Lab 4
advertisement

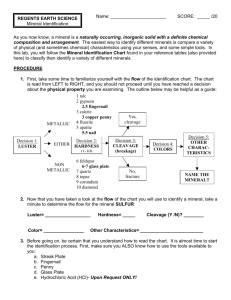
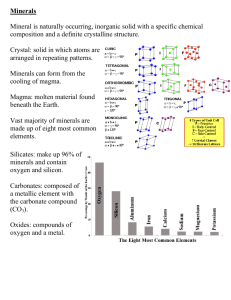
Lab 4 - Minerals • Minerals 1. Inorganic 2. Naturally occurring 3. Have characteristic chemical composition - Crystalline structure (orderly 3D arrangement of atoms/molecules) • Rocks - Aggregates of 1+ mineral(s) Mineral Properties 1. Color and Clarity - Color Clarity - Transparent = seethrough Translucent = foggy Opaque = can’t see through Mineral Properties 2. Crystal Form (Habit) - Geometric shape of the crystal - - - Cubes, pyramids, prisms, etc. Perfect crystal habit = only occurs when crystal has room to grow (rare) Different from cleavage way the crystal grows, not the way it breaks! Mineral Properties 3. Luster - How light reflects off an object Types: - Metallic luster (M) Non-metallic luster (NM) - Vitreous Waxy Pearly Satiny Earthy Greasy Porcelaneous Mineral Properties 4. Hardness - Measure of mineral’s resistance to scratching. Mohs Scale of Hardness - - Quantitative scale of relative mineral hardness 1 = talc (softest mineral) 10 = diamond (hardest mineral) Hardness of common objects: - Fingernail = 2.5 - Penny = 3.5 - Nail = 4.5 - Glass = 5.5-6 - Streak plate = 6.5 Mineral Properties 5. Streak - - Streak = the powder that remains when you scratch something against the streak plate Minerals harder than 6.5 do not leave their streak - - powder left behind = powder of streak plate Usually same for the same mineral even with different varieties of that mineral Crystal form Mineral Properties Cleavage 6. Cleavage and Fractures - Cleavage = breaks along flat, parallel surface Cleavage planes = parallel surfaces of weak chemical bonding - - - - May be one or more Cleavage direction = orientation of each set of cleavage plane Fracture = break in a mineral not along a cleavage plane Mineral Properties 6. Cleavage and Fractures - Cleavage direction may be: - - Excellent, Good, Poor Types: – – – – – – – Basal (mica) Cubic (halite) Octahedral (fluorite) Dodecahedral (garnet) Rhombohedral (calcite) Prismatic Conchoidal – ribbed, smoothly curved surfaces (like glass) Mineral Properties 7. Other properties - Reaction to acid – mineral fizzes when weak HCl is added - Carbonate minerals - Striations – straight, hairline grooves on the cleavage surface. - Feldspars - Magnetism – attracted to magnets - Specific gravity – ratio of the density of a substance divided by the density of water - How heavy is it? Notes on today’s lab • BEWARE OF COLOR! – The same mineral can be many different colors – Different minerals can be the same color • Identify consistently • Only write what you can see, don’t copy the book’s descriptions • 16 minerals, multiples for some – Minerals you will identify are all on your lab handout