Introduction to WIMAX broadband Technology
advertisement

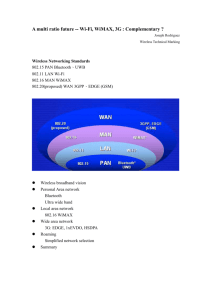
Authentication model for security aspect in Wimax Broadband technology Abstract In this proposal, I work on Wimax Broadband technology and its security aspect. In this authentication model and tracking mechanism is considered for rightful use of this communication. I will be discussing about some of basic architecture used in building wimax Broadband technology. I also take further review of various authentication procedures done by various authors and put forward some of methodologies and techniques by developing a model using MATLAB SIMULINK. In the proposal I try to make up simulink model for tracking and monitoring of IP from external hackers. Introduction to WIMAX broadband Technology Wimax stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. Wimax technology Enables ubiquitous delivery of wireless broadband service for fixed and/or mobile users, and became a reality in 2006 when Korea Telecom started the deployment of a 2.3 GHz version of mobile WiMAX service called WiBRO in the Seoul metropolitan area to offer high performance for data and video. In a recent market forecast published in April 2008, WiMAX Forum Subscriber and User Forecast (Cotanis, 2000) Study, the WiMAX Forum projects a rather aggressive forecast of more than 133 million WiMAX users globally by 2012 (WiMAX Forum, 2008c). The WiMAX Forum also claims that there are more Than 250 trials and deployments worldwide. Its air interface specifications consist of four related IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Standards, that is, IEEE Standard 802.16-2004, IEEE Standard 802.16-2004/Cor.1-2005, IEEE Standard 802.16e- 2005 and the IEEE Draft Standard P802.16-2004/Cor.2. Not all of the optional features defined in these IEEE Standards are implemented in WiMAX products and tested for certifications. Through extensive technical investigation analysis to build up the best competitive products, the WiMAX Forum Technical Working Group (TWG) published the first version of mobile WiMAX System Profile Release 1 In early 2006 (WiMAX Forum, 2007). 1 Recognizing the importance of security, the 802.16 working groups designed several mechanisms to Protect service provider from theft of service, and to protect customer from unauthorized information disclosure. The standard includes state-of-the-art methods for ensuring user data privacy, and preventing unauthorized access, with additional protocol optimization for mobility. A privacy sub layer within the Wi.MAX MAC handles security. WiMAX provides a flexible means for 1 White paper. (2007). “A comparative Analysis of Mobile WiMAX. WiMAX Forum . authenticating subscriber stations and users to prevent unauthorized use. The authentication framework is based on the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) EAP, which supports a variety of credentials, such as username/password, digital certificates, and smart cards. WiMAX terminal devices come with built-in X.509 digital certificates that contain their public key and MAC address. WiMAX operators can use the certificates for device authentication and use a username/password or smart card authentication on top of it for user authentication Aim The main aim of this proposal is to implement authentication process module, and tracking and monitoring of IP protocol details through Matlab Simulink Model. Objectives: The main objective include for taking up this proposal is given below 1) To discuss complete architecture of Wimax Broadband Technology 2) Discussing some persistent security loopholes in Wimax Internet Communication. 3) Using MATLAB SIMULINK model to showcase how security control can be enabled for this loopholes 4) Developing an ip tracking tool for checking misuse of account holder’s privacy and other benefits. 4. Literature Review Broadband is a generic term used to describe high-speed networking services, that is a set of digital communication technologies with the capacity to transmit significant amounts of data at a high rate, Supporting the delivery of a range of digital services some or all of which can occur simultaneously. It is usually a symmetrical service allowing fast in and outbound data capacity. Whilst there is still no universally accepted definition of the term ‘broadband’, it is generally agreed that it applies to services considerably faster than Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or conventional dial-up lines (Becta, 2003; OECD, 2003). 2 2 inglong Zhou, M. J. (2009). A Novel Link Quality Assessment Method for Mobile Multi-Rate Multi-Hop Wireless Networks. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Computer Science . Today, the telecommunication industry is undergoing two important developments with implications on future architectural solutions. These are the irreversible move towards IP-based networking and the deployment of broadband access in the form of diverse Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) technologies based on optical fiber and high capacity cable but also the WiMAX access (IEEE 802.16 Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) (wimax forum,2007). Overlay networks have recently emerged as a viable solution to the problem of content distribution with multicasting and QoS facilities. Overlay networks are networks operating on the interdomain level, where the edge hosts learn of each other and, based on knowledge of underlying network performance, they form loosely coupled neighboring relationships. These relationships are used to induce a specific graph, where nodes are representing hosts and edges are representing neighboring relationships. Graph abstraction and the associated graph theory can be further used to formulate routing algorithms on overlay networks (popescu, 2005). Review of Wimax Application Wimax is not the only solution for delivering broadband wireless services. Several proprietary solutions are already in the market. At the same coin, wireless networks represent an important example of such scenarios where capturing and forging packets is relatively easy; attacks against such networked system are becoming more complex and powerful. Thus, security is essential in wireless technologies to allow rapid adoption and enhance their maturity, while designing the standard, the IEEE 802.16 working group has taken into consideration the security aspects to avoid mistakes of IEEE 802.11. Standard security specifications can mainly be found within the MAC layer which is called security sub layer. 3 The security sub layer lies above the physical layer and below the MAC CPS, which is encrypted, authenticated and validated. However, header and control information added by the physical layer are not encrypted or authenticated. Thus physical layer information attached to the higher layer packets is vulnerable to analysis. 3 Guruprasad, B. W. (2002). Lowering the Barrier to Wireless and Mobile Experimentation. Computer Communications Review . Designed by the IEEE 802.16 committee, WiMAX was developed after the security failures that plagued early IEEE 802.11 networks. Recognizing the importance of security, the 802.16 working groups designed several mechanisms to protect the service provider from theft of service, and to protect the customer from unauthorized information disclosure. The standard includes state-of-the-art methods for ensuring user data privacy and preventing unauthorized access, with additional protocol optimization for mobility. A privacy sub layer within the WiMAX MAC handles security. In this proposal, we try to discuss issues pertaining to various authentication processes and how to build a model using MATLAB simulink and also develop a tracing module which can record theft of account usage in internet usage. It also find out, where it getting accessed. Support for privacy: User data is encrypted using cryptographic schemes of proven robustness to provide privacy. Both AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and 3DES (Triple Data Encryption St inward) are supported. Most system implementations will likely use AES, as it is the new encryption In our thesis work we have implemented a Wimax transmitter & receiver using MATLAB. Here we also connect a control system and a sensor to our transmitter for security purpose. Here is the whole scenario of simulation overview. By using this architectural used in research, we would develop another authentication model based on this simulation figure given below. Figure 1: Example simulink architecture for authentication model (Amin, 2008) SIMULINK implementation: Our SIMULINK has 4 major parts. They are: Security Transmitter Channel Receiver Security For our home security purpose we have used here: Sensor Control Unit Deliverables: By doing this proposal, I can able to know what are the futuristic roadblocks for wimax broadband technology, and aspects of previous methodologies proposed by various authors. Taking of analysis of each process of authentication and knowing few loopholes in communication through this. For this, I develop up a model using MATLAB SIMULINK and also use a model for tracking and monitoring interference which break security architecture of Wimax. From proposal, we can able to conclude that, issues on security for wimax technology can be addressed. Mainly; we address security aspect in respect authentication of user and tracking the theft done by another individual and monitoring it. As in broadband there is no limit of whose subscriber is, any individual with laptop enabled with pcmci card can used the internet. The main proposed work is making authentication of these wimax connection through MAC address and trying to track if other person trying to interfere and use the service. In this proposal, we build up a model using mat lab simulink for authentication and tracking ip configuration. Works Cited Amin, A. A. (2008). Study of WiMAX Simulation. Department of Computer Science and Engineering . Anon. (2007). Broadband Technology. Retrieved 06 20, 2010, from Wikipedia. Cotanis, N. D. (2000). Estimating Radio Coverage for New Mobile Wireless Services Data Collection and Pre-processing. IEEE paper . D. Couto, D. A. (2005). “A high-throughput path metric for multi-hop wireless routing,”. Wireless Networks . Hasan, M. A. (2007). Performance Evaluation of WiMAX/IEEE 802.16 OFDM Physical Layer. HELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY . Roca, A. (2007). Implementation of a WiMAX simulator in Simulink. Diplom-Ingenieurs unter Leitung von . The Matlab help: Communications Blockset. (2007). Retrieved 2010, from Communications Blockset: http://www.mathworks.com White paper. (2007). “A comparative Analysis of Mobile WiMAX. WiMAX Forum . Wicker, S. B. (1995). Error Control Systems for Digital Communication and Storage. School of Electrical and Computer Engineering . Milestones 1) What you have achieved? As per the project, my work on this project gave me a whole new perspective of Broadband technology and its working. I got study and know, major hurdles in authentication procedures and communication through various addressing protocol. I was able to analyze work of Wimax connectivity model and was able to build model to track interference and trace the ip. I got know various work related issue and practically worked on it. What if an obstacle does at a point of wave propagation? 2) What has gone to plan? In knowing the facts for this work, I have gone through various studies and methodologies of wimax Broadband technology .I analyzed various authentication procedures and models developed by authors. I developed a security model which can overcome future security authentication attacks and monitor ip and track interference of ip by other source. I built up a simulink model using MATLAB, which can make out better authentication and tracking mechanism. 3) What you have to change? From my aspect, I had to work on some basic technical authentication procedures, worked on it empirically and designed a model. It was able to reduce the hindrance scale. I used Matlab tool in knowing better performance analysis. 3) Mostly, the project was more of practical work on authentication procedures. It made me to further research in making better and safe connectivity.