Beginnings of Human Societies #2
advertisement

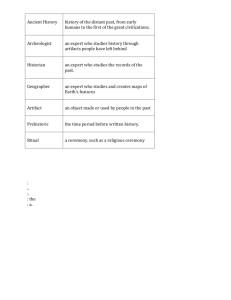
Beginnings of Human Societies Mrs. Rida Lesson 2 Unit 2 Time • How old is the universe? • How old is the earth? • When did humans appear on earth? What is the oldest thing in the room? How old is the air? • Part of air is hydrogen and helium which were created 13 billion years ago. • Other gases, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. were created in stars and range from 1-12 billion years ago. • Because our bodies are made up of these atoms, you too are billions of years old. Most of your weight which is water (hydrogen and oxygen) is 13 billion years old. Recap of Timeline • How far back did Homo Sapiens (the first species of human beings) first appear? • 200,000 years ago • Does it seem like a long time ago? • How does it compare to an individual person’s lifetime? • 1 minute vigil exercise How long is time? • How long do you think 200,000 minutes is? • Approximately 6 months….so 200,000 is a BIG number. • If those 200,000 years were SQUEEZED into 1 year, then the entire year of 2015 would have started at 11:58 PM on December 31 and ended at 12:00 AM. History of the world in 7 minutes • History of the World in 7 Minutes • Youtube • Every second in the video represents 50 years. • This IS A VISUAL TIMELINE • Watch the spacing of events, how far apart they are in the beginning and how close they are in the last four minutes of the video Things to ponder about • What types of artifacts seem to be left behind at the earlier parts of human history? • How does the video and pace of history change at the half way mark? • What surprised you about the video? World History • The field of history concerned with how Humans have evolved over time. Example: Studying how humans changed from hunter-gatherers to farmers, up until today. Study of History • Well imagine you know NOTHING about that life. Could you tell how people lived then? • How is it possible to study people who lived a long time ago if they did not leave written records of the way they lived? Archeology Groups of people who use scientific method to dig up and interpret the artifacts and the cultures of the past. • Example: Archeologists study old fossils and bones to learn about early humans. What does an Archeologist do? • What thought processes would an archeologist use when analyzing these objects? • How is this similar to when you see or hear new words while reading? Prehistoric The time or period before recorded or written history • Example: Prehistoric man used tools made from stones. Stone Age The earliest known period of human culture, marked by use of stone tools. • Example: The Stone age lasted through the Neolithic and Paleolithic periods. Cave Paintings Paintings on caves, walls and ceilings especially from prehistoric times. • Example: The cave paintings help us figure out how prehistoric people lived. Artifacts Any object made by mankind. • Example: Archeologists find artifacts from prehistoric people. The Cave Paintings of Chavet-PontD’arc The Cave Paintings of Chavet-PontD’arc Looking at the Maps: Before reading the excerpt… Purposes of Cave Paintings • Who painted the images on caves? • Why? Archeologists use the time period of the paintings to help them understand the image. • How do we figure out how old these paintings are? – Relative dating – Absolute Dating (Carbon Dating) Relative Dating Determine the age of object based on how old other fossils around it are. Example: Stone Tools found under many layer of earth are older than those on the top layers of the ground. Absolute Dating Determine the specific age of an object using a chemical process. Example: The archeologist used carbon dating to determine the exact fate of the skull found at the site.