industrial organic c..
advertisement

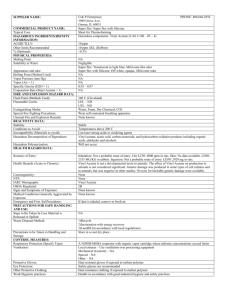
Lecture Topic 3: Industrial Organic Chemistry Ref: “Organic Building Blocks of the Chemical Industry”, by H.H. Szmant “Industrial Organic Chemistry”, by K. Weissermel and H.-J. Arpe Premise: Classification of organic chemicals by: • COST and PRODUCTION VOLUME • BUILDING BLOCKS derived from Goal: Ability to 1. identify bulk, fine and specialty chemicals 2. give examples of primary building blocks and of C1, C2, C3, C4 and higher acyclic and cyclic organic building blocks 3. trace the manufacture of a common chemical from primary sources to final products Which ge do we live in ? (A brief history of organic chemistry) 1850- Plants, Animals 1850+ 1920+ Coal Tar (side product of “coal gasification”) Acetylene (from CaC2, Reppe Chemistry) 1950+ Ethylene (from oil) 1973+ CH4, CO/H2 (syngas) Future: CO/H2 from Coal, exothermic (~400 years) CO2 fixation via: • Plants, Animals • CO2 fixation (endothermic) (endothermic) Cost vs. Demand in the Chemical Industry >100 Medicinals and other specialties Flavours, fragrances Dyes 10 Specialties Fine Chemicals 1 Common plastics Resins, Elastomers Pseudo-commodities Organic intermediates Commodities Primary organic building blocks 0.1 Inorganic heavy chemicals 0.01 105 106 107 108 109 Demand (lb/y) 1010 1011 1012 Organic Chemical Industry Characteristics INDUSTRY CHARACTERISTICS Product life cycle # of products Product volumes Product prices Product differentiation Value added Capital intensity R&D focus BULK CHEMICALS FINE CHEMICALS SPECIALTY CHEMICALS Long > 100 Moderate >1,000 Short/moderate >50,000 >10,000t/y <10,000t/y highly variable <5 $/kg >5 $/kg >10 $/kg none very low high low high high high process moderate process moderate/low application KEY SUCCESS FACTORS • technical service – • links with customer – • cost Example of a Specialty Chemical E.g., a heat-stabilizer additive for flexible PVC film Could be a mixture of: Zn and Ca stearates triisononyl phosphite epoxidized soybean oil Could be formulated as a liquid concentrate with a minimal amount of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate. The producer keeps the exact identities and proportions of the metal soaps, phosphite esters, epoxidized oils, and plasticizers secret, giving the customer only the proportions of additive to be used per 100g of resins. What is meant by a “Building Block”? A building block is any (organic) chemical that can be used to synthesize other (organic) chemicals. There are very few truly primary, large-volume organic building blocks. These are all obtained more or less directly from: • petroleum refining • natural gas • coal • ammonia • carbon dioxide • renewable resources Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Organic Building Blocks that are in the Top 50 Chemicals in the U.S. Economy Primary Building Blocks Secondary BBs Tertiary BBs Ethylene ethylene dichloride ethylene oxide ethyl benzene vinyl chloride ethylene glycol vinyl acetate Propylene propylene oxide acrylonitrile isopropyl alcohol cumene n-butyl alcohol acetone Benzene ethyl benzene cumene styrene phenol acetone bisphenol A Methanol acetic acid formaldehyde MTBE vinyl acetate Toluene Xylenes Butadiene Urea terephthalic acid A Closer Look at the Principle Sources of Primary Organic Building Blocks Boiling pt. Natural Gas: Liquid petroleum gasses (LPGs) Crude Petroleum : methane (85%) ethane (9%) propane (3%) butanes (1% nitrogen (1%) -161.4°C -88°C -42°C -0.5°C LPGs light naphtha or straight-run gasoline heavy naphtha ( C10) kerosene, jet fuel ( C16) gas oils, diesel fuel ( C25) lubricating oils light fuel oil, heavy fuel oil, bunker oil residue: asphalt 50-100°C 150-200°C 175-275°C 200-400°C 350+°C Coal is used as: fuel (electric power plants, etc.) precursor of coke (crude form of elementary C) source of syngas (synthesis gas) S CCl 4 MeOH, AcOH, Ac2O Rayon R2N S O NH3 (6%) CH4, H2S, CO, H2 (14%) Cl CS 2 Cl SiC CO H2 calcium cyanamide CaN C NH Oxo chemicals Coal CaC 2 Coke acetylene HC CH Water gas: H2 (51%), CO (42%), CO2 (6%), N2 (1%) Metallurgy Fuel & exports n Producer gas: N2 (75%), CO2 (14%), CO (10%), Ar (1%) Road Tar Coal Tar Tar O Electrodes and C fibers Pitch Naphtha BTX Indene Coumarone (benzene, toluene, xylenes) Tar bases CH 3 Anthracene Phenanthrene Light Oil CH 3 H2C CH 2 CH 3 N N N Tar acids OH Cresols Creosote Phenol Xylenols CH 3 Acenaphthene N H Carbazole CH 3 CH 3 C H2 Fluorene C1 Chemistry C1 building block Source Use CH4 (methane) Natural gas energy, H2, CO, CH(4-x)Clx CO (carbon monoxide) Coal (as Syngas) CH3OH, HCOOH, esters, amides, Oxo acids, etc. CH3OH (methanol) CO + 2H2 Cracking of C3H8, C4H10 H2CO, MTBE, CH(4-x)Clx, CH3COOH H2CO (formaldehyde) CH3OH, Cracking of LPG Polymers (UF, PF, POM) HCOOH (formic acid) CO + H2O Fine chemicals CO2 (carbon dioxide) Water-gas-shift rxn. Supercritical fluids (SCFs) CS2 (carbon disulfide) thiourea S8 + Coke or CH4 Cellulosics, M+SCN–, Cl2CO (phosgene) polyurethanes CO + Cl2 R-C=N=O for (H2N)2CO (urea) NH3 + CO2 Fertilizer, Resins (UF) HCN (hydrogen cyanide) HCONH2 - H2O byproduct (acrylonitrile) Methacrylonitrile, ClCN C2 Chemistry C2 building block Source Use CH2=CH2 (ethylene) thermal cracking of natural gas, refinery gas, crude oil Feedstock for ~30% of all petrochemicals!! Polymers (Polyethylenes etc.) Alphaolefins (LDPE), PVC Polystyrene, Polyvinyl acetate Polyethylene oxide CH3CH2OH (ethanol) fermentation, hydration of ethylene Gasoline additive (USA), Ethylene by dehydration (Brazil, India, Peru, Pakistan), Solvent, Esters (ethyl chloride, ethyl acetate) CH3CH=O (acetaldehyde) Wacker-Hoechst (ethylene) Monsanto process (MeOH) CH3COOH, Acetic anhydride, Peracetic acid CH3C(=O)OOH, Aldol condensation products CH3COOH (acetic acid)& CH3COOCOCH3 (acetic anhydride) Monsanto process (MeOH) Oxidation of C4-C8 hydrocarbons or acetaldehyde Vinyl acetate (PVA), Cellulose acetate, Solvent, Acetate salts, Chloroacetic acids HCCH (acetylene) Coal via CaC2 or from hydrocarbons 1,4-Butanediol, vinyl acetate C3 Chemistry C3 building block Source Use CH3CH2CH3 (propane) LPG Propylene, energy CH3CHCH2 (propene) Thermal cracking of LPG, natural and refinery gas Polypropylene, Acrylonitrile, Oxo products (butyraldehyde, butanol, etc.),Propylene oxide Isopropanol, Cumene, Oligomers (nonene, dodecene, heptene) CH3COCH3 (acetone) Hock process (coproduct) Isopropanol (dehydrogen’n) Wacker-Hoechst (propene) Methyl methacrylate, Methyl isobutyl ketone, Bisphenol A, Aldol condensation products, Solvent CH3CH2COOH (propionic acid) CH2CH2 (hydroformylation) Food preservative, Amyl and Vinyl propionate, Herbicides C4 Chemistry C4 building block Source Use C4H10 (butanes) LPG 1-Butene, Maleic anhydride, MTBE, thiophene C4H8 (butenes, isobutene) Cracking of Cn4 Polymer/alkylate gasoline, Polymers/copolymers, alcohols C4H9OH (butyl alcohols) Propene, acetaldehyde MEK, Solvent, Fuel additive CH3(CH2)2CHO (butyraldehydes) Propene, acetaldehyde 2-Ethylhexanol, Trimethylolpropane Maleic anhydride Oxidation of C4-feedstocks Benzene (V2O5 catalyst) Unsaturated polyester resins, Fumaric acid, Pesticides HO(CH2)4OH (1,4-butanediol) Acetylene 1,3-butadiene poly(1,4-butylene terphthalate) THF, H2N(C4H8)NH2 H2C=CHCH=CH2 (1,3-butadiene) Cracking of Cn4 Elastomers (i.e., synthetic rubbers), Chloroprene, THF O O O C5 and Higher Acyclic Building Blocks Primary Building Blocks Source(s) Use Petroleum: CnHn+2 (n5) (pentanes, hexanes, heptanes, etc., and other n-paraffins) Fossil fuels Solvent, Fuel, Lubricant, Alkylbenzenes, Alcohols, Chlorinated paraffins, Lower m.w. alkanes/olefins Mineral waxes: Ozocerite, Montan wax Fossil fuels (lignite) Coatings Fatty Acids: Lard, Tallow, Palm oil, Corn oil, Castor oil, etc. Renewable (animal/plant) PVC stabilizer, Surfactant, Glycerine, Methyl laurate, Fatty amines (antistatic agents) Tall-Oil Fatty Acids (TOFA) Renewable (pulp byproduct) Fuel in pulping operations, Dimer/trimer acids for coatings Terpenes Renewable (plant) Fragrance/flavour “essential” oils, Turpentine Fermentation Products: amyl alcohols, carboxylic acids, Monosodium glutamate (MSG) Renewable (plant) H2S removal from refinery gas, Food industry, Pharmaceuticals, Laundry products, etc. Cyclic Building Blocks - Aromatics Building blocks Source Use Benzene C6H6 Coal, Oil, Petroleum (thermal/catalytic process) Ethylbenzene (for styrene), Cumene (for phenol/acetone), Cyclohexane, Nitroenzene Toluene C6H5CH3 Coal, Oil, Petroleum (thermal/catalytic process) Solvent, Benzoic acid, Phenol, Nitrotoluenes, aminotoluenes Xylenes C6H4(CH3)2 Coal, Oil, Petroleum (thermal/catalytic process) Phthalic acids and anhydrides (plasticizers, synthetic fibers) Cumene C6H5CH(CH3)2 Benzene Hock process (phenol/acetone) Phenol C6H5OH Cumene (Hock process) Benzene, Toluene, Phenol resins, Bisphenol A, ε-Caprolactam Cyclopentadiene C5 cracking fractions, Coal tar Polymers (for resins, contact adhesives, printing ink resin) Cyclohexane Crude gasoline, Benzene (hydrogenation) Cyclohexanone (feedstock for nylon precursors) • Structural adhesives • Structural sealants Cl2 Allyl chloride Epichlorohydrin • Primer paints Epoxy resin • Electrical insulation Propylene • Dashboards • Electrical insulation • Vinyl tops • Floor mats • Upholstery • Modular window frame units BTX • Fiber reinforced plastic composites Bisphenol A or Brominated Bisphenol A Ethylene Vinyl Vinyl chloride monomer Cl2 • Body side moldings • Molded armrests • Exterior & interior trim • Tires • Rubber hoses • Foam for seats • Caulks & sealants • Bumpers & fenders CO2 Polyurethanes Polyisocyanates Phosgene Cl2 Aspirin O OH O O CH 3 OH OH O + T < 90C O Acetyl Salicylic Acid A.S.A. 90% yield H3C liquid phase 50C, 3-4 bar 1. CO2 2. H2SO4 O OH NaOH Shawinigan (Canada) Cu(acetate) 2 ONa H3C + O2 H Acetaldehyde 2. H2SO4 Phenol Kellogg/Monsanto H2SO4 liquid phase T & P > STP + catalytic processes CH 3 Acetic anhydride Kolbe-Schmitt reaction 1. O2 Benzene O Salicylic Acid Hock process Cumene O FOSSIL FUELS: LPG, Coal, Petroleum, etc. thermal cracking H2C CH 2 Ethylene Propylene thermal cracking PdCl2 / CuCl2 + 0.5 O2 Wacker-Hoechst Process Origin of the Other Reagents Cu Mined as an ore and refined Pd Mined and refined (Sudbury, Ontario: “anode slime” H2SO4 H2O + 0.5 O2 + SO2 O2 Fractional distillation of liquid air Acetate Acetic acid NaOH Electrolysis of brine (NaCl + H2O) “chloralkali cell” pyrometallurgical byproduct Methanol + CO (Monsanto process) Hydroformylation (“Oxo Process”