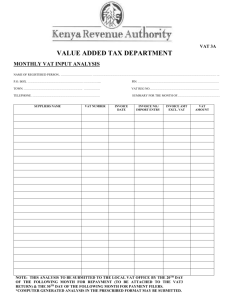
Microsoft Word Document / Unit 5 Assignment
advertisement
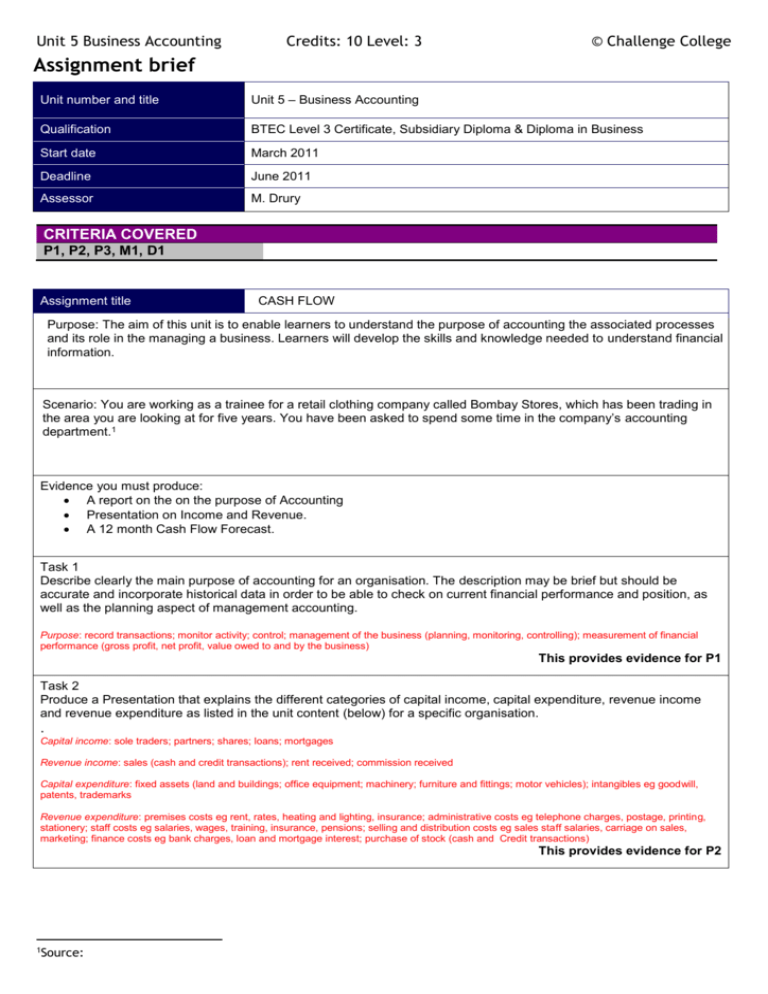
Unit 5 Business Accounting Credits: 10 Level: 3 © Challenge College Assignment brief Unit number and title Unit 5 – Business Accounting Qualification BTEC Level 3 Certificate, Subsidiary Diploma & Diploma in Business Start date March 2011 Deadline June 2011 Assessor M. Drury CRITERIA COVERED P1, P2, P3, M1, D1 Assignment title CASH FLOW Purpose: The aim of this unit is to enable learners to understand the purpose of accounting the associated processes and its role in the managing a business. Learners will develop the skills and knowledge needed to understand financial information. Scenario: You are working as a trainee for a retail clothing company called Bombay Stores, which has been trading in the area you are looking at for five years. You have been asked to spend some time in the company’s accounting department.1 Evidence you must produce: A report on the on the purpose of Accounting Presentation on Income and Revenue. A 12 month Cash Flow Forecast. Task 1 Describe clearly the main purpose of accounting for an organisation. The description may be brief but should be accurate and incorporate historical data in order to be able to check on current financial performance and position, as well as the planning aspect of management accounting. Purpose: record transactions; monitor activity; control; management of the business (planning, monitoring, controlling); measurement of financial performance (gross profit, net profit, value owed to and by the business) This provides evidence for P1 Task 2 Produce a Presentation that explains the different categories of capital income, capital expenditure, revenue income and revenue expenditure as listed in the unit content (below) for a specific organisation. . Capital income: sole traders; partners; shares; loans; mortgages Revenue income: sales (cash and credit transactions); rent received; commission received Capital expenditure: fixed assets (land and buildings; office equipment; machinery; furniture and fittings; motor vehicles); intangibles eg goodwill, patents, trademarks Revenue expenditure: premises costs eg rent, rates, heating and lighting, insurance; administrative costs eg telephone charges, postage, printing, stationery; staff costs eg salaries, wages, training, insurance, pensions; selling and distribution costs eg sales staff salaries, carriage on sales, marketing; finance costs eg bank charges, loan and mortgage interest; purchase of stock (cash and Credit transactions) This provides evidence for P2 1 Source: Unit 5 Business Accounting Credits: 10 Level: 3 © Challenge College Task 3 1) Explain what a cash flow forecast is and how it helps businesses 2) Construct a 12-month cash flow forecast from the information given in (additional information) below, accurately calculating each month’s receipts, payments, opening and closing balances . Cash flow forecast: structure; timescale; credit periods; receipts (cash sales, debtors, capital, loans, other income); payments (cash purchases, trade creditors, revenue expenditure, capital expenditure, Value Added Tax (VAT)); opening and closing cash/bank balances This provides evidence for P3 Task 4 Analyse the cash flow problems a business might experience by commenting on the cash flow, highlighting any problems that are evident. Cash flow management: problems within the cash flow forecast eg insufficient cash to meet payments due; This provides evidence for M1 Task 5 Justify actions a business might take when experiencing cashflow problems by making appropriate recommendations to solve these cash flow problems, such as re-timing large payments or arranging an overdraft. You should show awareness of the dangers and costs of poor financial planning. Cash flow management: solutions eg overdraft arrangements, negotiating terms with creditors, reviewing and rescheduling capital expenditure This provides evidence for D1 Sources of information: Bevan J, Dransfield R, Coupland-Smith H, Goymer J and Richards C – BTEC Level 3 National Business Student Book 1 (Pearson, 2009) ISBN 9781846906343 Bevan J, Goymer J, Richards C and Richards N – BTEC Level 3 National Business Student Book 2 (Pearson, 2009) ISBN 9781846906350 Coupland-Smith H and Mencattelli C – BTEC Level 3 National Business Teaching Resource Pack (Pearson, 2009) ISBN 9781846906367 www.bbc.co.uk/business BBC Business website www.bbc.co.uk/news BBC News website www.becta.org.uk British Educational Communications and Technology Agency www.bized.ac.uk Business education website including learning materials and quizzes www.careers-in-business.com Information on a variety of business careers www.carol.co.uk Online company annual reports www.direct.gov.uk Gateway to public services This brief has been verified as being fit for purpose Assessor Signature Date Internal verifier Signature Date P1 describe the purpose of accounting for an organisation [IE] P2 explain the difference between capital and revenue items of expenditure and income [TW] P3 prepare a 12-month cash flow forecast to enable an organisation to manage its cash [CT, RL, SM] M1 analyse the cash flow problems a business might experience D1 justify actions a business might take when experiencing cashflow problems Additional Information for cash Flow forecast: Unit 5 Business Accounting Credits: 10 Level: 3 © Challenge College Create a 12-month cash-flow forecast using the details given below: Sales and Purchases for the 12 months will be as follows: January Total Sales 37800 Purchases 27000 February 34020 24300 March 31500 22500 April 37800 27000 May 37800 27000 June 36540 26100 July 31500 22500 August 21420 15300 September 37800 27000 October 44100 31500 November 50400 36000 December 60000 44000 These sales and purchase figures do not include VAT, so you must also have rows for VAT on sales and VAT on Purchases. VAT will be added at 20%. In March the company will purchase a company vehicle. The owner will be injecting £5000 of their own savings to the business and borrowing a further £3000 from the bank. Both of these amounts will enter the bank account in March, and in the same month the vehicle will be paid for, costing £9000. Repayments on the loan will begin the following month; the amounts will be £50 per month capital repayment and £25 interest. The owner has some living accommodation above the shop which they rent out. The rent is £250 per month. The business mortgage on the shop costs £950per month. Business rates are likely to be £360 per month, which is payable in 10 monthly instalments beginning in March. The owner’s drawings will be £1700 per month and will pay £175 per month on advertising. This is expected to rise to £300 in September and October and $450 in November and December. Insurance will be £110 per month. The wage bill will be £7600 per month rising to £8000 per month in June. The owner is contemplating taking on another employee to help as the shop has been busy lately. If this happens the new employee would start in June and their wages would be £750 per month. Overdraft interest would be charged at 12% per annum on a monthly basis. Interest will be paid monthly based on the previous months closing balance. The opening balance will be £1050. Do not forget to claim back excess VAT or pay excess VAT collected on your forecast. This needs to be shown every 3 months as a Payment to HMRC or it being reclaimed. To calculate this work out the total VAT received on sales and deduct it from the VAT paid on purchases. If you end up with a positive figure the business can reclaim this amount!