Governing Italy
advertisement

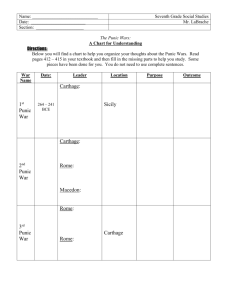
Governing Italy • Conquered subjects = allies of Rome (The Roman Confederation) – Why? • Conquered subjects’ rights and requirements – POSITIVES: • • • • Limited taxation or no taxation Internal government Crossculturalism and intermarriage Potential for citizenship? – NEGATIVES • Military/political alliances with other states? • Military service to Rome Foreshadowing the 2nd Punic War: Carthage on the Rise • Hamilcar Barca and Hannibal – Military strategy • "Hannibal, then about 9 years old, was childishly teasing his father to take him to Spain with him. His father still angry at the loss to Rome led him to the altar and made him swear to be the enemy of Rome as soon as he was able.” -Livy • Resubjugation of Spain (238 – 219 B.C.E.) • The Barcid dynasty established – intermarriages • Hamilcar dies (229 B.C.E.) • Hannibal prepares for his Roman conquest (219 B.C.E.) Hannibal’s War Strategy • Navy? • Sicilian invasion? • Army? • Crossing the Alps??? – Why? The Second Punic War (218 – 201 B.C.e.) • Hannibal in Italy – The Battle of Trebia (218 B.C.E.) – The Battle of Lake Trasimene (217 B.C.E.) – The Battle of Cannae (216 B.C.E.) • Hannibal’s problems: – – – – Reinforcements? Local support? Supplies? Naval ports? Rome on the Offensive • First Macedonian War (214 B.C.E.) – Philip V (Antigonid Emperor = ally of Carthage) • Invasion of Hispania (Spain) – The Scipio brothers (and son) – Publius Scipio and Scipio Calvus die (211 B.C.E.) – Scipio Africanus (son and nephew) takes control for revenge (210 B.C.E.) • Hasdrubal Barca in Spain – Loses to Scipio Africanus (208 B.C.E.) – Abandons Spain and heads to Italy with reinforcements – Hasdrubal loses and dies at the Battle of the Metaurus River (207 B.C.E.) Scipio Africanus • P. Cornelius Scipio = Scipio the Elder = Scipio Africanus • Battle of Ilipa (206 B.C.E.) – Acquires Spain • • • • Consul of Rome (205 B.C.E.) Joins the war effort in Africa (203 B.C.E.) Attempted peace talk with Hannibal (202 B.C.E.) Battle of Zama (202 B.C.E.) – Elephants fail for Hannibal • Peace Treaty (201 B.C.E.) – Rome gains control of the W. Mediterranean Sea Conquest of the Mediterranean • Conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (SPAIN/PORTUGAL) – 197 – 133 B.C.E. • Cynoscephalae (197 B.C.E.) – Rome vs. Antigonid Empire – Rome acquires Greek allies (Aetolian League) – Rome leaves Greece (196 B.C.E.) – significance? – Battle of Pydna (168 B.C.E.) – Rome controls Greece • End of Antigonid dynasty • So what does Rome control now? • Rome controls the Mediterranean Sea – Superior to the Ptolemaic and Seleucid empires too! The Third Punic War 149 – 146 B.C.E. • Carthaginian growth of military Roman distrust • Siege of Carthage (149 – 146 B.C.E.) • Battle of Carthage (146 B.C.E.) – Scipio Aemilianus enters • End result of the Third Punic War: – Destruction of the city of Carthage – Annexation of all Carthaginian lands – Death/enslavement of all Carthaginians The Carthaginian empire (3rd Century B.C.E.) Conflict begins with Carthage • • • • • • Empire Tunisia Sea trade and commerce Naval power Sicily Hiero II of Syracuse, the tyrant – Messana asks for help (264 B.C.E.) • If Carthage helps surround Rome • If Rome wins gain power in Med. Sea • What will Rome do? • Syracuse makes peace (262 B.C.E.) – What’s wrong now? At The Start Of THE FIrst Punic War The First Punic War (264 – 241 B.C.E.) • Roman naval fleet is formed (264 – 260 B.C.E.) – Land battles on water? • Corvus • Hamilcar Barca, Carthaginian general • Blockades and Sieges • Invasion of Carthage (256 B.C.E.) – Storms, invasions, etc. • Roman navy wins (241 B.C.E.) – Rome gets Sicily – Corsica and Sardinia will be captured