Higher-throughput Cleavable ICAT Analysis using CEM Microwave
advertisement
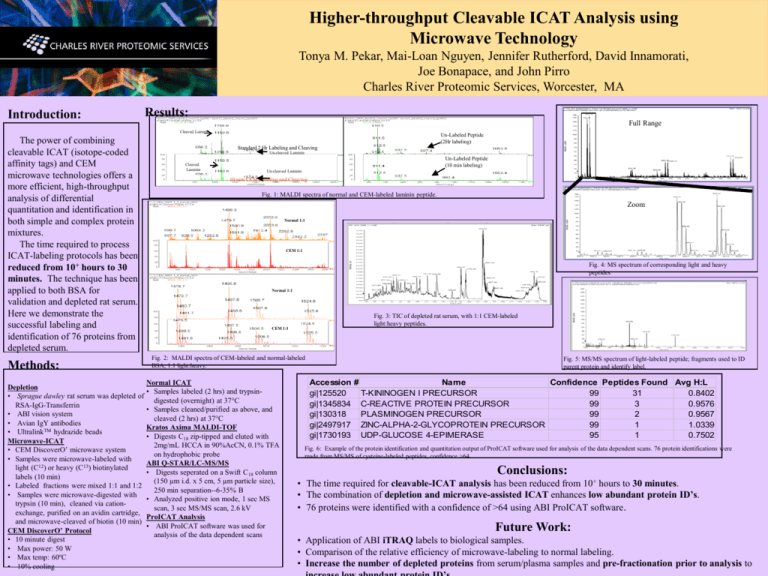
Higher-throughput Cleavable ICAT Analysis using Microwave Technology Tonya M. Pekar, Mai-Loan Nguyen, Jennifer Rutherford, David Innamorati, Joe Bonapace, and John Pirro Charles River Proteomic Services, Worcester, MA Introduction: Results: Full Range Cleaved Laminin The power of combining cleavable ICAT (isotope-coded affinity tags) and CEM microwave technologies offers a more efficient, high-throughput analysis of differential quantitation and identification in both simple and complex protein mixtures. The time required to process ICAT-labeling protocols has been reduced from 10+ hours to 30 minutes. The technique has been applied to both BSA for validation and depleted rat serum. Here we demonstrate the successful labeling and identification of 76 proteins from depleted serum. Methods: Depletion • Sprague dawley rat serum was depleted of RSA-IgG-Transferrin • ABI vision system • Avian IgY antibodies • UltralinkTM hydrazide beads Microwave-ICAT • CEM DiscoverO’ microwave system • Samples were microwave-labeled with light (C12) or heavy (C13) biotinylated labels (10 min) • Labeled fractions were mixed 1:1 and 1:2 • Samples were microwave-digested with trypsin (10 min), cleaned via cationexchange, purified on an avidin cartridge, and microwave-cleaved of biotin (10 min) CEM DiscoverO’ Protocol • 10 minute digest • Max power: 50 W • Max temp: 60ºC • 10% cooling Un-Labeled Peptide (2Hr labeling) Standard 2 Hr Labeling and Cleaving Un-cleaved Laminin Cleaved Laminin Un-Labeled Peptide (10 min labeling) Un-cleaved Laminin 10 min CEM Labeling and Cleaving Fig. 1: MALDI spectra of normal and CEM-labeled laminin peptide. Zoom Normal 1:1 CEM 1:1 Fig. 4: MS spectrum of corresponding light and heavy peptides. Normal 1:1 Fig. 3: TIC of depleted rat serum, with 1:1 CEM-labeled light:heavy peptides. CEM 1:1 Fig. 2: MALDI spectra of CEM-labeled and normal-labeled BSA; 1:1 light:heavy. Normal ICAT • Samples labeled (2 hrs) and trypsindigested (overnight) at 37°C • Samples cleaned/purified as above, and cleaved (2 hrs) at 37°C Kratos Axima MALDI-TOF • Digests C18 zip-tipped and eluted with 2mg/mL HCCA in 90%AcCN, 0.1% TFA on hydrophobic probe ABI Q-STAR/LC-MS/MS • Digests seperated on a Swift C18 column (150 µm i.d. x 5 cm, 5 µm particle size), 250 min separation--6-35% B • Analyzed positive ion mode, 1 sec MS scan, 3 sec MS/MS scan, 2.6 kV ProICAT Analysis • ABI ProICAT software was used for analysis of the data dependent scans Fig. 5: MS/MS spectrum of light-labeled peptide; fragments used to ID parent protein and identify label. Accession # Name Confidence Peptides Found Avg H:L gi|125520 T-KININOGEN I PRECURSOR 99 31 0.8402 gi|1345834 C-REACTIVE PROTEIN PRECURSOR 99 3 0.9576 gi|130318 PLASMINOGEN PRECURSOR 99 2 0.9567 gi|2497917 ZINC-ALPHA-2-GLYCOPROTEIN PRECURSOR 99 1 1.0339 gi|1730193 UDP-GLUCOSE 4-EPIMERASE 95 1 0.7502 Fig. 6: Example of the protein identification and quantitation output of ProICAT software used for analysis of the data dependent scans. 76 protein identifications were made from MS/MS of cysteine-labeled peptides, confidence >64. Conclusions: • The time required for cleavable-ICAT analysis has been reduced from 10+ hours to 30 minutes. • The combination of depletion and microwave-assisted ICAT enhances low abundant protein ID’s. • 76 proteins were identified with a confidence of >64 using ABI ProICAT software. Future Work: • Application of ABI iTRAQ labels to biological samples. • Comparison of the relative efficiency of microwave-labeling to normal labeling. • Increase the number of depleted proteins from serum/plasma samples and pre-fractionation prior to analysis to