Do Now
advertisement

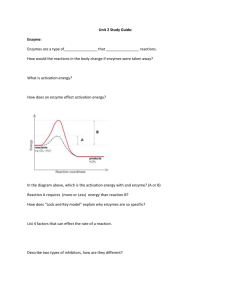
Do Now!! What is matter? What are elements? What is the periodic table used for? Objectives To list the different elements found in living things. To explain what bonds are used for. To determine the different functions of the 4 macromolecules as well as water in the body. Chapter 2 “How Cells Function” A. Elements and Matter What is matter? Anything that has mass and takes up space A. Elements and Matter i. All living and non-living things can be broken down into elements. ii. Elements: pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical means. Periodic Table Information Atomic number- tells us the # of protons (and electrons) Symbol- unique for each element. Atomic Mass- # of protons plus # neutrons 6 C 12.02 A. Elements and Matter iii. Each element has it’s own set of properties. Ex: Oxygen Colorless Odorless gas B. Elements in the body i. Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Calcium Phosphorus 19 others B. Elements in the body ii. Can be found as a pure element or as a compound.** Compound: atoms of 2 or more elements joined together by chemical bonds. Ex: H2O (has both elements hydrogen and oxygen in it) C. Atoms Elements are made up of atoms i. Atom: smallest unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element. C. Atoms Building blocks of matter Contain 3 parts + Protons: positively charged, contain mass of 1 Neutrons: no charge, contain mass of 1 - Electrons: negatively charged, insignificant mass Do Now!! What is a compound? Give an example Name 3 elements found in our body. What are the 3 parts of an atom and where are they located? Objectives To define chemical reactions To compare and contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions To illustrate these reactions in a lab activity Chemical Reactions Why do we need chemical reactions? ii. Chemical Reactions: bonds between atoms are broken or formed to make different molecules in the body: Broken bonds: release energy Formed bonds: store energy C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP (energy) Reactants Products Types of Reactions Exothermic- releases heat energy: o The energy of the product is LOWER than the energy of the reactants. o Ex: Types of Reactions (cont.) Endothermic - absorbs heat energy The energy of the products is HIGHER than the energy of the reactants. Ex: Objectives To identify the essential macromolecules To compare and contrast simple and complex carbohydrates To discuss the importance of lipids, proteins and nucleic acids Macromolecules Macro= BIG 4 different macromolecules all doing a different job in our body! A. Carbohydrates Give us energy!! Made up of C, H, O A. Carbohydrates (cont.) Types of Carbs: Simple: sugars like glucose, fructose, galactose Ex: cookies, candy Monosaccharides and Disaccharides Complex: starches, glycogen, cellulose (fiber) Ex: potatoes, leafy vegetables Polysaccharides Disaccharide Monosaccharide (glucose) Polysaccharide B. Lipids (fats, oils, waxes) Store energy, insulation, protection Made up of C,H,O Contain a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Fats are hydroPHOBIC- do not dissolve in water. B. Lipids (fats, oils, waxes) Types: Saturated: solid fat, BAD FOR YOU , comes from animals Ex: lard, butter, fat on steak or chicken Unsaturated: liquid, better for you , comes from vegetables Ex: vegetable oil, peanut oil, canola oil o Trans: worst type of fat o Mostly man-made o Raises bad cholesterol, lowers good Do Now!! What are carbohydrates used in our bodies for? Name some examples of foods containing carbohydrates. What are lipids used in our bodies for? Name examples of foods that contain saturated and unsaturated fats. Objectives To understand why we need protein in our diet. To explain the function of nucleic acids in our bodies. To understand how water provides a medium for chemical reactions in our body. C. Protein Growth, repair, enzymes, transport Made of C,H,O,N, and sometimes sulfur Structure is repeating amino acids Body makes some, we must EAT to get others. Order of amino acids tells the protein what job it has. D. Nucleic Acids Holds genetic information!! Made up of C,O,H,N,P Structure is repeating nucleotides D. Nucleic Acids Types: DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (the blueprints for our cells) RNA: ribonucleic acid (helps take the blueprints and make protein) E. Water Chemical reactions take place in water!! Known as the “universal solvent” because it dissolves things. Ex: lemonade, kool aid, etc. Made up of 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen E. Water Makes up 70% of your body mass Cannot dissolve lipids (fats): Our cell membranes are made up of lipids WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?? Do Now!! What are the four macromolecules? What functions do proteins have? What are they made up of? Objectives To define and give an example of an enzyme To discuss the role of enzymes and why they’re important To observe an enzymatic reaction between catalase and hydrogen peroxide What you should know about enzymes! Type of Enzyme Substrate -Specialized proteins that act as “catalyst” (speeds up a reaction) - Usually end in “ase” -Not consumed in the reaction -They are reused! Product Protease Protein Amino Acid Lipase Fats Fatty Acid Lactase Lactose Glucose Amylase Carbohydrates Glucose Pepsin Protein Amino Acid What do they do? o Lower the activation energy needed!! o Activation energy barrier is like a wall between two parts of a pond. o If an enzyme lowers the wall, more frogs have enough energy to reach the other side. How do they work? A substrate fits in the active site of an enzyme: Specific to one kind of substrate Lock and key model This forms an enzyme substrate complex. They then break or form bonds. Do Now!! What is the difference between a catalyst and an enzyme? What is a substrate? What is the enzyme-substrate complex? Denaturing Enzymes Enzymes have specific optimal conditions: Temperature pH If those conditions change, enzyme is permanently damaged: Denatured! Cannot do its job How do they work? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTUm-75-PL4 Enzymes in liver.. In our cells, hydrogen peroxide is produced as byproduct: Poisonous Would kill cells if not broken down or removed right away Catalase: breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen Catalase 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 So ponder this… What happens if we mix liver (a source of catalase) with hydrogen peroxide??? Do Now!! What is an enzyme substrate complex? Explain what denaturing an enzyme means. Give 2 factors that will denature an enzyme. Do Now!! What was the enzyme in the liver lab? What was the substrate? What does pH measure? Acids and Bases pH scale: measures how acidic or basic a solution is Acids: pH less than 7 Closer to 0, stronger the acid Bases: pH more than 7 Closer to 14, stronger the base Neutral: pH of 7 Neutralization Reaction Chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form water and salt: Neutralizes! Ex: HCl + NaOH (Acid) (Base) H2O + NaCl (Water) (Salt) Let’s talk about catalase… Optimum temperature: about 37ºC (98.6ºF) Let’s talk about catalase… Optimum pH: around 7.0-8.0 Do Now!! What are the 4 macromolecules of life? What do we get from carbohydrates? What makes up proteins? Objectives Complete periodic table review sheet Discuss the importance of lipids and nucleic acids To complete a macromolecule webquest Do Now!! How many neutrons does carbon have? How many protons does chlorine have? How many electrons does hydrogen have? Explain to the person next to you how you determine the number of neutrons! Objectives To complete Biochemistry WebQuest. To finish notes on macromolecules. To run our experiments!!! Solutions o Solution- Mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent Solute- substance that is dissolved Solvent- substance that the solute dissolved in. Ex. Hot chocolate (Water and Coco Powder) Mixtures Heterogeneous Homogeneous What is the difference? Mixtures Homogeneous- has a uniform composition throughout (a.k.a solutions). Heterogeneous- components remain distinct. Do Now!! What is an enzyme? What does an enzyme act on? Why does an enzyme have a specific shape?