TPSS Computer Literacy - Tangipahoa Parish Schools
advertisement

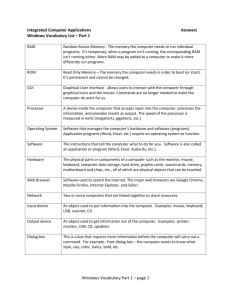
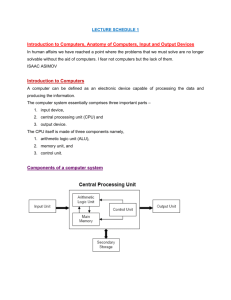
Topic 1: The Role of Computers Objective: Describe the role of computers in our daily life. The Role of Computers: A computer is an electronic device that you can use to store and process information. Computers help you perform a variety of tasks such as receiving and sending e-mail messages to family and friends, making presentations, and maintaining records. Computers are used for various business and recreational activities. You can save time, effort, and money by using computers. Computers play a major role in our daily lives. They are used virtually everywhere we go, such as industries, schools, government offices, and shops. The following slides describe the use of computers in various fields. Education Business & Finance Healthcare Scientific Research Government Affairs Arts & Entertainment Publishing Education In the field of education, trainers can use computers to perform various tasks such as deliver training through audio-visual learning aids, maintain student records to track performance, search for information on different topics, and create assignments. Business and Personal Finance In the field of business, you can use computers to maintain accounts, create personnel records, track inventory, prepare presentations and reports, manage projects, and communicate by e-mail. You can use computer technology to view the details of your bank account, get instant information on stock markets, trade stocks, and manage investments. Healthcare In the field of healthcare, computers can be used to perform various tasks such as reviewing medical records of patients. Using computers, doctors can easily search information about latest drugs that are available to treat a disease. In addition, doctors use computer technology to discuss and share information about various diseases. Scientific Research Scientists use computers for research, scientific modeling, and data analysis. For example, scientists use computers to perform complex mathematical computations, to view and analyze images from space, and to publish information on their recent research. They also use computer programs to simulate a structure, organism, or arrangement and then evaluate how it performs under different situations. Government Affairs In government organizations, you can use computers to organize information by storing and maintaining records. Computers are also used for providing services to citizens. For example, you can view information on current policies and government issues on a computer. Arts and Entertainment You can use computers to create drawings and paintings. Photographers use computers to edit and enhance pictures. Writers use computers to write content for their books and to create illustrations. Using computers, writers can make changes in the content easily and save time. You can also use computers for entertainment. You can listen to music, watch movies, store and print photographs, send greetings, and play games by using a computer. Publishing You can use computers to design any type of publication ranging from simple newsletters to fashion magazines, marketing materials, books, or newspapers. Think It Through You have seen that computers play a role in virtually every aspect of our life. Create a Tree Map that describes how you and your family interact with computers in the seven areas we looked at: Education, Business & Finance, Healthcare, Scientific Research, Government Affairs, Arts & Entertainment, and Publishing. For each area, write a complete sentence that explains how a computer plays a role in your or a family members life. Tree Map Computers Education Business & Personal Finance Healthcare Scientific Research Government Affairs Arts & Entertainment Publishing For each area, write a complete sentence that explains how a computer plays a role in your or a family members life. The light blue boxes will grow as you type. Tree Map TOP SECRET --No Peeking!— Computers Education Business & Personal Finance I can conduct research for school projects and check my grades online. My mom can access money online or at an ATM even when the bank is closed. Healthcare My medical records are stored on computers at the doctors office. Scientific Research Government Affairs Arts & Entertainment Weather scientists use computers to predict when a Hurricane will hit our area. I can go online to email my mayor, congressma n or senator about things that I want changed. Many films that I watch use 3D effects and digital effects that are not possible without computers. Publishing I can email pictures to be printed and my favorite magazine is created on computers. (Delete or drag this box over to check your answers) For each area, write a complete sentence that explains how a computer plays a role in your or a family members life. Think It Through Writing: Write a short story that describes one day in your life without computers. Consider that virtually everything with a digital display is a computer: from your phone to your car. How would your life be different, better, worse and the same? Remember to include a good introduction, write clearly, use good word choice and correct grammar/ spelling. Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 1: The Role of Computers. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 2: The Parts of a Computer Objective: Identify the external and internal parts of a computer. Parts of a Computer A computer has various parts inside and out. Each part performs a specific function. First, you will learn to identify the parts of the computer visually. Later, you will learn the functions of these different parts. 2 External Front 1 1. Optical Drive (CD/ DVD Drive) 2 2. Empty Bays (If you want to add an extra Optical Drive) 3 5 7 4 3. Power Button 4. Extra USB Ports 5. Sound Input Port (Microphone) 7 6. Sound Output Port (Headphones) 7. Sound Output (Speaker) External Back 1 1. Power Supply with cooling fan 2. Keyboard and Mouse Ports (These are being replaced with USB ports in new PCs) Purple-Keyboard Green- Mouse 2 3 4. Video Port- For Monitor or Projection System (Video Card) 5 5. Parallel Port- For Printers or Scanners without a USB cord (pretty rare now) 6 7 6. Ethernet Port- To connect to Internet (NIC Card) 4 4 3. USB (Universal Serial Bus) Ports 7. Empty Bay- Allows extra room for other cards to be added later. 8 6 8. Sound Input/Output (Sound Card) Pink- Headphones Green- Speakers Blue- Microphone Internal 6. Optical (CD) Drive 1 1. Power Supply Optical Drive 2 or Empty Bay Back Empty Bay 2. CPU w/ Fan CPU 9.with RAM Fan 7. 3.5 Floppy Drive 8. Hard Drive Behind Wall 3. Video Card 4. Sound Card 5. NIC Card 10. Motherboard Front Computer Part Access From The Front Access From The Back Power Supply X (on Button) USB Ports X (USB Ports) Found on the front and back of tower for ease of use. Video Card (Graphics) Sound Card X (Power Cord) What It Does Provides Power to the system Allows devices to connect to computer X Displays picture on the monitor (Video Port where you plug in the monitor) X (Sound Ports) Found on the front and back of tower for ease of use. Sends sound to speakers/ headphones X (Ethernet Port) Allows connection to Internet or LAN Modem Card (Connectivity) Optical Drive Access From Operating System X (CD ROM) Reads/Writes CD-ROMs Hard Drive X (C Drive) Reads/Writes files to internal storage CPU X Tells all the parts what to do Motherboard with RAM Memory X Circuit board that CPU, components & cards plug into. Think It Through Use the pictures and labels on the following slides to test your memory. Can you drag the labels to the correct the parts of the computer inside and out? Work alone, then work with a partner and help each other check your work. Think It Through Power Supply Sound Card NIC Card CPU with Fan Motherboard RAM Optical Drive Video Card CPU Hard Drive Think It Through Power Supply TOP SECRET --No Peeking!— Optical Drive RAM CPU with Fan CPU Video Card Hard Drive (Delete or drag this box over to check your answers) Sound Card NIC Card Motherboard Think It Through 1 2 3 5 6 7 4 4 8 6 Power Supply Keyboard & Mouse Ports Sound Input/ Output USB Ports Video Port Parallel Ports Ethernet Port Empty Bay Power 1Supply 2 3 Think It Through TOP SECRET No Peeking!— 4 USB Ports Parallel Ports 5 6 Ethernet Port 7 put 4 Bay ag this box over toEmpty check your answers) 8 6 Think It Through 2 1 Power Button Optical Drive Sound Input Port Microphone USB Ports Sound Output Port Headphone Sound Output Speaker 2 3 5 7 4 Empty Bay 7 Empty Bay 2 Think It Through Optical Drive 1 TOP SECRET --No Peeking!— 2 Power Button 3 5 7 Input ophone Sound Output Port Headphone 4 USB Ports or drag this box over to check your answers) 7 Sound Output Speaker Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 2: The Parts of a Computer. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 3: The Functions of a Computer Objective: - Identify the four major functions of a computer. - Identify basic computer terms. Computer Functions: A computer has four functions: 1. To Accept dataInput 2. To Process dataProcessing 3. To Produce output- Output 4. To Store resultsStorage …… Input Output Input Everything a user “tells” a computer. Commands are given to the computer in different ways depending on the type of Interface being used. They can be a typed command, selected from a menu, or clicked with a mouse. Running programs, software, uploading data and responding to a computers question are also considered Input. Input Processing The thinking that the computer does - the calculations, comparisons, and decisions. A computer’s speed is often compared to its central processing unit (CPU), the part of the computer where all computer processing takes place. However, speed is also affected by the amount of RAM memory that is available. …… Output Data that has been processed into useful form, now called Information. It can be described as: Hard copy: printed on paper or other permanent media Soft copy: displayed on the screen or by other nonpermanent means Output Storage If you do not save your work to a Storage Device like the computer’s Hard Drive, a USB Drive, a CD or a Network Drive like the Assignment Drive, that information will be lost when you close the program. Memory Speed measures the time it takes to move data in or out of memory. It is measured in megahertz (MHz). Memory Capacity measures the amount of data that a device can hold. It is measured in bytes. The Prefix Mega (MB), Giga (GB) and Tera (TB) describe if the bytes are numbered in the Millions, Billions or Trillions. Storage Devices You use storage devices to keep computer information for later use. Storage devices come in many forms. Some examples are hard drive or disk, CD-ROM, floppy disk, and DVD-ROM. Storage devices can be divided into two types, internal storage devices and external storage devices. Some common storage devices are : Hard Disk Floppy Disk CD-ROM or DVD-ROM USB Flash Drive Cloud Storage Hard Disk Drive & Floppy Disk Hard disk drive. A magnetic disk that is usually the main storage device on most computers. It can be an external or an internal device. Floppy disk. A portable storage device that allows you to store a small amount of data. A disadvantage of this disk is that it can be easily damaged by heat, dust, or magnetic fields. CD and DVD ROM CD-ROM. A portable storage medium that allows you to store 400 times more data than on a floppy disk. It is less prone to damage than a floppy disk. DVD-ROM. A portable storage medium that is similar to a CD-ROM; however, it can store larger amounts of data than a floppy disk or a CD-ROM. A DVD-ROM is commonly used to store movies and videos. Flash Storage USB flash drive. A small portable storage device that is typically the size of a thumb. They can be plugged into any computer with a USB drive and as such are a very popular medium of storage. Flash Memory Cards. Used in digital cameras, cell phones, video game consoles and MP3 players, flash memory cards come in many shapes and sizes. You will need a card reader to retrieve the information once it is removed from the device. Cloud Storage Cloud storage service. A modern, fast growing storage service that uses the Internet and central remote servers to maintain and store data and applications. For example, iTunes allows you to back up your devices to Cloud Storage. There are many free and paid cloud storage services available. Mass Storage Capacities Type Extra Info Capacity Floppy Disk Rarely Used Anymore _1.44_MB CD- ROM- Install Program CD-R/ CD-RW (Save to) Replaces 500 Floppies! _650_ MB - _700_MB USB Flash Memory Stick (Jump Drive) 1GB= $10-$20 __52_MB -__6_GB iPOD Shuffle= 1GB iPOD Nano= 2-4GB ___52___MB-__1__GB Our Computer= 100 GB _100_ GB - _500_GB iPOD Touch= 8-64GB _16__GB- __1__TB Flash Memory Card (SD Card) The new SDHC go up to 10 GB Hard Drive External/ Portable Hard Drive Cloud Storage Unlimited (as long as you can afford it!) Hardware Hardware refers to all the physical components of a computer. It includes all input devices, processing devices, storage devices, and output devices. The keyboard, mouse, motherboard, monitor, hard disk, cables, and printer are all examples of hardware. You use hardware to provide input to a computer and also to get the desired output. For example, when you play a musical instrument, such as a piano, you provide input by pressing the keys and get the desired output in the form of music. Similarly, computers also need input and output devices to perform tasks. Software Software refers to instructions that tell a computer how to perform a function. Software can also be referred to as a program or application. Software must be downloaded to a computer and installed before it can be used. The distinction between software and hardware is sometimes confusing because they are so integrally linked. Clearly, when you purchase a program, you are buying software. But to buy the software, you need to buy the disk or device (hardware) on which the software is stored. Networks You can connect your computer to other computers to share information and hardware components. A group of computers and associated devices that are linked together to facilitate sharing information is called a network. Networks can also be used to share data and devices such as printers. You can also communicate with other computer users on the network. Our entire school is connected on a network. You can access the “Template” Drive from any computer in our school. You can send a document from any classroom to print in the office. LANs & WANs Depending upon the area covered, a network can be categorized as a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN). LAN - A Local Area Network connects devices within a limited area, such as a home or a small group of offices. It commonly includes computers and shared resources such as printers and scanners. WAN - A Wide Area Network is a network that connects devices in geographically separated areas. You can use the resources of a WAN to connect two or more LANs by using long wires, optical cables, and satellites. Many organizations use a WAN to connect their networks across different countries. The Internet is an example of a WAN. Generally, a LAN is connected by cables that physically meet each other. Whereas a WAN uses the Internet to connect the computers and components. Internet The Internet is a worldwide collection of public networks that are linked to each other (WAN) for information exchange. The Internet started as a network to facilitate communication between government and educational departments in the United States. When other networks were connected to this network, it became a vast medium for exchanging information and ideas. Today, the Internet connects many commercial, government, and educational networks, as well as individual computers, which share data. You can use the Internet and its services to send messages to other Internet users, search and apply for jobs, watch movies, and buy and sell products. Programs Programs, also called applications, use hardware and the operating system together to perform tasks. There are many types of programs. Some programs allow you to perform tasks such as writing letters, doing calculations, or sending e-mail messages. Other programs allow you to create illustrations, play games, watch movies, or communicate with other computer users. Think It Through Choose 4 items on the next slide. Think about how the computer in that item works. For each device, describe the Input, Processing, Output, and Storage. (Some devices may not have all four functions) Ex : ATM Machine Input: Card swipe, type in PIN, press buttons Processing: The machine has to “Think” as it finds the acct #, checks if your PIN is correct and checks how much money you have available. Output: Display on the screen, receipt, and $$ Storage: It has to store the transaction to remove/ add money from your acct. Some also record video. Think It Through Remote Control MP3 Player Digital Camera Your Car Calculator Television Cell Phone Coke Machine Price Scanner at Wal-Mart Remember: Input- How YOU “talk” to the computer to give a command Processing- What the computer does while it is completing your command. The human just waits. Output- How the COMPUTER “talks” or communicates with you. Storage- What type of memory does the computer have? Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 3: The Functions of a Computer & Basic Terms. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 4: Input and Output Devices Objective: - Identify and define commonly used input and output devices. Input Devices You use input devices to provide information to a computer or to give instructions to a computer for performing a task. Some examples of input devices are: Mouse Keyboard Microphone Scanner Webcam Stylus Trackball Mouse Mouse. A device that you use to interact with items displayed on the computer screen. A standard mouse has a left and a right button. You use the left button to select items and provide instructions by clicking an active area on the screen. You use the right button to display commonly used menu items on the screen. Keyboard Keyboard. A set of keys that resembles a keyboard on a typewriter. You use the keyboard to type text such as letters or numbers into the computer. Microphone Microphone. A device that you can use to talk to people in different parts of the world. You can record sound into a computer by using a microphone. You can also record your speech and let the computer convert it into text. Scanner Scanner. A device that is similar to a photocopy machine. You can use this device to transfer an exact copy of a photograph or document into a computer. A scanner reads a page and translates it into a digital format that a computer can read. For example, when you scan photographs of your family using a scanner, it gets converted into a digital format that your computer can read. Webcam Webcam. A device that is similar to a video camera. It allows you to capture and send live pictures to other users. For example, a Webcam allows your friends and family to see you when you are communicating with them. Stylus Stylus. A pointing device, similar to a pen, used to make selections and enter information by tapping on a touch sensitive surface. For example, many stores have a stylus attached to their debit/credit card reader to make selecting icons and signing your name easier. Trackball Trackball. A pointing device that is an alternative to a mouse. A trackball consists of a ball that is rotated to move the pointer on a computer screen. You can use a trackball when you have limited desk space. Output Devices You use output devices to get feedback from a computer after it performs a task. Some examples of output devices are. Monitor Printer Speaker/Headphone Monitor Monitor. A device that is similar to a television. It is used to display information in the form of text and graphics. Printer Printer. A device that you use to transfer text and images from a computer to a paper or to another medium, such as a transparency film. You can use a printer to create a paper copy of whatever you see on your monitor. Speaker/ Headphones Speaker/Headphone. A device that allows you to hear sounds. Speakers may either be external or built into the computer. Think It Through • Drag the pictures to the correct square Input Output Think It Through TOP Input SECRETOutput --No Peeking!— • Drag the pictures to the correct square (Delete or drag this box over to check your answers) Think It Through • Create an advertisement for an Input or Output Device. • Use Persuasive Writing to describe your device in a way • - that makes a customer want to purchase your product. Include: The devices name A price 3-4 Sentences that describe and persuade someone to buy your product An illustration. Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 4: Input & Output Devices. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 5: The Motherboard Objective: - Identify and define the components attached to a Motherboard that run a computer. CPU & Motherboard Apart from input and output devices, a computer uses processing devices to work on the input data and generate the desired output. The most important processing device is the CPU. It is the brain of the computer that processes the input to generate the output. A motherboard is a large circuit board that connects input, output, and processing devices. The motherboard circuits provide pathways that allow data to pass through these various components. It also contains chips that determine how, when, and where data can flow through the computer. CPU & Memory The CPU is a device that interprets and runs the commands that you give to a computer. It is the control unit of a computer. The CPU is also referred to as the processor. Memory is where information is stored and retrieved by the CPU. There are two main types of memory. CPU is located under this fan Memory Type 1: RAM Random access memory (RAM). It is the type memory a computer uses for processing and can affect how fast the computer can complete tasks. This short term memory allows the computer to temporarily store commands and data. The CPU reads data and commands from RAM to perform specific tasks. RAM is volatile, which means it is available only while the computer is turned on. The contents of RAM must be copied to a storage device if you want to save the data. Memory Type 2: ROM Read only memory (ROM). It is the memory that retains its contents even after the computer is turned off. ROM is nonvolatile, or permanent, memory that is commonly contains the minimum instructions that the computer needs to turn on, boot up, find files and read information. Motherboard The motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer. It has tiny electronic circuits and other components on it. The motherboard connects input, output, and processing devices together and tells the CPU how to run. Other components on the motherboard are the video card, sound card, and circuits that allow a computer to communicate with devices like a printer. Motherboard Expansion Cards An expansion card is a circuit board that can be attached to a motherboard to add features such as video display and audio capability to your computer. An expansion card improves the performance of your computer and enhances its features. Expansion cards are also called expansion boards. Some types of expansion cards are: Video Card Network Interface Card Sound Card Video Card Video card. It is connected to a computer monitor and is used to display information on the monitor. Network Interface Card Network Interface Card (NIC). It allows a computer to be connected to other computers so that information can be exchanged between them. (On a network connected through the internet) Sound Card Sound card. It converts audio signals from a microphone, audio tape, or some other source to digital signals, which can be stored as a computer audio file. Sound cards also convert computer audio files to electrical signals, which you can play through a speaker or a headphone. You connect microphone and speakers to a sound card. Ports and Connections A port is a channel through which data is transferred between input/output devices and the processor. There are several types of ports that you can use to connect a computer to external devices and networks. Some types of ports are: Universal Serial Bus (USB) Network Port Parallel or Serial Port Display Adaptor Power USB Universal serial bus (USB) port. You use this to connect input and output devices such as a mouse, modem, keyboard, or printer to a computer. Network Port & Parallel Port Network port. You use this to connect a computer to other computers to exchange information between the computers. Parallel port and serial port. You use these ports to connect printers and other devices to a personal computer. However, the USB port is now preferred to connect peripheral devices because it is faster and easier to use. Display & Power Display adapter. You connect a monitor to a display adapter on your computer. The display adapter generates the video signal received from a computer, and sends it to a monitor through a cable. The display adapter may be on the motherboard, or on an expansion card. Power Supply. A motherboard and other components inside a computer use direct current (DC). A power supply takes alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet and converts it into DC power. Think It Through Complete the Brace Map on the following slide that lists the parts of a computer attached to the motherboard. Drag the labels and examples into the correct positions. Remember that a Brace Map shows parts of a whole, so all of these parts are needed for a computer to function. Hint: Zoom out on the next slide to more easily see all the labels. Blue labels go in the left column. Green go in the right column. Storage RAM, ROM Ports & Connections C ophone, Webcam ay, Power CPU what to do Monitor, Printer, Speakers, Lights, Motion Expansion Input Mouse, Keyboard, Microphone, Webcam Output Monitor, Printer, Speakers, Lights, Motion TOP SECRET --No Peeking!— CPU Central Processing Unit Memory RAM, ROM Motherboard Circuits and components that tell the CPU what to do Expansion Cards Sound, Video, Network (Delete or drag this box over to Hard check your Storage Disk, CD, Flash,answers) Cloud Ports & Connections USB, Parallel, Network, Display, Power Think It Through • Read the examples on the next slide and decide if the situation is describing RAM, ROM or a computer’s Mass Storage. Remember: • ROM is only used when the computer is starting up. • RAM helps increase processing speed and is temporary memory. • Mass Storage is where you store files and programs on the computer that you want to keep for a long time. RAM, ROM or Mass Storage? 1. I can transfer a newly downloaded MP3 to my iPOD 2. It takes my computer about 15 seconds to download a song from 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. iTunes My computer shut down overnight after it installed Windows updates and this morning I had to restart it. It took so long, I didn’t get to check my Facebook before school :( I received a new iPOD for my birthday and when I plugged it into the computer, it installed iTunes onto the Hard Drive. You watch the blue bar move across the screen as a computer loads an internet page Internet Explorer is stored in the “Programs” Folder of the Hard Drive I hate using mom’s computer- its old and takes forever to boot. If you want to move your Internet bookmarks from one computer to another, you can save them to a USB Drive and install them on another computer. RAM, ROM or Mass Storage? 1. I can transfer a newly downloaded MP3 to my iPOD 2. It takes my computer about 15 seconds to download a song from iTunes. RAM 3. My computer shut down overnight after it installed Windows updates and this morning I had to restart it. It took so long, I didn’t get to check my Facebook before school :( ROM or RAM 4. I received a new iPOD for my birthday and when I plugged it into the computer, it installed iTunes onto the Hard Drive. Storage 5. You watch the blue bar move across the screen as a computer loads an internet page. RAM 6. Internet Explorer is stored in the “Programs” Folder of the Hard Drive 7. I hate using mom’s computer- its old and takes forever to boot. ROM (Delete or drag this box over to check your answers) or RAM 8. If you want to move your Internet bookmarks from one computer to another, you can save them to a USB Drive and install them on another computer. Storage TOP SECRET --No Peeking!— Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 5: The Motherboard. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 6: Computer Functions & Performance Objective: - Explain the different types and functions of computers available for use today. - Explain the factors that limit & improve the performance capabilities of computers. Computing Devices Different types of computers are available in the market today. The most common computer is the Personal Computer (PC), typically used by individuals and business organizations. A personal computer is used in the workplace to create documents, manage business records, and communicate with others. It is used in schools to teach lessons, research over the Internet, and work on assignments. You can also use a personal computer to play games, view videos, and listen to music. Depending on the size and the purpose of a personal computer, it can be categorized into different types: desktop, laptop, netbook, handheld, or tablet. Desktop Desktop computers are made up of individual components such as a monitor, a keyboard, a system unit, and a printer. These computers are generally placed on the surface of a desk or a table and are not easily portable. The components of desktop computers can easily be replaced or upgraded. Desktop computers usually have more memory, a larger hard drive, more ports, and a bigger display than other personal computer types. Desktop computers run on electricity and can be used continuously for long periods of time. Laptop & Netbook Laptop computers are portable lightweight personal computers. They are smaller in size as compared to a desktop computer and are designed for travel. Laptop computers are also called notebook computers. The main feature of laptop computers is that they are small and portable. Laptop computers run on electricity or on batteries that can be recharged. They consume more power than desktop computers with an almost similar hardware setup. Laptop computers perform the same tasks as desktop computers, but laptop computers generally cost more than desktop computers. Netbook computers are smaller, less powerful and less expensive than laptop computers. Tablet Tablet computers are fully functional tablet-sized portable computers that allow you to write directly on the screen by using your finger or a pen called stylus. You can also use the stylus to perform mouse functions. Tablet computers, therefore, do not need a keyboard and a mouse. Handheld Handheld computers are computing devices that are small enough to fit in your hand. You can input data by writing directly on the screen using a stylus or by touch commands. Handheld computers help you perform basic word-processing activities, accessing the Internet, e-mail, and taking pictures or video. Personal digital assistants (PDAs) and Smart Phones are examples of handheld computers. Smartphone Smartphones are handheld computers that have telephone capabilities. They have a range of applications such as calendar, phonebook, and organizers that can be personalized. Smartphones can be synchronized with other devices such as a personal computer or laptop to keep files updated. Category Desktop Computer Laptop Computer Netbook Computer Tablet Computer Handheld Computer Size Portability Full-sized. Low portability. Notebook sized. Easy to carry around. Mini-laptop. Lightweight and easy to carry around. Tablet-sized. Easy to carry around. Pocket-sized. Easy to carry around. Performance Best performance among the different computing devices. High upgrade capabilities. Limited multimedia, games, and graphic capabilities as compared to laptops. Limited upgrade capabilities. Graphic and multimedia capabilities are better than a netbook computer. Limited upgrade capabilities. Limited multimedia and graphic capabilities. Limited upgrade capabilities. Hardware components A larger hard drive, more memory, more ports, and a bigger display. Performs better than all the other portable computing devices, but rarely as well as equivalently-priced desktops. Limited upgrade capabilities in comparison to a desktop computer. Smaller hard drive, lesser memory, lesser ports, and a smaller display in comparison to a desktop computer. No media drives. Smaller hard drive, lesser memory, lesser ports, and a smaller display in comparison to a laptop computer. Memory card slots are available for memory upgrade. No media drives. Memory card slots are available for memory upgrade. Input device Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone, Scanner, Webcam. Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone, Scanner, Webcam. Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone, Webcam, Scanner. Stylus, Fingers. Stylus, Microphone, optional Keyboard. Power supply Electricity. Electricity or rechargeable batteries. Electricity or rechargeable batteries. Rechargeable batteries. Rechargeable batteries. Factors that affect performance Amount of memory – Computers depend on RAM to run processes and applications; When a computer with too little RAM is attempting to run several processes, each one may not have access to as much RAM as it requires to run optimally, so they will slow down, taking noticeably more loading time to complete any commands. • Speed of the processor- The CPU is the primary driver of how fast a computer works. All user input is processed by the CPU once every cycle. The CPU does everything in its power to perform more than one instruction per cycle. Cycles are what most processors are measured in. A "Ghz," means one billion hertz, or cycles per second. The higher the number, the more often a processor can process. Factors that affect performance Type of Video Card- A top-of-the-line graphics card will have its own memory and processor built into the card. By having a CPU and memory dedicated solely to graphics, it frees up those components to help the computer run smoothly. Having a lower grade video card will slow down computer performance when playing video games or working in graphic design programs like Photoshop. Type of Internet Connection- When surfing the Internet, streaming videos or downloading files from the internet, your internet connection speed will affect the performance of the computer. The faster connection you have, the faster pages and files will load, download and play. You can find out what Operating System, Processor and amount of RAM your computer is running by going to Start> Computer> System Properties You can find out what Video Card your computer at home has by going to Start> Control Panel> Personalization> Adjust Screen Resolution> Advanced Settings>Adaptor Tab. However, access to these features have been blocked on our school computers. Think It Through Create a Double Bubble Map or Venn Diagram to compare and contrast two of the devices that were described in this lesson. Choose one of the five devices that were described and write a Persuasive Letter to a parent or relative asking them for one of the devices as a gift. Think about the advantages of the device you have chosen. Which features of that device would convince them that it would be a good investment for you? Double Bubble Venn Diagram Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 6: Computer Functions & Performance. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! Topic 7: Computer Operation Objective: - Explain the steps necessary for computer operation at school. (Start Up, Logging in, Use of Keyboard and Mouse, Logging Off) Start-Up To turn on a computer, press the power button on the system unit. When you turn on the computer, lights on the keyboard may blink briefly, and you may also hear a beep. This is an indication that the power-on self test (POST) has started. The computer performs a sequence of quick tests to check whether the motherboard, memory, hard drive, and other components are working. If you hear a series of beeps, the monitor may display a message indicating that a component is not functioning. After POST, the computer starts the operating system. The operating system controls the computer’s hardware and manages the different operations of the computer, such as logging on, logging off, and shutting down. Logging In When the computer starts a Welcome screen appears. This screen displays the links to existing user accounts. To log on, type in your TPSS username & password in the boxes and click the arrow or press enter on the keyboard. If another student’s name is listed, click “Switch User”. After you log on to your computer, wait a few seconds before clicking the “Start” Button. If you do not give the computer enough time, it will not load the Templates or Assignments Drive correctly and they will not work. TANGI Your desktop should look like this: After you click the “Start Button”, you should see your name listed in the menu. STUDENT NAME Mouse Most mouse devices have at least two buttons, left and right. Most of the actions are performed by clicking the left button. The right button is used for specific functions. Most mouse devices also have a wheel that helps you to scroll through documents or pages. To scroll, place your finger on the wheel and roll it back and forth. This action moves the document up and down. Mouse Functions • Click- Press a mouse button and release it. Usually the left • • • • • button. (Single Click) Double-click- Press a mouse button twice quickly Right click- Press the right mouse button and release it. Drag- Hold a mouse button down while moving the mouse. Usually what the mouse pointer was over on the screen will move or be highlighted when you drag. Scroll- Rolling the wheel between the L and R button will move the screen up and down Drop- To Release the mouse button so it will deselect an item (often to move it into a new location). Keyboard The keyboard is an input device that you can use to type commands or text into a computer. Different keyboards have different key layouts. In addition, the functions of some keys may vary from program to program. Most keyboards have keys labeled from F1 to F12. These keys are the function keys, which differ from program to program. The function of the F1 key in most programs is to access the help file associated with a program. Most keyboards include a special key called the Windows logo key. This key is used to open the Start menu, or is used in combination with a second key to perform common Windows tasks. If for some reason your mouse does not work, you can still access all menus using the Windows Logo, TAB , Directional (arrow) and Enter Keys. Keyboard Cont The Insert, Number Lock and Caps Lock keys are toggle keys. This type of key is switched on or off each time it is pressed. A light will appear on the keyboard when they are on. Navigation Keys are the arrow keys, HOME, END, PAGE UP, and PAGE DOWN . Use Navigation Keys to move through lines and sections of text in a document or presentation. Most keyboards have a numeric keypad that is located on the right side. It has a set of 17 keys with numbers from 0 to 9, the decimal point, mathematical symbols, and navigation symbols. The NUM LOCK key on this keypad allows you to switch between the numeric and the navigation keys. If you are having trouble typing in your password when you log in, it is probably because NUM LOCK is off. Logging Off and Shutting Down You can end your computer session by saving your work and logging off. Only shut down if your teacher has asked you to. When you install new software on your home computer or encounter problems while using the computer, you can use the Restart option to restart the computer. (You should never install any programs on a school computer) You should never use the actual power button on the front of the system unit to turn off the computer. Use the log off or shut down menu unless the computer has stopped responding. End your computer session by logging off. To log off, click the “Shut Down” button in the Start Menu and choose “Log off”. Only shut down if your teacher has asked you to. STUDENT NAME Think It Through Create a computer user-guide for new students at our school. Explain to them in simple steps how to login to a TPSS computer, access the start menu and log off. You may write your user-guide using a Flow Map, a list or a multi-step paragraph. Flow Map Strive For Success Time to check your understanding of Topic 7: Computer Operation. Our class will take a quiz on ____(Quiz Date)_______. Use your Study Guide and Think It Through Activities to strive for success on the quiz! This file was created the summer of 2014 for the Tangipahoa Parish School System to teach 7th Grade Computer Literacy. Information found within this presentation was collected from Microsoft Digital Literacy & Support websites or created by the author. Digital Literacy: https://www.microsoft.com/about/corporatecitizenship/citizenship/giving/programs/up/digit alliteracy/default.mspx Support: http://support.microsoft.com/ Images included in the presentation were found using a Google Image Search, specifically images tagged “Labeled for Reuse”. Screen Captures were taken from the TANGI Windows 7 Operating System or a program within the Microsoft Office 2013 Suite. Only Tangipahoa Parish School System teachers may copy, edit and reproduce this file and others within the series. Please email any questions regarding use of this and other files in the series. JLEE