Art History - San Pasqual Valley Unified School District
advertisement
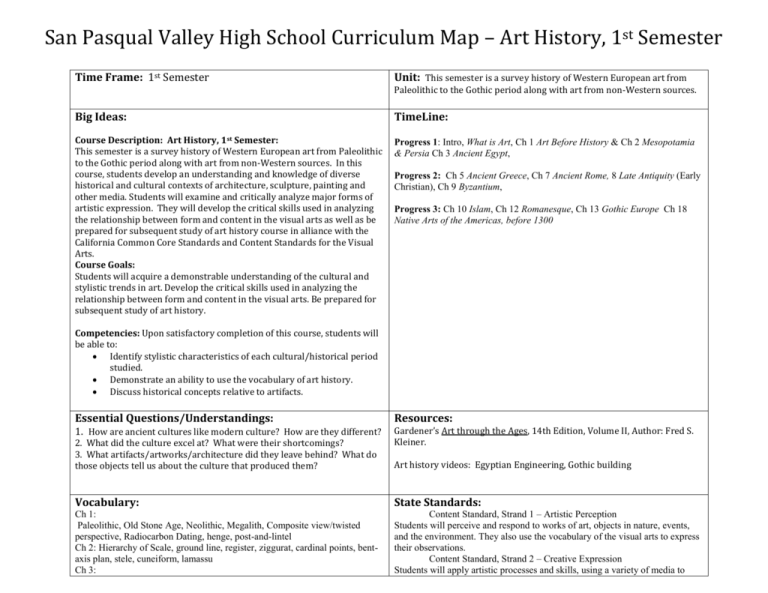
San Pasqual Valley High School Curriculum Map – Art History, 1st Semester Time Frame: 1st Semester Unit: This semester is a survey history of Western European art from Big Ideas: TimeLine: Course Description: Art History, 1st Semester: This semester is a survey history of Western European art from Paleolithic to the Gothic period along with art from non-Western sources. In this course, students develop an understanding and knowledge of diverse historical and cultural contexts of architecture, sculpture, painting and other media. Students will examine and critically analyze major forms of artistic expression. They will develop the critical skills used in analyzing the relationship between form and content in the visual arts as well as be prepared for subsequent study of art history course in alliance with the California Common Core Standards and Content Standards for the Visual Arts. Course Goals: Students will acquire a demonstrable understanding of the cultural and stylistic trends in art. Develop the critical skills used in analyzing the relationship between form and content in the visual arts. Be prepared for subsequent study of art history. Progress 1: Intro, What is Art, Ch 1 Art Before History & Ch 2 Mesopotamia & Persia Ch 3 Ancient Egypt, Paleolithic to the Gothic period along with art from non-Western sources. Progress 2: Ch 5 Ancient Greece, Ch 7 Ancient Rome, 8 Late Antiquity (Early Christian), Ch 9 Byzantium, Progress 3: Ch 10 Islam, Ch 12 Romanesque, Ch 13 Gothic Europe Ch 18 Native Arts of the Americas, before 1300 Competencies: Upon satisfactory completion of this course, students will be able to: Identify stylistic characteristics of each cultural/historical period studied. Demonstrate an ability to use the vocabulary of art history. Discuss historical concepts relative to artifacts. Essential Questions/Understandings: Resources: 2. What did the culture excel at? What were their shortcomings? 3. What artifacts/artworks/architecture did they leave behind? What do those objects tell us about the culture that produced them? Art history videos: Egyptian Engineering, Gothic building 1. How are ancient cultures like modern culture? How are they different? Gardener’s Art through the Ages, 14th Edition, Volume II, Author: Fred S. Kleiner. Vocabulary: State Standards: Ch 1: Paleolithic, Old Stone Age, Neolithic, Megalith, Composite view/twisted perspective, Radiocarbon Dating, henge, post-and-lintel Ch 2: Hierarchy of Scale, ground line, register, ziggurat, cardinal points, bentaxis plan, stele, cuneiform, lamassu Ch 3: Content Standard, Strand 1 – Artistic Perception Students will perceive and respond to works of art, objects in nature, events, and the environment. They also use the vocabulary of the visual arts to express their observations. Content Standard, Strand 2 – Creative Expression Students will apply artistic processes and skills, using a variety of media to Palettes, Pharaohs, papyrus, mummification, engaged columns, mastaba, Sphinx, High relief, rock cut tomb, hypostyle, clerestory, column, shaft, capital, pylon temple, Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom, Armarna Period Ch 5: Pediment, Krater, Geometric, Amphora, Archaic, Classical, Hellenistic, Kore, Kouros, Cornice, Trigylph, Metope, capital, Stylobate, Entablature, Volute, Base, Frieze, Cella, Pronaos, Caryatids, Basilica, Contrapposto, Peristyle, Peripteral, Ch 7: Barrel Vault, Groin Vault, Fenestrated Groin Vault, Hemispherical Dome, Veristic, Domus, Atrium, Cubiculum, Peristyle, Tablinium, Triclinium, Pompeian Fresco Painting: First Style, Second Style, Third Style, Fourth Style, Aqueduct, Triumphal Arch, Equestrian Statue, apse, oculus, insula, Ch 8: Catacomb, Nave, Transept, Apse, Transept, Central Plan, Atrium, narthex, codex, diptych, illuminated manuscript, parchment, vellum Ch 9: mosaic, Theokotos, Pantocrater, Triptych, Pendentive, Squinch Ch 10: caliph, hejira, iman, Muhammad, iwan, minaret, minbar, mirhab, quiblah wall, squinch, Koran, ewer, Kufic, Calligraphy, Ch 12: Ambulatory, barrel vault, bay, buttress, campanile, compound pier, groin vault, alternating support system, choir, compound pier, crossing, engaged columns, radiating chapel, transverse arch, tribune, rib vault, sexpartite vaults, three story elevation, quadrant arch, Ch 13: flying buttress, clerestory, nave arcade, pinnicle or finial, triforum, vaults, fan vault, ogee arch, Ch 18: Quetzacoatl, lost wax process, backstrap loom, staff god, effigy mound, gorget, kiva, communicate meaning and intent in original works of art. Content Standard, Strand 3 – Historical & Cultural Context Students will analyze the role and development of the visual arts in past and present cultures throughout the world, noting human diversity as it relates to the visual arts and artists. Content Standard, Strand 4 – Aesthetic Valuing Students will analyze, assess, and derive meaning from works of art, including their own, according to the elements of art, the principles of design, and aesthetic qualities. Content Standard, Strand 5 – Connections, Relationships, Applications Students will apply what they learn in the visual arts across subject areas. They develop competencies and creative skills in problem solving, communication, and management of time and resources that contribute to lifelong learning and career skills. They also learn about careers in and related to the visual arts. Assessment Instructional Methods/ Evaluation Procedures: Students will be engaged in note taking, class and group discussion, group work, guided practice, writing activities, studio assignments, oral and written assessments and educational games & activities. Class-work/Worksheets/Group-work Composition/Writing, formal and informal Participation/Citizenship Tests Mid Term Exam Final Exam 20% 20% 30% 20% 5% 5%