Lesson-11 Information System Development
advertisement

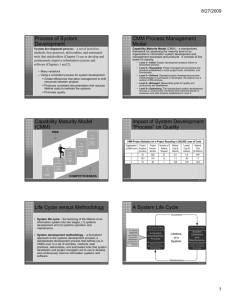
Lesson-11 Information System Development • Describe the motivation for a system development process in terms of the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) for quality management. • Differentiate between the system life cycle and a system development methodology. • Describe eight basic principles of system development. • Define problems, opportunities, and directives—the triggers for systems development projects. • Describe the PIECES framework for categorizing problems, opportunities, and directives. • Describe the traditional, basic phases of system development. For each phase, describe its purpose, inputs, and outputs. • Describe cross life cycle activities that overlap all system development phases. Lesson Map Process of System Development A system development process is a set of activities, methods, best practices, deliverables, and automated tools that stakeholders (Lesson 7) use to develop and maintain information systems and software. The CMM Process Management Model The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a framework to assess the maturity level of an organization’s information system development and management processes and products. It consists of five levels of maturity as measured by a set of guidelines called the key process areas. – Level 1—Initial: System development projects follow no prescribed process. – Level 2—Repeatable: Project management processes and practices are established to track project costs, schedules, and functionality. – Level 3—Defined: A standard system development process (sometimes called a “methodology”) is purchased or developed, and integrated throughout the information systems/services unit of the organization. – Level 4—Managed: Measurable goals for quality and productivity are established. – Level 5—Optimizing: The standardized system development process is continuously monitored and improved based on measures and data analysis established in Level 4. Capability Maturity Model (CMM) RISK Level 5 OPTIMIZED Level 4 MANAGED Level 3 DEFINED Level 2 REPEATABLE Level 1 INITIAL COMPETITIVENESS Life Cycle versus Methodology • A system life cycle divides the life of an information system into two stages, systems development and systems operation and support. • A system development methodology is a very formal and precise system development process that defines (as in CMM Level 3) a set of activities, methods, best practices, deliverables, and automated tools that system developers and project managers are to use to develop and maintain information systems and software. A System Life Cycle Conversion LIFE CYCLE STAGE System Development using System Development Methodology LIFE CYCLE STAGE Lifetime of a System Obsolescence System Operation and Support using Information Technology Principles of System Development • Get the owners and users involved. • Use a problem-solving approach. • Establish phases and activities. • Establish standards. • Justify systems as capital investments. • Don’t be afraid to cancel or revise scope. • Divide and conquer. • Design systems for growth and change. Phases of a Representative Methodology Overlap of System Development Phases 2004 ID 2005 Task Name May 1 Project management 2 Preliminary investigation 3 Problem analysis 4 Requirements analysis 5 Decision analysis 6 Design 7 Construction 8 Implementation 9 Operations and support Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Project Identification and Initiation • Problems are undesirable situations that prevent the organization from fully achieving its purpose, goals, and/or objectives. • Opportunities are chances to improve the organization even in the absence of specific problems. • Directives are new requirements that are imposed by management, government, or some external influence. The PIECES Problem-Solving Framework P the need to improve performance I the need to improve information (and data) E the need to improve economics, control costs, or increase profits C the need to improve control or security E the need to improve efficiency of people and processes S the need to improve service to customers, suppliers, partners, employees, etc. FAST System Development Phases Cross Life Cycle Activities Cross life cycle activities are activities that overlap many or all phases of the methodology. – Fact-finding – Documentation and presentation – Feasibility analysis – Process and project management Sharing Knowledge via a Repository A repository is a database where system developers store all documentation, knowledge, and products for one or more information systems or projects.