Texas Special Report - Midland Independent School District
advertisement

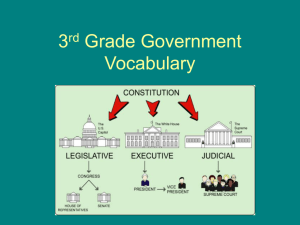
Texas Government Special Unit Constitutions-Texas • Texas has had 7 constitutions in its entire history as a state, country or territory. • 1824-Constitution of Coahuila y Tejaspolicies of Mexico, gave Texans few rights or powers. • 1836-Republic of Texas-included privileges for citizens; a league (4,400 acres) of free land for every Texas head of household. • Abolished debtor’s prison • Prohibited leaving entire inheritance to eldest son. Constitution-Texas • 1845-Texas admitted to the Union as a state-Constitution resembled those of southern states. • Made Austin the capital • Established structure and duties of state government • Allowed slavery • Did not grant women or minorities the right to vote Constitution-Texas • 1861-1865-Constitution under the Confederate States of America. • 1866-1869-military rule under Reconstruction. Military rule ended once Texas its Reconstruction Constitution. • 1869-1876-Reconstruction Constitution-placed considerable power in the hands of the governor. • Restricted rights for secessionists. • Governor controlled militia and most law enforcement. • Increased taxes, spent more money on education, public works and relief for the poor. Constitution-Texas • Constitution of 1876-set up as a reaction against strong governorship during Reconstruction. • Prevents any one branch of government from becoming too strong • Reduced the salaries of elected officials • Shortened terms of office. • Restricted state spending • Drastically limited power of governor making him a weak executive. Constitution of 1876 • Gave more power to local governments and citizens • Included a Bill of Rights (29 total-The Constitution has 17 articles). • 3 Branches of government with restricted powers and duties. • By the year of 2009 (81st session), The Texas Constitution had a total of 467 amendments. The Texas Legislature • Feature • • • • • • • • House Senate Size 150 31 Term 2 years 4 years Committees 40 15 Debate Limits 10 minutes none Calendars 4 2 Officer selection-House elects representatives from single-member districts, then fellow representatives elect Speaker of the House Senate-Lt. Governor is elected statewide and serves same role that V.P does in the U.S. Senate (TODAY THE TEXAS LEGISLATURE IS IN ITS 82nd SESSION-ENDS MAY 30, 2011) Texas Elected Officials- Governor-Rick Perry Lt. Governor-David Dewhurst • http://www.senate.state.tx .us/ Speaker of the Texas House-Joe Strauss • http://www.house.stat e.tx.us/ Midland State Congressmen Representative-District 82-Tom Craddick State Senator District 31Kel Seliger Qualifications for Texas Public Office • Governor-30 years old, U.S. Citizen, 5 years resident in Texas. • Lt. Governor-same as Governor. • Senate-26 years old, qualified Texas voter, resident of senatorial district 2 years. • House-21 years old, qualified Texas voter, resident of district 1 year. Pay Rates For Texas Elected Officials • Governor-$115,345+use of the Governor’s Mansion(burned down during Perry Administration). • Lieutenant Governor-$7,200 • Representatives-$7,200 • Senators-$7,200 • The average salary for a congressman in the 9 other largest states- $61,000 How a Bill Becomes a Law in TexasSENATE • Step1-Bill is introduced, numbered, given first reading, referred to committee. • Step 2-Committee holds hearings, deliberates, and either pigeonholes the bill, reports it unfavorably, or reports it favorably. Favorable report may include amendments or be a substitute bill. Committee report is printed and distributed to Senate. • Step 3-Senate has second reading, holds debate, amends bill, possibly has a filibuster. Senate then has third reading, debate, amendments only by two thirds vote. Passed bill is sent to House.(Record filibuster1977-Senator Bill Meier-43 hours straight-WORLD RECORD) How a Bill Becomes a Law in Texas-HOUSE • Step 1-House has first reading, and bill is referred to committee. • Step 2-Committee action is the same as in Senate. • Step 3-Floor action is similar to Senate except that no filibuster is possible and scheduling for debate is more complex. Amended bill is returned to Senate. How a Bill Becomes a Law in TexasSENATE AND HOUSE • Step 4-Conference Committee irons out differences in House and Senate versions of the bill. Both houses vote on conference compromise bill. Clean copy of the conference bill is prepared. Bill is enrolled and certified in both houses, and sent to the governor. How a Bill Becomes a Law in TexasGovernor • Step 5-Governor may sign the act, let it become law without his or her signature or veto it. The Texas Judiciary • Judicial Branch • Attorney General-independently elected executive has two important functions within the judiciary. • Chief lawyer-represents state agencies that sue a private individual or another agency when they are sued. • Represents the state in Federal Court. • He also issues advisory opinions-advises legislature and governor on constitutionality of laws and actions of government. • Child support enforcement. Attorney General Greg Abbott State Supreme Court • Hears only civil cases. • 9 Justices elected to 6 year terms. • Qualifications-10 years legal experience either as a practicing attorney or as a judge of a court of record. • Pay-$150,000. • Has jurisdiction on appeals from courts of appeal • Spends much time considering applications for writs of error. • Writs of mandamus-orders to corporations or persons including state officials to perform certain acts. Court of Criminal Appeals • • • • • Appointed by Governor Considers writs of error Writs of habeas corpus Can overturn convictions Qualifications and pay are the same as the Supreme Court. The Court of Appeals • • • • • • • • Elected by districtsMulti judge courts that operate without juries. Consider only the written records of lower courts 14 courts of appeal Qualifications same as Supreme Court. Pay-$137,500 Associate Justice $140,000 for Chief Justice Jurisdiction-civil-appeals from county, district and of criminal cases except capital. State Trial Courts-District Courts • Principal Trial Court • Over 400 District Courts in Texas. • Has both Criminal and Civil Jurisdiction except in metropolitan areas.(Big cities have courts that specialize) • Felony jurisdiction, divorce, suits over titles to land, election contests, civil suits over $200. Shares some civil jurisdiction with county court. • Salary-$125,000 • 4 year term • Qualifications-attorney-licensed to practice law in Texas, 4 years experience as lawyer or judge in Texas. State Trial Courts-District Courts continued • At least one court in each county must be designated as juvenile court to handle criminal cases with defendants younger than 17. These courts can be district, county or constitutional county courts. • http://www.co.midland.tx.us/dcourts/ County Courts • • • • Elected-4 year term. Pay-ranging from $10,000 to $100,000. Have both original and appellate jurisdiction. Criminal misdemeanor cases where fine exceeds $500 or jail time may be imposed. • Also hear appeals in criminal cases from JP courts. • In civil matters have concurrent with JP courts when amount in controversy is between $200 and $5000. • http://www.co.midland.tx.us/ccl/ Justice Courts (JP) • • • • • • • • Elected Both criminal and civil jurisdiction. Misdemeanor cases with fine as punishment. Civil cases of $200 or less and concurrent jurisdiction with county and district courts in cases between $200 and $5000. Presides over small claims court, act as notary public, authorized to perform marriages. May function as coroner unless county has a medical examiner. No Constitutional or statutory qualifications Pay ranges from virtually nothing to $60,000. • http://www.co.midland.tx.us/jp/ J.P Precincts-Midland • Voting Nov 2010.pdf Municipal Courts • Handle minor criminal matters-Class C misdemeanors, fine less than $500 with no possibility of imprisonment. • Exclusive jurisdiction over municipal ordinances and can impose fines up to $2500. • No civil jurisdiction. • Most cities appoint municipal judges, however some cities do use non-partisan elections. • Term 2 years. Courts Continued • Grand Juries-chosen from a list prepared by commissioners. Judge selects 12 people who sit for a term of 3 months. • Trial Juries • Lower courts-jury consists of 6 people. • District courts-12 • Call to duty on a trial jury is determined through the use of a jury wheel list generated from the county voter registration, driver’s license and state identification lists. Crime and Punishment in Texas Capital Offenses-Possibility of Life in Prison without parole or Capital Punishment • • • • The following crimes are Capital Murder in Texas: murder of a public safety officer or firefighter; murder during the commission of kidnapping, burglary, robbery, aggravated sexual assault, arson, or obstruction or retaliation; murder for remuneration; (hire) murder during prison escape; murder of a correctional employee; murder by a state prison inmate who is serving a life sentence for any of five offenses (murder, capital murder, aggravated kidnapping, aggravated sexual assault, or aggravated robbery); multiple murders; • murder of an individual under six years of age. • • • • First Degree Felonies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Confinement for life or from five to ninety-nine years and a possible fine not to exceed $10,000 Possibility of community supervision Examples: Aggravated assault of public servant Aggravated kidnapping Aggravated robbery Aggravated sexual assault Attempted capital murder Arson of habitation Burglary of a habitation with intent to commit or commission of a felony Causing serious bodily injury to child, senior citizen, or disabled person Escape from custody (if serious bodily injury occurs) Murder Solicitation of capital murder Trafficking of persons under the age of fourteen Second Degree Felonies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Two to twenty years in prison and possible fine not exceed $10,000 Possibility of community supervision Examples: Aggravated assault Arson Bigamy Bribery Evading arrest (and death of another occurs) Improper relationship between educator and student Indecent contact with a child Intoxication manslaughter Manslaughter Online solicitation of a minor under fourteen Possession of fifty to 2000 pounds of marijuana Robbery Sexual assault Stalking—second offense Trafficking of persons Third Degree Felonies • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Two to ten years in prison and possible fine not to exceed $10,000 Possibility of community supervision Examples: Aggravated perjury Bail jumping of a felony arrest Deadly conduct with a firearm Escape from felony custody Indecent exposure to a child Intoxication assault Possession of a firearm by a felon Retaliation Stalking DWI (third offense) Tampering with evidence Violation of protective order (third offense) State Jail Felonies • • • • 180 days to two years in a state jail and possible fine not to exceed $10,000 Possibility of community supervision Possibility of punishment as Class A misdemeanor Examples: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Burglary of a building Coercing a minor to join a gang by threatening violence Credit card abuse Criminally negligent homicide Criminal nonsupport Cruelty to animals DWI with child passenger Evading arrest in a vehicle False alarm or report Forgery of a check Fraudulent use or possession of identifying information Improper photography or visual recording Interference of child custody Possession of less than one gram of a controlled substance Theft of something valued between $1500 and $20,000 Unauthorized use of a vehicle Class A Misdemeanors • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Up to one year in the county jail and/or a fine not to exceed $4000. Up to two years of community supervision or three years with an extension Examples: Assault with bodily injury Bail jumping of misdemeanor offense Burglary of coin operated machine Burglary of a vehicle Cruelty to animals DWI (2nd offense) Escape from misdemeanor custody Evading arrest on foot Interference with 911 call Obscenity Perjury Possession of two to four ounces of marijuana Promoting gambling Public lewdness Resisting arrest Stealing check Unlawfully carrying a weapon Class B Misdemeanors • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Up to 180 days in the county jail and/or fine not to exceed $2000 Up to two years of community supervision or three years with an extension Examples: Criminal Trespass DWI False report to police officer Fraudulent degree Harassment Indecent exposure Possession of 2 ounces or less of marijuana Prostitution Riot Silent Calls to 911 Terroristic threat Class C Misdemeanors • • • • • • • • • • • Fine not to exceed $500 Examples: Assault by threat Disorderly conduct Gambling Issuance of bad check Leaving child in a vehicle Minor in possession of alcohol Possession of alcoholic beverage in motor vehicle Public intoxication Use of Laser pointers City Government- Texas City/Local Governance • Council-Manager Form-Majority of Texas cities use this format. A city council of 5 to 15 members is elected atlarge or by district, and in turn appoints a city manager who is responsible for the hiring and firing of department heads and for the preparation of the budget. • A mayor elected at large or by council is a member of the council and presides over it but otherwise has only the same powers as any other council member. • City manager is head of the council and does all of the hiring and firing of city department employees. • System is designed to separate politics from administration. • Examples-Dallas, San Antonio, Midland 2010 Midland City Council • Top left) Jerry Morales At-Large, Michael Trost District Four, John James District Three, Jeff Sparks District One, (Bottom left) Vicky Hailey District Two, Mayor Wes Perry, Scott Dufford At-Large. City Manager • Courtney Sharp City Manager Mayor of Midland Wes Perry Mayor Council Form • Council members are elected at large or by geographic districts and the mayor is elected at large (city-wide) • Weak Mayor-Council Form-city attorney and treasurer are elected. • Strong Mayor-Council Format-mayor has power to appoint and remove city executives. • Prepares budget, subject to council approval. • Mayor can veto acts of council, but in a weak form fewer votes are needed to override. City Governance • Mayor-Manager Form-city manager reports only to the mayor not the council as a whole and focuses on fiscal/administrative policy and implementation. • Commission Form-originated in Galveston following devastating hurricane of 1900 in which 7200 died. • Elected commissioners collectively compose the policymaking board and as individuals are administrators of various departments. • Elected at large. Midland City Officials • • • • • • • • • • • • City Department Director City Manager Courtney Sharp City Attorney Keith Stretcher City Secretary Amy M. Turner Chief of Police Price Robinson Fire Chief Robert Isbell Finance Director Robert McNaughton Community Services Director Tina Jauz Director of Airports Marv Esterly Director of Utilities Stuart Purvis Director of General Services Robert Patrick Director of Development Services Rick Crownover