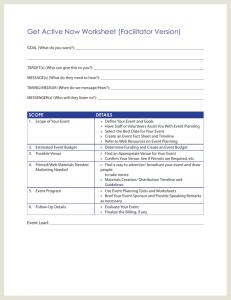
PPT Prepare & deliver a presentation 290812
advertisement

PREPARE AND DELIVER A PRESENTATION Unit Code:D1.HSM.CL5.04 D2.TCS.CL5.19 Slide 1 Prepare and deliver a presentation This unit comprises three Elements: Prepare a presentation Deliver a presentation Review a presentation. Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from employer/supervisor. Slide 3 Prepare a presentation Performance Criteria for this Element are: Describe different types of presentation that may be made Identify the logistics of the presentation Identify audience for the presentation (Continued) Slide 4 Prepare a presentation Research the topic for the presentation Select material for inclusion in the presentation Plan and write the presentation Develop and/or acquire supporting materials and visual aids for the presentation (Continued) Slide 5 Prepare a presentation Determine presentation equipment required for the presentation Trial and practice the presentation Revise the presentation on the basis of the trial. Slide 6 Describe different types of presentation Presentation may be conducted for: Sales and marketing events – conducted on-site or at client’s location Mentoring and coaching – on the floor, in training room, in office of staff member (Continued) Slide 7 Describe different types of presentation Staff meetings and briefings – in the Board room, within a department, in a training room Conferences addresses – in the workplace, at a conference centre Business planning meetings. Slide 8 Identify the logistics of the presentation Planning and preparation is vital for all presentations. ‘Logistics’ refers to: All the details that need to be attended to so a presentation occurs as planned and achieves the required outcomes. Slide 9 Identify the logistics of the presentation Logistics for a presentation means determining: Date Time Duration Location (Continued) Slide 10 Identify the logistics of the presentation Style of venue where presentation is to occur Content and topic or topics to be covered Nature of the presentation. Slide 11 Identify the logistics of the presentation Objectives for the presentation Context of the presentation Guidelines imposed or required for the presentation. Slide 12 Identify the logistics of the presentation Reasons to plan and prepare: To ensure all topics and requirements are covered To give you confidence To meet expectations To project the ‘right’ image To demonstrate professionalism To show respect. Slide 13 Identify audience for the presentation You must identify your audience as part of the planning process. This involves finding out: How many there will be Ratio of males to females Seniority and status of those attending (Continued) Slide 14 Identify audience for the presentation Level of existing knowledge those attending have about the topic What they expect to get from the presentation Required seating arrangements. Slide 15 Research the topic for presentation ‘Research’ is a critical element of planning and preparation. A presentation will not be effective if there is: Only one research option No research Insufficient research. Slide 16 Research the topic for presentation In relation to research for a presentation: It determines the success or failure of the actual event “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail” Research provides focus and direction Information provided must be factual A failed presentation can always be traced back to a lack of research and/or planning. Slide 17 Research the topic for presentation All information provided in a presentation must be: Current Comprehensive Accurate Relevant. Slide 18 Research the topic for presentation Research may require studying ‘internal’ information such as: Documents/documentation Enterprise policies Establishment procedures (Continued) Slide 19 Research the topic for presentation Schedules Price lists Database information (Continued) Slide 20 Research the topic for presentation Product information sheets Promotional brochures Contracts Inclusions in packages. Slide 21 Research the topic for presentation ‘External’ information may relate to: Suppliers and manufacturers Carriers Service providers (Continued) Slide 22 Research the topic for presentation Government agencies Competitors Industry peak bodies National and international bodies. Slide 23 Select material for inclusion in the presentation Research could also include: Talking to others Collecting workplace information from management Reading media Searching the internet. Slide 24 Research the topic for presentation Research for presentations should seek to identify: Established trends Emerging trends. Slide 25 Research the topic for presentation You should also seek to identify if similar presentations have previously been made so as to: Lessons learned Discover existing content Identify strategies and techniques used Obtain script (Continued) Slide 26 Research the topic for presentation Determine duration Learn about activities and inclusions Seek inspiration Save time Provide a draft outline for next presentation Identify who made the presentation Identify resources required. Slide 27 Research the topic for presentation Check information you have is approved for release to others and is not deemed ‘commercial-in-confidence’: Industry and wholesale prices Costs and sales Security matters Information about other clients/customers Negative information Legal issues involving the business. Slide 28 Select material for inclusion in the presentation All materials to be used must be checked to: Determine relevancy Confirm validity Guarantee currency Ensure they address all required need Verify content. Slide 29 Select material for inclusion in the presentation Materials for use in a presentation may include: Handouts Hard copy print outs of PowerPoint slides Sample products Reports, photographs and advertisements Fact sheets (Continued) Slide 30 Select material for inclusion in the presentation Workplace policies and procedures Legislation Computer-based simulations and present Diagrams, models and charts Models DVDs/videos Flip charts and posters Gift vouchers and promotional merchandising. Slide 31 Select material for inclusion in the presentation It may also be possible to use: An enterprise-specific DVD/video Comparative advertising Audio and/or visual support or effects Company advertising and signage. Slide 32 Plan and write the presentation Planning a presentation can be seen as an 8-Step process: Step 1 - Obtain the necessary information about and for the presentation Step 2 – Work out the structure of the actual presentation Step 3 – Arrange all required information in the required sequence Step 4 – Identify the key points to be made in the presentation (Continued) Slide 33 Plan and write the presentation Step 5 – Write a draft presentation Step 6 – Rehearse the draft presentation Step 7 – Develop or acquire the necessary presentation aids and materials Step 8 – Practice the total presentation. Slide 34 Plan and write the presentation Step 1 – Obtain necessary information about and for the presentation. Gather together all the information related to: Topic that is the focus of the presentation Achieving identified objectives for the presentation Meeting stated requirements of the audience. See ‘Identify the logistics of the presentation’ notes Slide 35 Plan and write the presentation The ‘Introduction’ should include: A welcome/greeting Thanks An overview of the presentation Explanation of purpose of the presentation Information about audience involvement. Slide 36 Plan and write the presentation Questions to be answered at this stage include: How will you begin the presentation? How long will the Introduction last? Who will do it? What will you use? (Continued) Slide 37 Plan and write the presentation How will you generate immediate interest? • Anecdotes • Use of actual examples or samples • Statement of facts • Use of DVD or PowerPoint presentation • Reading from an article (Continued) Slide 38 Plan and write the presentation The ‘Main Body’ of the presentation: Should contain the information necessary to achieve identified objectives Must be presented clearly Should use ‘sections; to separate information into ‘chunks’ that flow logically and sequentially Should cover topics mentioned at Introduction Should use AV supports. Slide 39 Plan and write the presentation The ‘Main Body’ of the presentation. Points to note are: Keep focussed Put information into context Move from ‘known’ to ‘unknown’ Move from ‘simple’ to ‘complex’ Move from ‘concrete’ to ‘abstract’ (Continued) Slide 40 Plan and write the presentation Cover all necessary legal issues Include relevant organisational policies and procedures Use AV aids and technology Ensure logical flow of information Explain new terms or industry terminology (Continued) Slide 41 Plan and write the presentation Strive for clarity of information presented Involve and engage the audience Promote the wider enterprise. Slide 42 Plan and write the presentation ‘The Ending’: Also known as the Conclusion or the Summary Should be brief Must summarise the presentation More on later slides. Slide 43 Plan and write the presentation Points about ‘Questions’: Encourage them Respond enthusiastically Never get annoyed by them or the person asking them Provide concise answers (Continued) Slide 44 Plan and write the presentation Acknowledge good incisive questions Observe confidentialities in the answers to questions Never be afraid when you do not know an answer Thank people for their questions. Slide 45 Plan and write the presentation Step 3 – Place the information in order: Write down a series of sub-headings you want to present in the Main Body Arrange these headings into a logical order/sequence Number each item of information in each sub-heading. Be prepared to re-order and re-number. Slide 46 Plan and write the presentation Step 4 – Identify key points. The number and nature of key points will depend on: Objectives Type of presentation Information available Audience Time Personal knowledge and experience. Slide 47 Plan and write the presentation Points to note about Step 4: Consider using a checklist Avoid information overload Give each key point a name/title Be prepared to provide ‘could know’ and/or ‘nice to know’ information in take-away form Slide 48 Plan and write the presentation Step 5 – Prepare a draft: Sets out what will be covered Identifies what will be said Identifies what will be used Allocates time Determines where activities and strategies will be included. Slide 49 Plan and write the presentation When writing a presentation draft: Clarify each key point Use headings and sub-headings Stay focussed on objectives Do not get ‘blown off course’ (Continued) Slide 50 Plan and write the presentation Keep audience characteristics or profile in mind Always ask ‘is this the best or most effective way?’ Use clear language and short sentences Ensure it is ‘interesting’ and ‘informative’ (Continued) Slide 51 Plan and write the presentation Identify where use of AV would be best option Write ‘Intro’ and ‘Ending’ after writing Main Body Be prepared to re-write the first draft – sometimes several times. Slide 52 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids This is Step 7: All presentations require support materials/visual aids Some materials have to be created, some can simply be acquired Materials/visual aids add variety and interest Materials/visual aids may be the most effective option for presenting statistics and other information. Slide 53 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids Also note: Materials must reflect identified need and contribute to the presentation Options include: • PowerPoints • Slides • Handouts • Samples/examples • Combination of all the above. Slide 54 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids Tips on preparing visual aids: Do not overload slides Make sure they are clear and concise Use large print and easy to read fonts Use dot points (Continued) Slide 55 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids Only use high clarity and quality pictures and photographs Ensure diagrams and charts are easy to read and interpret Summarise statistics Keep images simple (Continued) Slide 56 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids Use same font and slide structure throughout entire presentation Make use of colours One image = one idea Check for spelling and grammar. Slide 57 Develop and/or acquire supporting material and visual aids Common mistakes when developing slides/visual aids: Trying to fit too much on the one slide Using elaborate diagrams Applying a difficult to read font. Slide 58 Determine presentation equipment required Presentation equipment must reflect materials/visual aids to be used and how the presentation will be delivered – options include: Microphone Lectern Overhead projector Slide projector Screen (Continued) Slide 59 Determine presentation equipment required PowerPoint projector Laptop computer Video monitor/TV DVD player Tape player White board Chalk board. Slide 60 Determine presentation equipment required In relation to presentation equipment: Check it is available, you know how to use it and it is working properly Check and adjust the microphone Position and check the OHP – focus and keying Position and check the data projector – trial some slides Check the slide projector – focus, sequence of slides, correct way up (Continued) Slide 61 Determine presentation equipment required Check video player – cue tape, adjust volume Check DVD player – ensure correct DVD Check TV – right channel, volume Check audio equipment – volume, clarity Check recording equipment is operational Check whiteboard – clean, non-permanent markers, duster Verify audience can see. Slide 62 Determine presentation equipment required ‘Plan B’ – what will you do if there are problems or equipment fails? Convert everything to verbal presentation Use the whiteboard more Convert overheads and slides to handouts Cancel and/or re-schedule. Slide 63 Determine presentation equipment required Consider developing your own ‘Presentation Kit’: Toothbrush and toothpaste Pain relief tablets Extension cords Power boards Extra connection cords Shoe shine kit (Continued) Slide 64 Determine presentation equipment required Spare globes Instruction/Operator/User manuals for equipment Portable printer Whiteboard markers Chalk Name tags Business cards. Slide 65 Trial and practice the planned presentation Step 6 – Practice your verbal presentation: Read it aloud Be prepared to make changes Time it Record your practice Evaluate your performance. Slide 66 Trial and practice the planned presentation Things to look for when practicing: Information that does not flow smoothly Information that is too wordy – or not sufficiently detailed Sections that are unclear Topics best presented in another way Areas which present difficulty to you personally. Slide 67 Trial and practice the planned presentation Practice should also: Use the technology intended to be used Distribution of materials Involve wearing the clothes intended Operation of all ancillary equipment and items anticipated. Slide 68 Trial and practice the planned presentation After several trials you might also benefit by: Practicing by delivering to a trusted colleague to obtain feedback Delivering to a simulated audience (a group of people) to get experience of delivering to a group. Slide 69 Revise the presentation on the basis of the trial Need for revision to draft can be identified as a result of: Feedback received Timing issues Personal feelings Analysis of recordings made. Slide 70 Revise the presentation on the basis of the trial Changes may be needed to Intro, Main Body and/or Ending: Language – terms used, phrases Sequence/order of content Addition or deletion to script Activities used Room layout Technology used. Slide 71 Revise the presentation on the basis of the trial When changes have been made to the draft, rehearse the entire presentation (Step 8): Read what is intended to be read Use the technology/AV materials and aids Determine your physical stance Identify pace the presentation needs to take Control breathing Integrate other presenters. Slide 72 Revise the presentation on the basis of the trial Further points to consider: Practice more than once More practice is required early in your career There tends to be more need for practice where the presentation is off-site Factor in time for Q and As Never do a presentation without practice. Slide 73 Summary – Element 1 When preparing a presentation: Identify what your employer uses presentations for Determine how your workplace uses presentations Find out the basic facts relating to the presentation – date, time, duration, location, numbers attending, objectives, topics/content (Continued) Slide 74 Summary – Element 1 Determine the audience for all presentations as part of preparation Plan all presentations Research the presentation to obtain current, comprehensive and accurate facts Select relevant material for inclusion in the presentation (Continued) Slide 75 Summary – Element 1 Try to use a variety of materials and delivery styles for each presentation Prepare a script/written plan for the presentation Generate or obtain supporting materials and aids to assist delivery of the presentation (Continued) Slide 76 Summary – Element 1 Ensure necessary delivery equipment is available to enable use of prepared materials Trial and practice the planned/scripted presentation Revise the planned presentation on the basis of the trial/practice, as required. Slide 77 Deliver a presentation Performance Criteria for this Element are: Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Thank audience for the opportunity to make the presentation Make the presentation according to prepared plan (Continued) Slide 78 Deliver a presentation Modify presentation to optimise impact and success as required on the basis of immediate feedback from audience Respond to questions as required Conclude presentation. Slide 79 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Set up the venue before the presentation and make basic checks: Who is attending? Do a final review of your presentation: • Recap your notes • Double check everything needed is, in fact, present Prepare the venue – see following slides. Slide 80 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Tips for setting up the room/venue for a presentation: Divert phones Adjust lighting Set/adjust air conditioning Check catering has arrived (Continued) Slide 81 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Eliminate or control external noise and/or distractions Position directional signage – on door to room, at entrance, in lobby Advise others not to interrupt you Lay out support materials (Continued) Slide 82 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Turn cell phone off Verify seating is as required Check and test all equipment Ensure appropriate personal presentation. Slide 83 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Proper personal presentation is vital because: It shows respect for audience/client It helps generate self-confidence It indicates or infers competence It shows the presentation has merited time and trouble. Slide 84 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable Personal presentation checks: Visit and use the toilet Check appearance in mirror Brush teeth Brush/comb hair Brush shoes Check/spot clean clothes. Slide 85 Set-up and organise the venue, where applicable To help overcome anxiety: Arrive early Take confidence from the planning and preparation you have done – you are ready! Put the presentation into context Practice breathing techniques Focus on the presentation – not the audience. Slide 86 Thank audience for opportunity to make the presentation Starting a presentation (Introduction) should: Thank the audience for the their time and the opportunity to present Demonstrate respect for the attendees Explain the purpose, aim and content of the presentation Engage with audience members Build your self-confidence. Slide 87 Thank audience for opportunity to make the presentation When starting a presentation: Begin on time Introduce self Thank attendees Provide an overview of the presentation Give rationale for the presentation (Continued) Slide 88 Thank audience for opportunity to make the presentation Introduce others Give an idea of how long the presentation will take Advise the audience in relation to handouts (Continued) Slide 89 Thank audience for opportunity to make the presentation Advise about materials given prior to the presentation Advise about scheduled breaks, when they will occur and what they will entail. Slide 90 Make presentation according to prepared plan When delivering your presentation: Stick to the plan Stick to the script Be astute enough to identify the need to modify the plan or script Be flexible enough to make necessary changes. Slide 91 Make presentation according to prepared plan ‘Speech delivery’ is difficult for many and can be learned with practice. Tips include consideration of: Volume Speed/pace Tone, pitch and modulation Pronunciation and enunciation. Slide 92 Make presentation according to prepared plan During the presentation: Focus on the prepared message Involve the attendees using eye contact Breathe normally. Slide 93 Make presentation according to prepared plan Gestures and facial expressions: People believe non-verbal language more than verbal Smiling is positive and conveys a relaxed disposition Use a comfortable stance Minimise hand movements or gestures. Slide 94 Make presentation according to prepared plan Try to look relaxed Use a range of expressions and gestures Avoid nervous mannerisms and movements Avoid fidgeting. Slide 95 Make presentation according to prepared plan Cue cards: Jog the memory Remind of difficult concepts or ideas Provide focus to help stay on track Give the correct sequence for information Enable correct facts and figures to be quoted. Slide 96 Make presentation according to prepared plan Humour in presentations: Use with caution May best be avoided May be OK for internal presentations but not for external ones Adhere to company policies Avoid contentious or controversial topics No bad, offensive or suggestive language or gestures. Slide 97 Make presentation according to prepared plan Stories and anecdotes can be used to give: Realism Personal experience Build personal credibility Experiences of a third party Enhancement to a point. Slide 98 Make presentation according to prepared plan Finish by the expected time: It is OK to finish early Be prepared to omit certain points Conduct the Q and A session after the presentation Speed up Skip a non-important part. Slide 99 Modify presentation to optimise impact and success on basis of feedback Be alert to the need to modify your plan and: Always be prepared and willing to modify it Never show annoyance at having to modify the presentation Engage the audience. Slide 100 Modify presentation to optimise impact and success on basis of feedback Indicators of the need to modify a presentation: Direct request from the audience An overheard comment from the audience Your interpretation of body language. Slide 101 Modify presentation to optimise impact and success on basis of feedback Analyse the feedback: Is it just one person or the group? What is the status of the person giving the feedback? What is your ‘gut feeling’? Can it be ignored? Ask the audience – what is their suggestion? What will produce the greatest good for the greatest number? Slide 102 Modify presentation to optimise impact and success on basis of feedback Modifications may include: Changing pace of delivery Departing from the plan Using extra or different examples to illustrate a point (Continued) Slide 103 Modify presentation to optimise impact and success on basis of feedback Adjusting the environment Talking louder – or quieter Avoiding activities or delivery strategies the audience says they do not like Omitting points identified as not being necessary. Slide 104 Respond to questions as required Answering questions is a critical part of every presentation – they may be answered: At the end of the presentation in a specific Q and A session As they arise during the presentation. Slide 105 Respond to questions as required Tips for dealing with questions: Try to anticipate questions and prepare appropriate responses Consider using ‘Dorothy Dixers’ Indicate complex questions – or questions you cannot answer – will be handled at the end (Continued) Slide 106 Respond to questions as required Ask for clarification if unsure about the question Consider repeating the question aloud for the benefit of others in the audience Think before you answer Make sure the person asking the question has finished talking before you start responding (Continued) Slide 107 Respond to questions as required Refer an irrelevant question to the end of the presentation Nominate the person whose question you will take if there are multiple people asking a question Take questions from all sections of the audience Refer a ‘boring’ question till after the presentation Slide 108 Conclude the presentation Presentations should ‘conclude’ and not just ‘stop’ – important considerations are: Stick to the script, stick to the plan Never rush the conclusion. Slide 109 Conclude the presentation When concluding a presentation: Be brief Summarise information Address key points only Indicate future action attendees could/should take Give contact details (Continued) Slide 110 Conclude the presentation Indicate your availability after the presentation Nominate others who are available to provide information/answer questions Invite attendees to take refreshments Thank the audience. Slide 111 Conclude the presentation Use a DVD to close the presentation? Provide a set of conclusions or recommendations? Arrange for another presentation – or enquire if one is required Organise a follow-up meeting (Continued) Slide 112 Conclude the presentation Apologise for any problems encountered Mention action you will take to follow-up as promised during the presentation List questions you will follow-up on, as promised. Slide 113 Summary – Element 2 When delivering a presentation: Arrive early Set-up the venue in readiness for the presentation before the audience arrives (where possible) Check all items to be used in the presentation to ensure they are available and working as expected (Continued) Slide 114 Summary – Element 2 Welcome attendees Start the presentation by thanking audience for opportunity to make a presentation Implement the script/plan for the presentation Stick to the script, stick to the plan (Continued) Slide 115 Summary – Element 2 Tell ‘em what you’re going to tell ‘em; Tell ‘em’; Tell ‘em what you told ‘em Be prepared to modify the plan as required on the basis of feedback received and/or other factors Respond to questions as determined in the planning phase – either throughout the presentation or in a Q and A session at the end of the presentation Thank the audience for their time, interest and opportunity to present. Slide 116 Review a presentation Performance Criteria for this Element are: Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation Evaluate personal performance in the planning and delivery of the presentation Slide 117 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation Following a presentation: Followup Expect there to be a need to follow-up Take notes about anything and everything requiring follow-up action A follow-up should be seen as a ‘request for more information’. Slide 118 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation Examples of possible follow-up action: Contacting people. The most common requirement: • In the manner agreed • Providing extra information or clarification • Responding to issues • Seeking to close a sale • Involving others (Continued) Slide 119 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation Follow-up may require you to ‘provide information’ which can include: Supplying extra copies of materials Providing extra information Giving information in a different form Forwarding draft contracts or agreements. Slide 120 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation Points to note about provision of information: One request can trigger other requests – expect them Be alert to the need to explain information – not just provide it Supply hard copy information whenever possible Physically hand material to potential customers or clients. Slide 121 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation ‘Responding to issues raised’ during a presentation may involve: Clarification of points Updating and/or verifying currency of information Preparing revised proposals Negotiating prices and/or deals. Slide 122 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation When responding to issues raised: Thank customer for their request Respond promptly Provide necessary detail and information Check to determine the extra information has, in fact, effectively addressed the issue. Slide 123 Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation ‘Distribution of materials’ refers to provision of: More/different materials Electronic or paper-based materials Promotional merchandise Documentation for signing Anything that was promised during the presentation. Slide 124 Evaluate personal performance You should evaluate your presentations in order to: Determine the extent to which intended objectives were achieved Identify lessons learned. Slide 125 Evaluate personal performance Evaluations of presentations: Not every presentation needs to be formally evaluated – only the ‘more important’ ones Informal evaluations include: • Personal reflection • Review of materials • Consideration of feedback. Slide 126 Evaluate personal performance Keys in evaluating personal performance in relation to presentations are: Be honestly critical of your own performance Seek objective feedback Consider: • The planning and preparation phase • The delivery of the presentation. Slide 127 Evaluate personal performance Criteria for evaluation include ‘Time and activities in planning stage’. For example: Did you allocate enough time to planning and preparation? Was the planning and preparation rushed? Did you give the presentation the priority it deserved? Was there plenty of time available but you were just lazy? Slide 128 Evaluate personal performance Evaluate ‘support materials used’: Were sufficient quantities available? Were materials appropriate? Were support materials used or referred to at the most appropriate time? Did support materials distract from the presentation, or enhance it? Slide 129 Evaluate personal performance Evaluate ‘content’ of the presentation: Was content arranged in most effective order to optimise understanding? Was the scope or extent of the content sufficient? Was the content accurate, or did it contain mistakes? Was content current with up to date prices, statistics, data and other information? Slide 130 Evaluate personal performance Your personal performance as a presenter must be evaluated: Presentation methods Subject/topic knowledge Personal enthusiasm Audience interaction Personal presentation and appearance. Slide 131 Evaluate personal performance Set-up of the venue should also be evaluated: Did you find out what was available at the presentation forum? Did you arrive early enough to set-up properly? Did the planned set-up for the presentation work? Could all attendees hear and see what was being presented? Slide 132 Evaluate personal performance Consider also: How many attended? Start and finish times Outcomes from the presentation Use of ‘critical friends’. Slide 133 Evaluate personal performance Obtain feedback from: Colleagues who assisted with planning and preparation Colleagues who assisted with/were present at the delivery Management. Slide 134 Evaluate personal performance Feedback from attendees is useful data for personal evaluation: Actively seek it: • Ask for it • Distribute ‘feedback’ sheets Observe attendees: • Observe and interpret body language • Listen for comments • Note comments made directly to you. Slide 135 Evaluate personal performance Take notes when evaluating personal performance: Focus on issues of concern Be customer-focussed Focus on areas where there have been complaints (Continued) Slide 136 Evaluate personal performance Concentrate on ‘trends’ Record the ‘why’ as well as the ‘what’ Create solutions for identified problems Act on identified issues Refer to these notes before the next presentation. Slide 137 Evaluate personal performance Additional evaluation information may be gleaned from: Taping, reviewing and critiquing presentations Using a ‘focus group’. Slide 138 Evaluate personal performance You must apply the results of your evaluations. Possible applications include: Adjusting content as required Adjusting delivery as required Adjusting planning as required Adjusting personal approach as required (Continued) Slide 139 Evaluate personal performance Adjusting personal approach Adjusting the environment Working with management or your workplace ‘decision maker’ Changing start and/or finish times Ensuring mistakes are not repeated. Slide 140 Summary – Element 3 When reviewing a presentation: Follow-up on matters raised during the presentation – such as promises for future action, information, research, contact, clarification, documents, quotations Accept follow-up is as important as the presentation itself Review the planning phase and the delivery phase (Continued) Slide 141 Summary – Element 3 Review your personal appearance and performance Review the materials used Review the presentation style, content and script Review the set-up activities (Continued) Slide 142 Summary – Element 3 Be as objective as possible Seek feedback from multiple sources Be proactive in seeking feedback Makes notes about lessons learned Apply lessons learned. Slide 143