IT Glossary: Computer & Networking Terms
advertisement

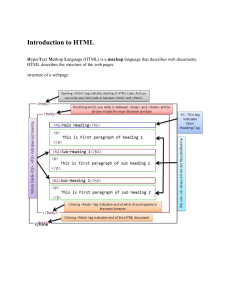
CRM – Customer Relationship Management – Software that examines customer data to understand the preference of a company’s customers. DNS – Domain Name System – A server that provides IP addresses for users who know only a target host’s host name. It also provides a hierarchical system for naming domains. FTP – File Transfer Protocol – Early and still widely used protocol for transferring files between host computers. HTML – Hypertext Markup Language – The language used to create webpages. IP – Internet Protocol – The protocol that governs operations at the internet layer. Governs packet delivery from host to host across a series of routers. ISP – Internet Service Provider – Carrier that provides Internet access and transmission. LAN – Local Area Network – A network within a smaller geographical site. MAC – Media Access Control – The process of controlling when stations transmit; also, the lowest part of the data link layer, defining functionality specific to a particular LAN technology. NAP – Network Access Point – A site where ISPs interconnect and exchange traffic NIC – Network Interface Card – Printed circuit expansion board for a PC; handles communication with a network; sometimes built into the motherboard. NOS – Network Operating System – A PC server operating system. PSTN – Public Switched Telephone Network – The worldwide telephone network. RFID – Radio Frequency ID – A tag that can be read at a distance by a radio transmitter/receiver. SLA – Service Level Agreement – A quality-of-service guarantee for throughput, availability, latency, error rate, and other matters. TCP – Transmission Control Protocol – The most common protocol at the transport layer. Connection-oriented and reliable UTP – Unshielded Twisted Pair – Network cord that contains four twisted pairs of wire within a sheath. Each wire is covered with insulation. VPN – Virtual Private Network – A network that uses the Internet with added security for data transmission. WAN – Wide Area Network – A network that links different sites together. WPA – Wireless Protected Access – 802.11 security method created as a stopgap between WEP and 802.11i. SaaS – Software as a Service - a model of software deployment over the internet SAP – Systems Applications Products – ERP software suite SDLC – Systems Development Life Cycle – Systems analysis technique for software development. ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning - a system that is used to manage and coordinate all the resources, information, and functions of a business WWW – world wide web - a system of interlinked hypertext documents contained on the Internet HTTP – hypertext transfer protocol - an Application Layer protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems URL – uniform resource locator - a subset of the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that specifies where an identified resource is available and the mechanism for retrieving it GIS – geographic information system - any system that captures, stores, analyzes, manages, and presents data that are linked to location XML - Extensible Markup Language - a set of rules for encoding documents electronically W3C - World Wide Web Consortium - the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web RSS – Really Simple Syndication - a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works—such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video—in a standardized format. CSS – Cascading Style Sheets - a language used to describe the presentation semantics (that is, the look and formatting) of a document written in a markup language SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol - an Internet standard for e-mail transmission across Internet Protocol (IP) networks. IBM – International Business Machines - a multinational computer, technology and IT consulting corporation AITP – Association OF Information Technology Professionals – must say “of”, not “for”… our student organization for CMIS PHP – PHP Hypertext Preprocessor – server side web programming language IXP – Internet Exchange Points – large routers ISPs use to connect their WANs together SQL – Structured Query Language – a standard language for working with databases RGB – Red-Green-Blue – color value represented by the proportion of 256 shades of r, g, b SHA – Secure Hash Algorithm – function for password encryption UML – Unified Modeling Language – industry standard for working with object-oriented languages