Nucleic Acids
advertisement

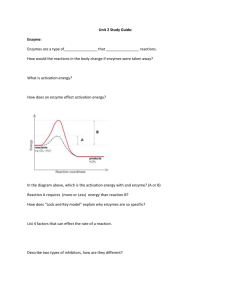
TEST DATE: __________ NAME: Regents Biology Homework Packet Unit 4: Biochemistry Use your Biology by Miller & Levine textbook to complete and help with the following homework assignments. (1) Read the assigned pages, (2) Define the vocabulary, and (3) Answer the questions. Neatness counts. Number the definitions. Write the page and number of the questions. Do your work in ink or even type the homework. Staple the definitions and questions to the HW packet. The homework assignment is due the day before the test. We will use the HW packet as a test review. The completed and corrected HW packet will be collected on the day of the test. Late homework assignments receive no credit (0). If the assignment is not turned in by the last day of the quarter the zero grade (0) will change to -5. Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life Read pgs. 32 - 59 p. 34 Vocabulary (11) p. 40 Vocabulary (12) p. 45 Vocabulary (9) p. 50 Vocabulary (7) Additional vocabulary (6): denature peptide bond glycogen p. 38 #1a p. 44 #1b, 3a p. 49 #2a, 2b p. 53 #1a, 3a, 3b, 3c Regents Review pgs. 56 – 59 #1 - 21 glucose starch cellulose Biochemistry The chemicals of Living Organisms Basic Chemistry: ___________ : the smallest unit of matter; protons distinguish the element (specific type of atom); electrons determine how the atom acts. Specific Elements: Element Symbol Bonds 1. H 2. O 3. N 4. C MOLECULES / COMPOUND: specific combinations of atoms; combine together by sharing electrons; make covalent bonds (lines between the letters). Chemical bonds store ________________. ____________ – H2O _______________ – CO2 _______________ – C6H12O6 Inorganic Compounds: Simple molecules that do not contain __________ and __________ in the same molecule. Organic Compounds contain carbon and hydrogen together in the same molecule. Polymers: are ________ _________ __________ units. Many organic compounds are polymers of smaller repeating units. They are made by the process of _____________________________ and broken down by _____________________________. For Example: Many carbohydrates are polymers of glucose. The glucose molecules are chemically combined and form new molecules with completely different properties. The hexagon represents glucose and they are combined together with O (oxygen between the sub units) Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Then the proteins form different shapes. Carbohydrates ____________________ : are simple sugars; they are the basic building blocks of all carbohydrates _____________________ : are combinations of 2 monosaccharides Examples: Maltose and Sucrose Combine molecules by the process of DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS In dehydration synthesis 2 __________ and 1 __________ atoms are removed from the molecules. It makes room for the two molecules to bond to each other. C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 C12H22O11 + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 = C12H24O12 minus water H2O C12H22O11 + H2O Since H2O came out as a product it was removed from the original molecules. That is why it is dehydration synthesis, water was taken out of the reactant molecules. Notice the # of atoms of each element is the same on both sides; it is a balanced equation (more of that in chem). Hydrolysis is the process that _________ molecules. It is the exact opposite of Dehydration Synthesis, instead of taking away water; water is used to break down atoms. Enzymes break the bond holding the two molecules together and 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen are added to keep the molecules separated. Polysaccharides: are _______________, they are long polymers of monosaccharides; Starches are insoluble in water and thus can serve as storage depots of glucose. Plants convert excess glucose into starch for storage. The image shows starch grains (lightly stained with iodine) in the cells of the white potato. Rice, wheat, and corn are also major sources of starch in the human diet. Animals store excess glucose by polymerizing it to form glycogen. Examples of Starches: Cellulose, Chitin, Amylose Carbohydrates always have a specific ratio between the Hydrogen and Oxygen, 2 Hydrogen : 1 Oxygen. Does that remind you of any other molecules? Carbohydrates provide the bulk of the ______________ (4 kcal/gram) in most diets. Lipids Fats, Oils, Waxes that are used to store energy Made from 1 Glycerol molecule and 3 Fatty Acids ___________ = 3 Carbon chain with hydroxide groups (OH) attached to each carbon. __________________ = Long chains of Carbon and Hydrogen atoms with an acid group (carboxyl group) at the end (-COOH). ______________ Fatty Acids have single bonds between the carbon atoms ______________ Fatty Acids have double or triple bonds between the carbons ______________ fats, the good fats for you; have many double and triple bonds Like polysaccharides, Lipids are made through the same process, Dehydration Synthesis. In this instance it happens 3 times to attach each of the fatty acids. The reverse process is also true. Lipids are broken down by the process of _______________. It is just the same formula but turn the arrow around. If you really wanted to, you could count the number and type of atoms before and after the reaction. What will be true about those numbers? Lipids chiefly function in _________________ (9 kcal/gram), protection, and insulation. They contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but the H:O is not in a 2:1 ratio (Like Carbohydrates). Lipids tend to be large molecules. fats found chiefly in animals oils and waxes found chiefly in plants - oils are liquid at room temperature, waxes are solids lipids along with proteins are key components of _________ _________________ steroids are special lipids used to build many reproductive hormones and cholesterol Proteins Make up the structure, enzymes, and characteristics of organisms ________________ = are the building blocks of all proteins. There are 20 different essential amino acids. All the proteins in your body Alanine Arginine Asparagine Aspartic Acid (billions of them) are Carnitine Citrulline Cysteine Cystine made from different Gaba Glutamic Acid Glutamine Glutathione combinations of these Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine essential amino acids. Lysine Methionine Ornithine Phenylalanine ProlineSerine Taurine Threonine Tryptophan All amino acids have the Tyrosine Valine same basic structure, an amino group, an acid group, and a variable chain (R) in the middle. *Notice the CH3. That variable group makes this amino acid Alanine. For each of the 20 essential amino acids the variable group is composed of different atoms. Peptides Peptides are chains of amino acids. The amino acids are held together by peptide bonds, a bond between the nitrogen atom in the amino group to the carbon atom in the carboxyl group. They are created by the process of D S and broken down by H The order of amino acids determines the shape of the peptide. When peptides come together proteins are formed. The shape of the protein determines the proteins function. Proteins are used for structure and function (bones and muscles), enzymes, antibodies, hormones, buffers (stabilize pH), and pigments. The proteins in your body make up your characteristics Enzymes Enzymes are __________________________ that are organic catalysts. Organic Catalysts are molecules that __________________ the rates of reactions. Most enzyme names end in –ase. Enzymes lower the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. (activation energy) It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between enzyme and substrate is thought to form a close physical association between the molecules and is called the enzyme-substrate complex. 3. While the enzyme-substrate complex is formed, enzyme action takes place. 4. Upon completion of the reaction, the enzyme and product(s) separate. The enzyme molecule is now available to form additional complexes. ** Although enzymes may be reused in cells, they eventually are destroyed and new ones must be synthesized. ________________________: A substrate is the molecule(s) that the enzyme acts on. Enzymes can build up or break down molecules. In the end of the reaction the substrate becomes the product. ________________________: The active site is the specialized area on the enzyme that comes in contact with the substrate. ________________________: Coenzymes are molecules that attach to enzymes to make them work better. Usually coenzymes are vitamins and minerals. Enzyme Action 1. Lock and Key Model - each enzyme is specific for one and ONLY one substrate (one lock one key). In this theory the enzyme and substrate fit exactly together. It is the easier way to think of the situation. 2. Induced Fit Model – enzymes have the ability to change shape to fit around the substrate. This theory allows enzymes to work on multiple substrates. Factors that Affect Enzyme Action 1. ______ - the optimum (best) in most living things is close to 7 (neutral). High or low pH levels usually slow enzyme 1. At what pH level does the enzyme activity. pepsin (a protein enzyme) seem to work best? 2. At what pH level does the liver enzyme seem to work best? 3. What would happen if you took a lot of Pepto-Bismol to help reduce your stomach acid? 4. One of the many things that our liver enzymes do is to break down toxins. Toxins are poisons in our bodies. What would happen if your liver pH increased? Would your health be affected? 5. So...what does this tell you about enzyme activity and pH? 2. ___________________ - strongly influences enzyme activity. Optimum temperature for maximum enzyme function is usually about 3540 C. Reactions proceed slowly below optimal temperatures. Above optimal temperatures, around 45 C in humans, most enzymes are _____________ (change in their shape so the enzyme active site no longer fits with the substrate and the enzyme can't function). 1. What happens to the enzyme catalase when it is exposed to high temperatures? 2. What happens to the enzyme lactase when it is exposed to high temperatures? 3. So...what does this tell you about enzyme activity and temperature? 3. ____________________________________ - When there is a fixed amount of enzyme and an excess of substrate molecules -- the rate of reaction will increase to a point and then level off. This leveling off occurs because all of the enzymes are used up and the excess substrate has nothing to combine with. If more enzyme is available than substrate, a similar reaction rate increase and leveling off will occur. The excess enzyme will eventually run out of substrate molecules to react with. Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA Nucleic acids are the instructions to make peptides. ________________________ : are the subunits of nucleic acids. _____________________: are long chains of nucleotides. 1. ______: Ribonucleic Acid RNA is a single strand of nucleotides. It is found in the nucleus, ribosomes, and the cytoplasm of cells. The nucleotides sometimes bind with complimentary pairs, C-G and AU. The primary role of RNA is to carry the genetic message from the nucleus to the ribosome for the production of peptides (protein synthesis). 2. _____: Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is a double strand of nucleotides (double helix). The nucleotides bond together in complimentary pairs, A-T, and CG. It is found inside the nucleus of cells. It can also be found inside chloroplasts and mitochondria. It carries the genetic information and controls the cell’s activities. Every nucleotide is made up of three different parts. 1. _____________ group = PO4 2. ____________ in DNA the sugar = ________________ in RNA the sugar = ________________ 3. ________________ = Nitrogen contain molecule, makes each nucleotide different 1. ____________ (G) 2. ____________ (C) 3. ____________ (A) 4. ____________ (T) only found in DNA 5. ____________ (U) only found in RNA Organic Compound Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Elements Subunit Structure Function Example Understand the Concepts 1. Distinguish between a solute and a solvent. 2. Balance the following equation: ___ CO2 + ___ H2O ___ C6H12O6 + ___ O2 3. Distinguish between a structural formula and a molecular formula. 4. What might be the result of mixing two solutions of equal volume, one of which has a pH of 9 and the other, a pH of 5? 5. Why do atoms share electrons? 6. Name the three types of atomic particles and describe where each is found in the atom. 7. What do you think a "double" covalent bond is? 8. Why are a hydrogen and hydroxyl(OH) removed during a dehydration synthesis reaction? 9. Why are a hydrogen and hydroxyl necessary for hydrolysis? 10. Why can organic molecules get so large? 11. How is a peptide bond formed? 12. How are the two chains of a double helix held together? 13. Why are small amounts of enzymes sufficient to catalyze a large number of chemical reactions? 14. Explain how glucose, fructose, and galactose can be different molecules even though they all have the same molecular formula (C6H12O6). Covalent bonding between Oxygen and Hydrogen 1. In a covalent bond atoms share pairs of __________. 2. How many electron vacancies does an atom of hydrogen have?___ 3. How many bonds can hydrogen make?___ 4. How many electron vacancies does oxygen have?___ 5. How many bonds can oxygen make?___ 6. How many atoms of hydrogen bond to oxygen to form water?___ 7. What is the chemical formula of water?__________ Dehydration Synthesis of a Lipid Dehydration Synthesis of a Peptide Know the Terms Select the most appropriate words from the list to complete the following paragraphs. nucleic acids hydrolysis polysaccharide fatty acids enzymes organic compounds monosaccharides thymine hydrogen lipids deoxyribose carbohydrates adenine disaccharide DNA dehydration synthesis cytosine peptide bond oxygen glycerol carbon ribose amino acids proteins saturated guanine RNA unsaturated Living organisms are composed of a special category of molecules called _______________(1). Molecules must have both _______________(2) and _______________(3) atoms in them to be in this category. In addition they usually contain _______________(4) as well. Sugars and starches are _______________(5), which always have a hydrogen to oxygen ratio of 2:1. They are composed of building blocks called _______________(6). Two of these units can be attached to each other through a process called _______________(7), which results in a _______________(8). If more subunits are hooked on, we get a _______________(9). This type of molecule can be broken into its building blocks again through the reverse reaction, called _______________(10). _______________(11) have a hydrogen to oxygen ratio greater than 2:1 and include fats, oils, and waxes. If the carbon-to-carbon bonds in these molecules are all single bonds, they are said to be _______________(12). lf there are any double bonded carbons, the molecule is said to be _______________(13).The building blocks of these molecules are _______________(14) and _______________(15). The group of organic molecules that contain nitrogen are called _______________(16). They have _______________(17) as their building blocks. The bond connecting two of these together is called a _______________ (18). Some of these molecules function as _______________(19), which catalyze chemical reactions within cells. The group of organic molecules that were first discovered in the nucleus of the cell are called _______________ (20). There are two kinds of these molecules. They are _______________(21) and _______________(22). One of these is described as a double helix. Its subunits are composed of a five-carbon sugar, called _______________(23), and one of four bases. MATCHTNG QUESTIONS From the list below, select the term that best fits each of the following descriptions. Each term may be used more than once, but there is only one correct answer for each question. a. radioactivity b. suspension c. acid d. neutralization e. solvent f. indicator g. fatty acid h. hydrolysis i. saturated j. nucleic acid k. enzyme l. peptide bond m. starch n. ribose o. substrate p. coenzyme q. denaturation r. amino group ___ 1. the reaction between an acid and a base ___ 9. splitting apart molecules by reacting with water ___ 2. having no carbon-carbon double bonds ___ 10. a component of RNA ___ 3. formed between two amino acids ___ 11. the bulk component of a solution ___4. mixture that separates on standing ___ 12. a part of a lipid molecule ___ 5. an organic catalyst ___ 13. produces H ions in solutions ___ 6. RNA and DNA ___ 14. that upon which an enzyme acts ___ 7. changes color with change in pH ___ 15. change in structure that can be caused by heating ___ 8. a polymer of glucose MODIFIED TRUE FALSE Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ____ 1. The basic unit of matter is the molecule. _________________________ ____ 2. A substance made up of only one kind of atom is a(an) element. _________________________ ____ 3. Scientists show the composition of compounds by a kind of shorthand known as a chemical formula. ____________________ ____ 4. The compound produced by a reaction between an acid and a base is an alkaline solution. _________________________ ____ 5. Lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. _________________________ ____ 6. Polysaccharides are formed through the process known as polymerization. _________________________ ____ 7. The substances that are present when a chemical reaction begins are the products. _________________________ ____ 8. Proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions in the cell without requiring high temperatures are antibodies. _________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Choose the best answer and write it on the answer blank. ___ 1. A covalent bond is formed as the result of a.) transfer of electrons b.) transfer of protons c.) sharing of an electron pair d.) sharing of a proton pair ___ 12. The main function of glucose is a.) to function as an enzyme b.) to assist in protein synthesis c.) to be part of nucleic acids d.) as a source of energy ___ 2. In chemical reactions, atoms are a.) created b.) rearranged c.) destroyed d.) neutralized ___ 13. Which of the following organic compounds is the main source of energy for living things? a.) carbohydrates b.) lipids c.) nucleic acids d.) proteins ___ 3. lf the pH of an acid solution and a basic solution were checked a.) both would be below 7 b.) both would be above 7 c.) the acid solution would be above 7; the basic solution would be below 7 d.) the acid solution would be below 7; the basic solution would be above 7 ___ 4. The total number of carbon atoms in the compound 2C6H12O6is a.) 2 b.) 6 c.) 12 d.) 24 ___ 5. When hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water, hydrogen would be a(n) a.) product c.) ionic bond b.) reactant d.) radioisotope ___ 6. Which of the following is an inorganic compound? a.) carbohydrate c.) water b.) amino acid d.) enzyme ___ 7. All the following statements about enzymes are true EXCEPT a.) Enzymes work best at a specified pH. b.) All enzymes work inside cells. c.) Enzymes are proteins. d.) Enzymes are organic catalysts. ___ 8. RNA and DNA differ from each other in that a.) RNA has guanine but DNA does not b.) DNA is single stranded but RNA is not c.) DNA has ribose but RNA has deoxyribose d.) RNA has uracil but DNA does not ___ 9. Amino acid is to protein as a.) fat is to lipid b.) DNA is to RNA c.) sugar is to fat d.) sugar is to starch ___ 10. A monosaccharide is a a.) carbohydrate c.) nucleic acid b.) lipid d.) protein ___ 11. Which is NOT a lipid? a.) fats c.) waxes b.) oils d.) enzymes ___ 14. Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? a.) store and transmit heredity b.) help to fight disease c.) control the rate of reactions and regulate cell process d.) build tissues such as bone and muscle ___ 15. Which statement is true? a.) Simple sugars are made of polysaccharides b.) Glycerol is made of fatty acids c.) Glycogen is made of starch d.) Amino acids are made of proteins ___ 16. Identify the reactant(s) in the chemical reaction, CO2 + H2O H2CO3. a.) CO2, H2O and H2CO3 b.) CO2 and H20 c.) H2CO3 d.) CO2 ___ 17. Which statement about organic compounds is CORRECT? a.) All contain carbon. b.) All can be produced in chemistry laboratories' c.) All contain hydrogen' d.) They contain most of the 90 elements. ___ 18. Which statement is TRUE? a.) Sugars are made of polysaccharides. b.) Glycerol is made of fatty acids. c.) RNA molecules are made of nucleotides d.) Amino acids are made of proteins. ___19. Which group of organic compounds includes the enzymes? a.) carbohydrates b.) lipids c.) proteins d.) nucleic acids ___20. Which characteristic allows enzymes to function in a specific way? a.) Each enzyme has a characteristic shape. b.) Enzymes are long, complex compounds composed of starch. c.) Enzymes are long, complex fats. d.) Each enzyme is made up of sugar, phosphate and base. ___ 21. Which represents an amino acid? CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE Answer each of the following questions. 1. What are the structural differences between the two types of nucleic acids? 2. Where are the bases located on a molecule of DNA? 3. Compare what happens to a water molecule during hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis. 4. Compare the lock and key model with the induced-fit model. 5. When your stomach produces excess HCl, you feel a burning sensation. a. What kind of substance can you use to relieve the stress caused by excess acid? b. What is the term for the type of reaction that will bring relief? c. Why does this reaction bring relief? d. What are the products of this reaction?