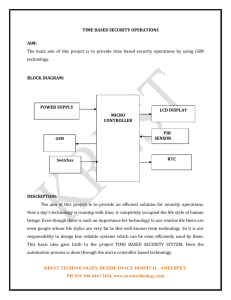
GSM: The European Standard for Mobile Telephony
advertisement

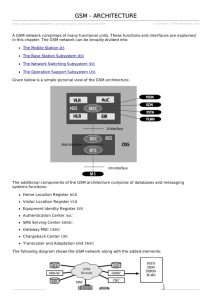
GSM: The European Standard for Mobile Telephony Presented by Rattan Muradia Requirement for course CSI 5171 Presentation Objective No discussion of mobile network concepts already covered (MSC, BSC, HLR, VLR, registration, call setup, roaming, handover, OSS etc..) GSM Architecture Focus on features specific to GSM Provide basic information required for presentations on CAMEL, GPRS and UMTS Evolution of Digital Mobile Systems 1st Generation, Analogue Cellular AMPS, ETACS, NMT, C-NET... 2nd Generation, Digital Cellular GSM, PDC, DAMPS, CDMA... 2nd Generation Cordless - DECT, PHS... 2nd Generation Satellite - Iridium, Globalstar.. 2.5 Generation GPRS... 3rd Generation Universal - IMT-2000, UMTS Digital Mobile Systems Americas CTAC Operating Manual Issue: 2.3 Standard PDC D- AMPS GSM 900 Frequency band Uplink 940-956 MHz 1429-1441 MHz 1453-1465 MHz 824-849 MHz 890-915 MHz Frequency band Downlink 810-826 MHz 1477-1489 MHz 1501-1513 MHz 869-894 MHz 935-960 MHz Channel separation 25 kHz 30 kHz 200 kHz Multiplexing Bearer Bits/ frequency channel 3 (6) channel TDMA 42 kbit/ s 46.6 kbit/ s 8 (16) ch TDMA 270 kbit/ s GSM Overview Developed in Europe One of first ‘intelligent’ networks with distributed processing International roaming 174 countries, 647 million subscribers 67% of world wireless market share GSM Network Mobile Station (MS) Base Station Subsystem (BSS) Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS) Operation and Support Subsystem (OSS) GSM Network Architecture CELL TRANSMITTER & RECEIVER INTERFACE TO LAND TELEPHONE NETWORKS HIERARCHY OF CELLS PHONE STOLEN, BROKEN CELLPHONE LIST ENCRYPTION, AUTHENTICATION SIM: IDENTIFIES A SUBSCRIBER LIST OF ROAMING VISITORS LIST OF SUBSCRIBERS IN THIS AREA SOURCE: UWC GSM Reference Model GSM Protocol Stack GSM Address and Identifiers International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) – 3 digit Mobile Country Code + 2 digit Mobile Network Code + 10 digit Mobile Subscriber Identification Number International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) – 19 digit unique ID, used by air interface, stored in EIR Mobile Subscriber ISDN Number (MSISDN) – upto 3 digit Country Code + 2-3 digit national Destination Code + max 10 digit Subscriber Number – mapped to MSRN by HLR Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) – temporary ISDN number assigned by VLR GSM Mobile Station Each MS identified by IMEI In addition to the physical equipment common to most MS, GSM equipment includes a SIM. Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) provides true mobility. Access to subscribed services: – regardless of location of the terminal – regardless of use of specific terminal SIM contains IMSI, secret key for authentication + more information GSM Databases Equipment Identity Register (EIR) – contains list of valid mobile equipment (IMEI) – an IMEI can be marked invalid if MS is stolen, unauthorized or defective Authentication Center (AuC) – protected database that stores authentication and encryption parameters – used to verify user identity and ensure confidentiality of each call GSM Call Delivery GSM Services Patterned after ISDN Bearer Services – sync, async data transport, represent layers 1-3 – also used by higher layers to offer teleservices Teleservices – voice, SMS, FAX, Teletext etc.. Supplementary Services – modify or supplement teleservices GSM Services - Phase 1 Offered by all operators in 1991. GSM Services - Phase 2 Introduced in 1996. Major rework of standards. Backward compatible. More supplementary services. GSM Phase 2+ Increased globalization using SIM, multiband systems and terminals Phase 2+ – increase network capacity via spectral efficiency – improve voice quality – group call (party line) – integration of packet services (on air interface) and higher data speeds (GPRS) – expand supplementary services (SMS Forwarding, Multiple Subscriber profile, Call Xfer etc..) (see GPRS presentation by Miao Lu and Nancy Samaan on April 5th). GSM Phase 2+ No complete revision of standards in Phase 2+ Each subject area treated separate, allowed to implement and introduce independently Standardize mechanisms for service introduction, not complete services Reduce time-to-market, allow differentiation GSM already has similarities with IN (MSC=SSP, HLR=SCP, SS7 signaling) Convergence of GSM and IN - CAMEL (see CAMEL presentation by Tina Deng and Yinyan Zhou on April 2th). Beyond GSM - 3G Road to UMTS/IMT2000 New generation of mobile systems based on IP Must support large number of subscribers Wide range of voice and data services Build on existing GSM infrastructure as much as possible. Higher bandwidth for multimedia applications – new radio interface – better use of spectrum (see IMT2000 presentation by Mingdi Zhao and Wei Lin on April 9th). Questions? GSM/GPRS/UMTS Backup slide 1 GSM Network Architecture backup slide Backup slide 2 SOURCE: UWC Backup slide 3 GSM Protocol Stack