Chapter 11: The Evolution of Populations
advertisement

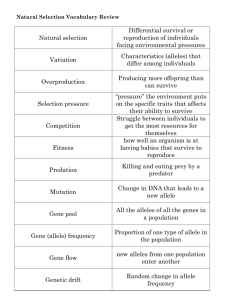
Chapter 11: The Evolution of Populations Mechanism for Evolution video Darwin stated that in a population there are variations • Population: – All the individuals of the same species in a given area. • Gene pool – The combined alleles (different form of the gene individuals in a population – Individual members of a population contribute their alleles to a common pool of genes. On an island, there are 7 boars. 2 are pure for the long bristles gene (BB), 3 are hybrids (Bb) for long bristles and 2 are pure recessive (bb) for short bristles. What is the likelihood of either allele (B or b) showing up in the next generation? • Allele frequency: – Measure of how common an allele is in the population – The likelihood of that allele showing up in the population. – 2 BB (Homozygous long bristles) – 3 Bb (Heterozygous long bristles) – 2 bb (Homozygous short bristles) 1. Count the number of each allele, remembering that each individual has 2 alleles for each trait 2. “B” (Long allele) “b” (Short allele) 2 BB 2x2=4 3 Bb 3 3 2 bb 2x2=4 7 “B” alleles 7 “b” alleles 3. 7/14 = 0.5 or 50 % 7/14 = 0.5 or 50% Therefore the chance of a “B” or a “b” allele for bristle length is 50/50 for this population How about something closer to home? Let’s look at the allele frequency for colorblindness in our classroom. # of “N” “n” alleles # of colorblind individuals = _____ # of carrier females = ____ # of homozygous dominant females = ___ # of normal males = ___ ____ ____ ____ ____ Normal allele ____ ____ Colorblind allele ____ Total # of alleles ____ Allele frequency Normal ____ Colorblind ____ ____ How did the short bristle or colorblind allele come about in the first place? • Mutation – – – – A random change in DNA of a gene May form a new allele for a gene Gene mutations are inheritable if in a gamete Spontaneous • Recombination – Due to meiosis (formation of gametes) new combinations of chromosomes and therefore genes may occur – Shuffling of genes Can the allele frequencies in a population change over time? Brown is dominant to Green What will happen to brown and green alleles in the gene pool once the brown beetles join the population? Before: Green alleles ____ Brown alleles ____ ____ Frequencies: _____ ____ After: Green alleles ____ Brown alleles ____ ____ Frequencies: _____ ____ The frequency of brown alleles in the gene pool will increase while the frequency of the green alleles will decrease. Changes in allele frequency within a gene pool can be caused by a number of factors 1. Gene Flow • • • • The movement of alleles from one population to another Migration of organisms into and out of the population Increases the genetic variation of the receiving population and decreases the variation of the other population. A lack of gene flow will lead to Speciation, the formation of different species. Did natural selection play a part in the loss of variation in the beetle population or was there another factor not related to natural selection? 2. Genetic Drift • In a small population (isolated one), a particular allele may occur more or less frequently even though it was purely due to chance. • Leads to loss of variation in a population Among the Amish population, polydactylism is very common. Why? Is it a favorable trait for working on farms & doing more “hand work”? Animation Sicilian family An Australian Aboriginal cave painting What would happen to the population of frogs illustrated below, in the next generation 3. Bottleneck effect – Effect of a destructive event that leaves a few survivors in a population – Form of Genetic drift Why is a peacock have such impressive feathers? 4. Sexual Selection – – – – Certain traits increase the likelihood of finding a mate and therefore, passing on your genes (making you fitter!) Since females need to be selective with their limited number of eggs, she wants to be certain that she selects the correct male who will increase the chances of having the fittest offspring. Why the peacock (male) is so brightly colored Compare the male to the female cardinal Mechanism for Evolution video The story of the fruit flies 1. 2. 3. 4. A bunch of flies were minding their own business feeding on bananas Suddenly, a hurricane washed the bananas & flies onto another island Since conditions & food are different on the new island, the flies evolve separately from their mainland relatives When some of the flies mix with the mainland relatives, they can no longer produce viable offspring when they mate. Speciation has occurred!! New island Mainland Mainland Look at the illustration above and discuss what might have happened. The original population was beige in color. They were feed different types of food, one high in starch and the other high in maltose which caused variations in the coloration, resulting in light variations and the darker variations of flies The light flies only mated with the light colored flies and the darker flies only mated with the darker flies, eventually resulting in two separate species Reproductive isolation Occurs when members of different populations can no longer mate and produce successfully with each other. Predict what will happen. Geographic isolation – A physical barrier such as a river, mountain, valley, … separates two populations resulting eventually in reproductive isolation with the formation of new species. – Most common form of isolation – Isolated populations become genetically different over time Geographic Isolation Animation Watch the videos of mating dances for a ruffed grouse, a peacock and a fiddler crab • Ruffed Grouse courtship display. – YouTube • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hgh7nhG zNUk • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jTBHiZtn CsA • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yCn6g3p Xc1s Behavioral isolation Isolation caused by differences in courtship or mating behaviors – Different chemical scents, dances, songs and signals If a shark and a dolphin both occupy the same niche, meaning they are top fast swimming predators, would they become more or less alike in appearance over time? Convergent evolution – Occurs when unrelated organisms occupy the same niche and tend to have similar characteristics – Analogous structures. – Shark and dolphin – Does not indicate common ancestry What is the ancestor of the modern dog? All the dog breeds (Canus familiaris) today share common ancestry with the wolf (Canus familiarus lupus) Divergent evolution – Closely related species evolved in different directions, becoming increasingly different Divergent evolution of the Galapagos finches Adaptive Radiation • Rapid evolution of many diverse species from ancestral species • Our beak activity showed this. Coevolution Two totally unrelated species evolve in response to changes in each other over time. Bees don’t see red, but do see yellow, blue, and UV. Thus, bee-pollinated flowers are mostly yellow or blue with UV nectar guides (landing patterns) to guide the bee Birds, like hummingbirds have good eyes which can see red Acacia tree and ants How quickly does evolution occur? • • Gradualism – evolution is a constant process and occurs at a steady rate Punctuated equilibrium- Periods of equilibrium followed by rapid periods of change. – – Change occurs w/ environmental pressures Species arise abruptly then have long periods of little change Gradualism versus Punctuated Equilibrium