Hypertension
advertisement

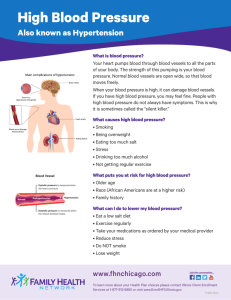
Hypertension Karen Ruffin RN, MSN Ed. Blood Pressure Arterial BP = Cardiac Output (CO) x Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) Cardiac Output = stroke volume x beats per min Systemic vascular resistance = force opposing the movement of blood within the blood vessels What is the effect on BP if SVR increased and CO remains constant? Blood Pressure Definition: the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels Adequate to maintain tissue perfusion during activity and rest Arterial blood pressure: primary function of cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance Mechanisms that Regulate Blood Pressure Sympathetic Nervous System Vascular Endothelium Renal System Endocrine System Hypertension Aldosterone Mechanism • Increased Aldosterone = • Increases sodium reabsorption = • Increases water reabsorption = • Increases blood volume = • Increases cardiac output Hypertension Regulatory mechanisms in the health person function in response to the demands on the body When Hypertension develops, one or more of these mechanisms are defective Sympathetic Nervous System Vascular Endothelium Renal System Endocrine System Hypertension Pathophysiology Primary (Essential) Hypertension: Elevated BP without an identified cause Accounts for 95% of all cases of hypertension Cause – unknown Contributing Factors: Increased SNS activity, overproduction of Na+ retaining hormones & vasoconstrictors, increased Na+ intake Risk Factors: Modifiable & Non-modifiable Primary Hypertension Pathophysiology Heredity – interaction of genetic, environmental, and demographic factors Water & Sodium Retention – 20% of pts with high Na+ diet develop HTN Altered Renin-Angiotensin Mechanism – found in 20% of patients Stress & Increased SNS Activity Insulin Resistance & Hyperinsulinemia Endothelial Cell Dysfunction Diagnosis of Hypertension Dx is made after multiple readings over several weeks NIH/Joint Committee Definition: Category Optimal Normal High Normal Systolic <110 <120 130-139 and and or Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 140-159 160-179 =>180 or or or Diastolic < 80 <85 85-89 90-99 100-109 => 110 Secondary Hypertension Pathophysiology Specific cause of hypertension can be identified Affects >5% of adults with hypertension What conditions can lead to or cause hypertension? Primary Hypertension Risk Factors Age Alcohol Cigarette Smoking Diabetes Mellitus Elevated serum lipids Excess Na+ in diet Gender Family History Obesity Ethnicity Sedentary Lifestyle Socioeconomic Stress Which risk factors are modifiable or non modifiable? Primary Hypertension Clinical Manifestations Organs that are affected by Hypertension: Myocardium – angina / left ventricular hypertrophy Brain – TIA / CVA Peripheral vascular – Peripheral pulse change Kidney – renal failure Creatinine / Proteinuria Eyes – Hemorrhages with or without papilledema Primary Hypertension Clinical Manifestations “Silent Killer” – asymptomatic and insidious Severe HTN – fatigue, reduced activity tolerance, dyspnea, dizziness, palpitations, angina Hypertension Medical Diagnosis History and Physical Examination Renal Function Serum Creatinine & Urine Creatinine Clearance Electrolytes – especially K+ Blood Glucose Serum Lipids/EKG Ambulatory BP Monitoring Primary Hypertension Medical Management Risk Stratification Level of BP Presence of Target Organ Disease Other Risk Factors Primary Hypertension Medical Management Lifestyle modification Nutritional therapy Alcohol consumption Physical activity Tobacco avoidance Stress management Drug Therapy Stepped Approach to Manage Hypertension Lifestyle modification Not at Goal BP Drug Therapy Not at Goal BP Substitute med / add a 2nd med/ increase dose Not at Goal BP Continue adding / changing meds until control Medical Management – Drug Therapy Diuretics Thiazide Loop K+ Sparing Adrenergic Blockers/ Inhibitors B-Adrenergic Blockers Central Acting Adrenergic Antagonists Peripheral Acting Adrenergic Antagonists A-Adrenergic Blockers Vasodilators Angiotensin Inhibitors Calcium Channel Blockers Antihypertensive Drug Therapy Lack of Responsiveness to Therapy Nonadherence to Therapy Drug-Related Causes Associated conditions Secondary Hypertension Volume overload Nursing Care for the Patient with Hypertension • What will you assess???? • What are some potential nursing diagnosis????? • What are your goals for those diagnosis???? • What are your interventions????? • How will you evaluate your goals????? Basic Human Needs • What Basic Human Need is being affected? • What other Basic Human Needs are effected by hypertension? Nursing Care for the Patient with Hypertension Concept Map • The patient with essential hypertension is prescribes the beta blocker metoprolol (Lopressor). Which assessment data would make the nurse question administering the medication? • • • • A. The patients blood pressure is 112/90. B. The patients apical pulse is 56. C. The patients ha an occipital headache. D. The patient is complaining of a yellow haze. • The nurse is preparing to administer the following medications. Which medications would the nurse question administering? • A. Vasodilator hydralazine(Apresoline) to the patient with blood pressure of 168/94. • B. Beta Blocker Lopressor(metoprolol) to a patient with a serum sodium level of 137. • C. Calcium Channel blocker diltiazem(Cardizem) to a patient with a glucose level of 280. • D. Loop Diuretic(Lasix) to a patient with a K+ of 3.1. Primary Hypertension Case Study