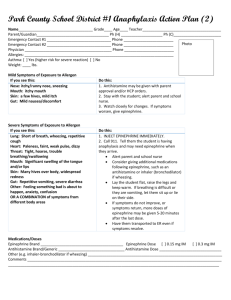
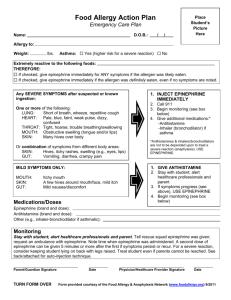
MR scanning and cont.. - University of Washington
advertisement

Radiology Life Support: Dealing with Acute Contrast Reactions William H. Bush, Jr., MD, FACR University of Washington Contrast Use Test Yourself Question # 1 A patient who has had a reaction to iodinated contrast is at higher risk for having a reaction to gadolinium agents. True or False ? Question # 2 Your patient is cool, clammy, and has perspiration on their forehead and upper lip. The reaction most likely occurring is: 1. Vagal reaction 2. Urticaria 3. Bronchospasm Question # 3 Your patient complains of shortness of breath. The most likely reaction occurring is: 1. Vagal reaction with bradycardia 2. Urticaria 3. Bronchospasm Question # 4 Which of these IMMEDIATE actions by you during response to a major allergic-like systemic contrast reaction is the most important ? 1. 2. 3. 4. I.V. access Airway / suction / oxygen Cardiac monitor / pulse oximeter Blood pressure Question # 5 Which of these IMMEDIATE actions by you during response to a major allergic-like systemic contrast reaction is the least important ? 1. Talk to the patient 2. Take their pulse 3. Take their blood pressure. Question # 6 The treatment for severe hypotension and bradycardia is: (a, b or c) a. IV fluids and atropine b. IV fluids and epinephrine c. Nitroglycerine Question # 7 The key finding for diagnosing a vagal reaction is: (a, b, c, or d) a. b. c. d. Rapidity of breathing Systolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure Pulse rate Question # 8 The adult dose of IV atropine for treating a vagal reaction is: (a, b, or c) a. 5-10 mg b. 1.0 mg c. 0.3 mg Question # 9 Initial treatment of laryngeal edema is: (a, b, c, or d) a. b. c. d. Atropine Benadryl® Beta-agonist inhaler Epinephrine Question # 10 Your patient is hypotensive; the most effective route for epinephrine administration is: (a or b) a. Intravenously b. Subcutaneously Question # 11 Adult dosage of IV epinephrine for treating a systemic anaphylaxis-like contrast reaction is: (a or b) a. 1 cc of 1:1,000 b. 1 cc of 1:10,000 Anticipate Potential Problems: Chemotoxic effects of contrast Anaphylaxis-like reactions CONTRAST-INDUCED NEPHROTOXICITY Gadolinium is not nephrotoxic if given in usual does for MR imaging, e.g. 0.1 mmol/kg. However, in larger doses, there is increased risk to the kidneys. GADOLINIUM, ADVANCED RENAL FAILURE, and SYSTEMIC TOXICITY Unresolved question of increased systemic toxicity to patients with advanced renal failure (e.g. GFR < 15cc/min) or on dialysis. Theory of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF): Free Gd triggers the process. Three dialysis treatments removes 99% of the gadolinium. Questions of Your Patient • Hemodialysis; advanced renal failure • Previous reaction to contrast * -obtain specifics • Asthma * • Allergies * * Allergic reactions are more likely when these patient factors exist. ACUTE, ANAPHYLACTIC-LIKE REACTIONS from iodinated LOCM Moderate, non-life-threatening: 0.2- 0.4% (1:250 injections) Severe, life-threatening: 0.04% (1:2500 injections) ACUTE, ANAPHYLACTIC-LIKE REACTIONS with gadolinium agents Very uncommon Mayo Clinic: epinephrine was needed to treat a serious reaction in 1:20,000 injections of a gadolinium agent. PREMEDICATION WHEN IS IT NECESSARY? History of a few scattered hives: No History of treatment for prior reaction: Yes PREMEDICATION Prednisone 50 mg, PO, q 6 h x 3 (e.g. 13, 7, 1 hr) Diphenhydramine 50 mg, PO 1 hour before contrast Greenberger and Patterson J Allergy Clin Immunol 87:867-872, 1991 PREMEDICATION Methylprednisolone (Medrol ®) 32 mg, PO, 12 and 2 hours before contrast Diphenhydramine 50 mg, PO 1 hour before contrast E. Lasser, et al N.Engl.J.Med 1987; 317:845-9 PREMEDICATION Corticosteroids: necessary to decrease risk of contrast reactions needing treatment Antihistamines: alone are not adequate PREMEDICATION Corticosteroids are essential Need minimum of 6 hours before contrast (preferably longer) ** Reduces risk but does not eliminate it Recognition & Treatment of Systemic Reactions Patient Presentations • Uncomfortable • Calm, poorly responsive to commands • Anxious, agitated Responding to a Possible Reaction • Quickly assess the situation • Call for help • Remove the patient from the MR suite (much of the emergency equipment is not MR- compatible) Responding to a Possible Reaction • Take their pulse • Talk with them Responding to a Possible Reaction • Taking their pulse: 1. Palpable: systolic is 80-90 mmHg 2. Rate: rapid or slow Responding to a Possible Reaction • Talking with the patient: 1. Assess for laryngeal edema 2. Assess degree of SOB 3. Assess responsiveness Uncomfortable • Skin reaction: Redness, itching, hives • Nausea & vomiting Uncomfortable • Skin reaction: Redness, itching, hives • Nausea & vomiting • Plan: observation (may be first signs of a more serious reaction) SERIOUS, LIFE-THREATENING REACTIONS RESPONDING TO A SERIOUS REACTION • Multiple tasks to accomplish 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • Airway / suction / oxygen Obtain pulse; I.V. access Leg elevation Provide medications Cardiac monitor / pulse oximeter Obtain Blood pressure Take “ownership” of a task Calm, Unresponsive • Hypotension • Hypoglycemia HYPOTENSION • With Tachycardia • With Bradycardia HYPOTENSION WITH TACHYCARDIA Treatment includes: • Leg elevation (approx. 60°) • Oxygen by mask ( 6-10 L/min ) • IV fluids (normal saline or Ringer’s lactate) HYPOTENSION WITH BRADYCARDIA Treatment includes: • Leg elevation (approx. 60°) • Oxygen by mask ( 6-10 L/min ) • IV fluids ( normal saline or Ringer’s solution) • Atropine IV VAGAL REACTION • Key finding = decreased pulse rate ATROPINE • Give if bradycardia is symptomatic • Recommended dose: • Adult IV dose range: 0.6-1.0 mg • My preference: 1.0 mg as initial dose Anxious, Agitated • HYPOXIA (lack of oxygen) ACUTE BRONCHOSPASM Recommended treatment: Beta-2 agonist inhaler (2 - 3 puffs) • Supplementary treatment: Epinephrine LARYNGEAL EDEMA Goals: Oxygenation Reduce edema of upper airway Treatment: Oxygen by mask Epinephrine, 1:10,000 IV EPINEPHRINE: Route of Administration With significant Hypotension – Use IV • If hypotension is not significant – can use I.M. or subcutaneous route Epinephrine for I.V. use EPINEPHRINE (Adrenalin) INTRAVENOUS: 1:10,000 (1 mg in 10 ml) 10 ml = 1000 mcg 1 ml = 100 mcg Start with 1 ml given slowly (deliver the 100 mcg over 2-5 minutes) EPINEPHRINE: Route of Administration • If hypotension is not significant – can use I.M. or subcutaneous route EPINEPHRINE (Adrenalin) SUBCUTANEOUS OR I.M. 1:1000 (1 mg in 1 ml) 1 ml = 1000 mcg 0.5 ml = 500 mcg 0.1 ml = 100 mcg Start with 0.1 or 0.2 ml ( * if not hypotensive ) EPINEPHRINE PROBLEMS: 1. Not giving it 2. Giving it too late 3. Giving too much 4. Giving it so that it is not absorbed effectively EPINEPHRINE Recommended initial I.V. Dose: 1 ml of 1:10,000 epinephrine (100 mcgm) given slowly over 2 – 5 minutes Additional amounts can be given if the patient does not respond adequately LARYNGEAL EDEMA Beta-2 agonist inhaler: may make edema worse Benadryl®: thickens secretions; may cause hypotension BENADRYL PEDIATRIC REACTIONS Children have good hearts If a problem develops, think AIRWAY RESUSCITATION Airway: – clear, suction – jaw lift – oral airway Ventilation: – mouth-valve-mask – bag-valve-mask (Ambu®) OXYGEN IS GOOD ! ( for all reactions ) OXYGEN Nasal cannula: 2 – 6 L/min provides only 25 – 40% concentration Simple mask: 6 – 10 L/min provides 35 – 60 % concentration (Flow rate at least 6 L/min to prevent carbon dioxide build-up in mask) OXYGEN • Via mask • High flow rate ( 6 – 10 L / min. ) RESPONDING TO A SERIOUS REACTION • Multiple tasks to accomplish 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • Airway / suction / oxygen Obtain pulse; I.V. access Leg elevation Provide medications Cardiac monitor / pulse oximeter Obtain Blood pressure Take “ownership” of a task QUIZ REVIEW Answer to Question # 1 A patient who has had a reaction to iodinated contrast is at higher risk for having a reaction to gadolinium agents. True or False ? (depending on the prior reaction, consider premedication for the gadolinium study) Answer to Question # 2 Your patient is cool, clammy, and has perspiration on their forehead and upper lip. The most likely reaction occurring is: 1. Vagal reaction 2. Urticaria 3. Bronchospasm Treatment: I.V. fluids + atropine Answer to Question # 3 Your patient complains of shortness of breath. The reaction most likely occurring is: 1. Vagal reaction with bradycardia 2. Urticaria 3. Bronchospasm Treatment: Beta-2 agonist inhaler; epinephrine Answer to Question # 4 Which of these IMMEDIATE actions by you during response to a major allergic-like systemic contrast reaction is the most important ? 1. 2. 3. 4. I.V. access Airway / suction / oxygen Cardiac monitor / pulse oximeter Blood pressure Answer to Question # 5 Which of these IMMEDIATE actions by you during response to a major allergic-like systemic contrast reaction is the least important ? 1. Talk to the patient 2. Take their pulse 3. Take their blood pressure. Answer to Question # 6 The treatment for severe hypotension and bradycardia is: (a, b, or c) a. IV fluids and atropine b. IV fluids and epinephrine c. Nitroglycerine Answer to Question # 7 The key finding for diagnosing a vagal reaction is: (a, b, c, or d) a. b. c. d. Rapidity of breathing Systolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure Pulse rate Answer to Question # 8 The adult dose of IV atropine for treating a vagal reaction is: (a, b, or c) a. 5-10 mg b. 1.0 mg c. 0.3 mg Answer to Question # 9 Initial treatment of laryngeal edema is: (a, b, c, or d) a. b. c. d. Atropine Benadryl® Beta-agonist inhaler Epinephrine Answer to Question # 10 Your patient is hypotensive; the most effective route for epinephrine administration is: (a or b) a. Intravenously b. Subcutaneously Answer to Question # 11 Adult dosage of IV epinephrine for treating a systemic anaphylaxis-like contrast reaction is: (a or b) a. 1 cc of 1:1,000 b. 1 cc of 1:10,000 THANK YOU