect during initiation. MYSTERY RELIGIONS 7. MYSTERIES • These usually involved: Saying prayers for the dead in the underworld • Burning candles and incense • Praying with the assistance of a string with knots, beads or jewels • Recognising each other by making the sign of T (for Tammuz). BABYLON TO ROME Babylon was eventually destroyed and all the ornaments, objects and hierarchy necessary to perpetuate the mysteries of Baal were carried off to Pergamos (modern Pegamum). From Pergamos they were eventually moved to a small town on 7 hills overlooking the Tiber river – Rome. The followers of Isis and Mithra considered Rome to be the sacred city and the centre of their worship. BABYLON TO ROME It was in Rome that Christians suffered the most. From 100 to 303 AD about 5 million Christians were martyred by the Caesars – the entire earth was covered in Baal worship centred in Rome. From 303 to 313 Emperor Diocletian murdered another 5 million Christians. BAAL WORSHIP References HWF Saggs: Everyday Life in Babylonia and Assyria. HWF Saggs: The Greatness that was Babylon. Sir Leonard Woolley: Excavations at Ur. Near Eastern Mythology. ZA Ragozin: The Story of the Nations – Chaldea. TC Pinches: The Religion of Babylon and Assyria. DA Mackenzie: Myths of Babylonia and Assyria. Alexander Hislop: The Two Babylons.