Monopolist 1.1 Multiple Choice 1.1.1 A monopolist, in comparison
advertisement

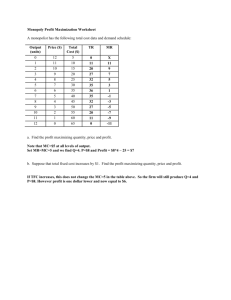
Monopolist 1.1 Multiple Choice 1.1.1 A monopolist, in comparison with a perfect competitor, will produce … A less and charge more. B more and charge the same. C more and charge less. 1.1.2 A B C The profit maximizing level of output for a monopolist is the one at which … total revenue is maximized. total revenue is equal to total costs. marginal revenue = marginal costs. 1.1.3 A B C Telkom is a typical example of … an oligopoly. a perfect market. a monopoly. 1.1.4 "I don't meet competition, I crush it." This statement was probably made by a … A perfect competitor. B monetarist. C monopolist. 1.1.5 Industries where economies of scale are so large that a single business can supply the entire market is typical of a … monopoly. A natural B legal C local 1.1.6 A B C The demand curve of a monopolist is the same as the … curve. average revenue total cost marginal revenue 1.2 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. 1.2.1 In this type of competition, the demand curve will be downward-sloping but the curve will be elastic. 1.3 Choose the word between brackets 1.3.1 All things being equal, one can expect a monopoly market to have higher prices and (higher/lower) output than in a perfect market. 1.3.2 High development costs can be a possible reason for the existence of a/an (perfect/imperfect) market. 1.3.3 The market for water and electricity is an example of a/an (natural/ artificial) monopoly. 1.3.4 The market supply (can/cannot) be controlled by the monopolist. 1.3.5 Eskom is an example of a/an (natural/artificial) monopoly. 1.3.6 In a monopoly market the marginal cost curve will always intersect the average (cost/revenue) curve at its minimum point. 1.4.7 A monopolist will maximise profit where marginal revenue equals (average/marginal) cost. 2.1 Data Response 2.1 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 Define the term imperfect market. Is the above graph indicating a short- or long-run equilibrium? What determines the optimum production level in a monopoly market? Indicate the profit area on the graph, by using the labelling system used in the graph. 2.1.5 Explain why the AR and MR curves are two different curves. 2.1.6 If you assume that the MC curve represents the supply curve for a perfect market, what will the effect on the price of goods be? (2) (2) (2) (2) (6) (2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 2.2.5 2.2.6 At which point is maximum profit made? (2) Identify the curve marked f. (2) Which point on the graph indicates optimum production? (2) Describe the nature of the product supplied. (2) What unit price will the monopolist charge to maximise profit? (2) Calculate the economic profit or loss that this monopolist makes. Show ALL calculations. (4) 3.1 Answer the following questions 3.1.1 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.1.4 List any THREE characteristics of a monopoly. (3 x 2) (6) Name any THREE characteristics of a monopoly. (3 x 2) (6) List any THREE characteristics of a monopoly. (3 x 2) (6) Draw a fully labelled graph to illustrate economic profit for a monopolist in the short run. (8) 3.1.5 Make a comparison between a perfect market and a monopoly with regard to prices, profit, quantities and cost. (8) 3.1.6 Explain how natural and artificial monopolies act as barriers to other producers wanting to enter the market. (2 x 4) (8) Essays asked in previous examinations EXEMPLAR 2008 A monopoly is a good example of a market where profit maximisation implies underprovisioning and overcharging of goods and services. This type of market is usually an unregulated market that fails to produce an ideal state of affairs. Write an essay explaining in detail the reasons for market failures. NOVEMBER 2009 ESSAY RESPONSE Examine the monopoly as a market structure and briefly compare it to the perfect market. MARCH 2011 Discuss monopoly as a market structure. Compare this market with conditions of perfect competition. (26) (10) MARCH 2012 QUESTION 8 50 MARKS – 40 MINUTES Discuss monopoly as a market structure (26) Illustrate, with the aid of a graph, how a monopolist can achieve economic profit. (10) March 2014 Pure monopolies seldom exist, although we often find characteristics of a monopoly present in businesses. • Discuss the monopoly as a market structure. (26) • Draw a fully labelled graph to illustrate economic profit for the monopolist. (10) November 2012 Distinguish between the market structure of a monopoly and a perfect competitor in detail. (26) In addition, draw a fully labelled graph to show the long-term equilibrium position of any ONE of the above markets. (10) • Your response can either be in tabular form or in paragraphs. • Full sentences are required. Monopolies Essays asked in previous examinations EXEMPLAR 2008 A monopoly is a good example of a market where profit maximisation implies underprovisioning and overcharging of goods and services. This type of market is usually an unregulated market that fails to produce an ideal state of affairs. Write an essay explaining in detail the reasons for market failures. NOVEMBER 2009 ESSAY RESPONSE Examine the monopoly as a market structure and briefly compare it to the perfect market. MARCH 2011 Discuss monopoly as a market structure. Compare this market with conditions of perfect competition. MARCH 2012 QUESTION 8 50 MARKS – 40 MINUTES (26) (10) Discuss monopoly as a market structure (26) Illustrate, with the aid of a graph, how a monopolist can achieve economic profit. (10) March 2014 Pure monopolies seldom exist, although we often find characteristics of a monopoly present in businesses. • Discuss the monopoly as a market structure. (26) • Draw a fully labelled graph to illustrate economic profit for the monopolist. (10) November 2012 Distinguish between the market structure of a monopoly and a perfect competitor in detail. (26) In addition, draw a fully labelled graph to show the long-term equilibrium position of any ONE of the above markets. (10) • Your response can either be in tabular form or in paragraphs. • Full sentences are required.