Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Speaker: Jerry Gao Ph.D.
San Jose State University
email: jerrygao@email.sjsu.edu
URL: http://www.engr.sjsu.edu/gaojerry
Sept., 2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Presentation Outline
- Overview of Micro-payment protocols and systems
- Millicent Protocol
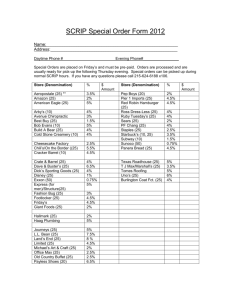
- SubScrip Protocol
- PayWord
- MicroMint
- Comparison of micro-payment protocols
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/20000
All Rights Reserved
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Overview of Online Payment Protocols and Systems
Classification of payment processing:
- Macro payments
Macro payments refer to large payment deal 10 - Small payments
- Micro payments
With micro-payments, efficiency and speed are dominant factors.
and security issues can be
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocols
- Objectives: ---> Micro-payment situations:
Although micro-payment systems share the similar requirements of other
payment systems, they focus on special markets, where:
- Low-value transactions involved less than the value of smallest coin.
- Non-tangible and network-deliverable merchandise
examples: archived magazines, journals, CD, software,…
- Special requirements:
- Fast and low cost payment transactions.
- Very small amount of value
- Reduced the number of involved parties
- High scalable
The issues of other payment systems:
- Account-based systems have high transaction costs.
- Transaction speed in electronic checking systems is slow.
- Electronic money systems involve more parties, have low transaction
speed, and cause poor scalability.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocols
- Objectives: ---> Micro-payment situations:
Although micro-payment systems share the similar requirements of other
payment systems, they focus on special markets, where:
- Low-value transactions involved less than the value of smallest coin.
- Non-tangible and network-deliverable merchandise
examples: archived magazines, journals, CD, software,…
- Special requirements:
- Fast and low cost payment transactions.
- Very small amount of value
- Reduced the number of involved parties
- High scalable
The issues of other payment systems:
- Account-based systems have high transaction costs.
- Transaction speed in electronic checking systems is slow.
- Electronic money systems involve more parties, have low transaction
speed, and cause poor scalability.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-payment Protocols:
- Millicent, developed by Digital Equipment Corp. in 1995.
- SubScrip, developed at the University of Newcastle, Australia.
- PayWord, developed by Ron Rivest (MIT) and Adi Shamir.
- MicroMint, developed by Ron Rivest and Adi Shamir.
- iKP micropayment protocol
Micro-payment systems do not available in conventional commerce.
They open many new areas of business.
Examples:
- Millicent payment system
- Micro Payment Transfer Protocol (MPTP) based on PayWord.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
- Important features of Micro-payment protocols and systems:
- Simplified verification
- Simple security mechanisms
- Very low cost transactions
- Very fast speed
- Simplified architecture
- Major factors on transaction costs:
- Payment methods
- Complexity of security mechanisms
- The number of involved parties
- Transaction model (on-line/off-line)
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: Millicent
Overview of Millicent:
Millicent payment protocol is designed for low-amount transactions over the Internet.
It is developed by Digital
- Support low-cost, secured transactions (less than one cent)
- Use non-expensive symmetric crytographic algorithms
- Use scrip as digital cash for customers to make purchases from vendors
- Provide decentralized validation of electronic cash at the vendor’s server
- Provide no additional communications, off-line processing.
Business market: electronic publishing, software and game industries.
Performance: 14,000 pieces of Scrip can be produced per second.
8,000 payments can be validated per second, with change Scrip being
produced.
A public trial of the Millicent system was scheduled for the summer of 1997.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
MilliCent model:
MilliCent protocols use a form of electronic currency called Scrip to connect three
involved parties:
- vendors, customers, and brokers.
Scrip is vendor specific.
A Millicent broker:
--> medicate between vendors and customers to simplify the tasks they perform.
--> aggregate micro-payments
--> sell vendor Scrip to customers
--> handle the real money in the Millicent system.
--> maintain customer accounts and vendors (subScripion services)
--> buy and produce large chunks of vendor Scrips (for licensed vendors)
Vendors: --> are merchants selling low-value services or information to customers
Customers: --> buy broker Scrip with real money from selected brokers.
--> use the vendor Scrips to make purchases.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Customer
Dealer
3
Internet
1
2
1. Customer sends broker-scripts.
2. Customer gets dealer-script.
3. Customer send dealer-scripts.
Broker
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Millicent Trust Model:
Customer make purchases
with vendor Scrips
Vendor
Customer
Vendor sell low-value
information and services
Broker sell vendor Scrip
Broker
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Brokers buy/produce large
chunks of “vendor Scrip”
for licensed vendors
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Customer
Broker
Vendor
1. Credit card # (macropayment protocol)
Start of week
2. $5.00 Broker
scrip(Millicent protocol)
1. $0.19 Vendor scrp + request
Uses current
change
2. $0.15 Vendor scrip change + article (cost $0.04)
Transaction Sequence
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Customer
Broker
Vendor
1.0 Broker scrip
2. $0.20 Vendor scrip
$4.80 Broker scrip
Purchasing
from a vendor
3. $0.20 Vendor scrp + request
4. $0.19 Vendor scrip change + purchased ino/service
Transaction Sequence
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Customer make purchases
with vendor Scrips
Vendor
Customer
Vendor sell low-value
information and services
Broker sell vendor Scrip
Broker
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Brokers buy/produce large
chunks of “vendor Scrip”
for licensed vendors
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
About Scrip:
---> a piece of data used to represent microcurrency within the Millicent systems.
Scrip has the following properties:
- Scrip is vendor specific, thus has value at one specific vendor only.
- Scrip can be spent only once by its owner.
- Scrip can be represented any denomination of currency.
- Scrip represents a prepaid value.
- Scrip make no use of public-key cryptography.
- Scrip cannot provide full anonymity. It can be traced and recorded.
Scrip like cash has a defined value and can be used to purchase merchandise.
Major differences between Scrip and cash:
- Scrip can only spent once, and cash can be spent many times.
- Scrip is vendor specific, and cash is not.
- Scrip can only spent by the customer who obtained it from the broker.
- Scrip has an expiration date and a digital signature.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Scrip Message Structure
Vendor
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Value
Scrip-id
customer-id expiration-date
info
certificate
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Millicent Security Checking: ---> Provide three different security levels.
All transactions should be protected, and fraud must be detectable and traceable.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Millicent Protocol
Efficiency Ranking
Secure
Private
Scrip in the clear
1
No
No
Encrypted connection
3
Yes
Yes
Request signatures
2
Yes
No
________________________________________________________________
.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Authentication and signature: Millicent protocol uses one-way has functions
- such as 128-bit MD5 and HMAC-MD5.
- The message is sent in clear, but is protected by the customer_secret in hash function.
- Upon receiving the request, the vendor calculates the hash function using
a pre-selected message digest function.
- The vendor returns, upon receiving this information, the customer can compute the
message digest to ensure authenticity.
- Signature: a request signature is generated based on the customer_secret by hashing
Encryption: No encryption,
but maintains a level of security that prevents Scrip being stolen.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Scrip
Customer secret
Hash eg. MD5
Request Signature
Generating a request signature
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Request
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
1. Scrip, Request, Request signature
Customer
Vendor
2. Change, Reply, Reply signature
Purchase using a request signature
Customer Secret
Scrip
Hash
Request
Request Signature
Compare
Request Signature
Vendor verifies the request signature
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Vendor secret keys
Master Scrip secret 5
Master Scrip secret 6
Master Scrip secret 7
Vendor Value
“certificate”
To customer
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Scrip-id
customer-id expiration-date info
Master Scrip secret 6
Hash eg. MD5
Scrip certificate generation
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: MilliCent
Vendor secret keys
Master Scrip secret 5
Master Scrip secret 6
Master Scrip secret 7
Vendor Value
Scrip-id
customer-id expiration-date info
Master Scrip secret 6
certificate
From
customer
compare
certificate
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Scrip validation
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Micro-Payment Protocol: Millicent
Overview of Millicent:
Millicent payment protocol is designed for low-amount transactions over the Internet.
It is developed by Digital
- Support low-cost, secured transactions (less than one cent)
- Use non-expensive symmetric crytographic algorithms
- Use scrip as digital cash for customers to make purchases from vendors
- Provide decentralized validation of electronic cash at the vendor’s server
- Provide no additional communications, off-line processing.
Business market: electronic publishing, software and game industries.
Performance: 14,000 pieces of Scrip can be produced per second.
8,000 payments can be validated per second, with change Scrip being
produced.
A public trial of the Millicent system was scheduled for the summer of 1997.
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Comparisons of Micro-Payment Protocol
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000
Topic: Micro-Payment Protocols and Systems
Analysis of Micro-Payment Protocol
Jerry Gao Ph.D. 5/2000