if that is interrupted, the entire circuit won't work
advertisement
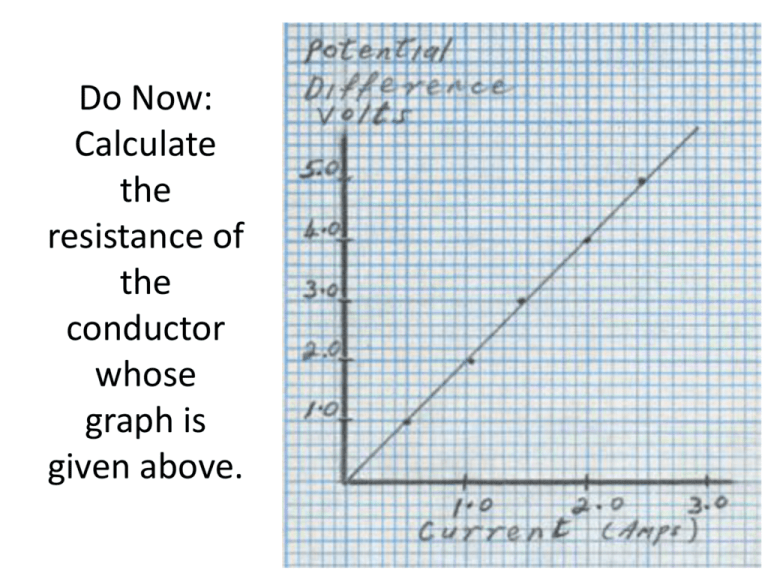
Do Now: Calculate the resistance of the conductor whose graph is given above. Power & Energy in Electric Circuits Series Circuits Power in Electric Circuits • Rate at which energy is supplied to circuit P = VI Example: • Calculate the rate at which energy is supplied by a 120-volt source to a circuit if the current in the circuit is 5.5 amperes. P = VI P= 2 V R V I= R Energy (W) E = VIt 2 E=I Rt E=Pt V2t E= R Example: • How much energy is produced by a 50-volt source that generates a current of 5.0 amperes for 2.0 minutes? Example: • An immersion heater has a resistance of 5.0 ohms while drawing a current of 3.0 amperes. How much electrical energy is delivered to the heater during 200. seconds of operation? • An operating 100.-watt lamp is connected to a 120-volt outlet. What is the total electrical energy used by the lamp in 60. seconds? SERIES CIRCUIT • Only ONE current path if that is interrupted, the entire circuit won’t work. SERIES CIRCUIT • Since only one path, current throughout the circuit is constant I = I1 = I2 = I3 = … SERIES CIRCUIT • Potential difference (V) across 2 points depends on the work needed to get between those 2 points V drops across each resistor (not constant) V = V1 + V2 + V3 +… SERIES CIRCUIT • Ohm’s law holds for each resistance V = IR SERIES CIRCUIT • Req = equivalent resistance of the system Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + … SERIES CIRCUIT We can find: Req = I= VR1= VR2= VR3= SERIES CIRCUIT Req = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 kΩ I = V/R = 1 mA VR1= IR1 = 3 V VR2= IR2 = 4 V VR3= IR3 = 5 V Find: Req, I, VR1, VR2, VR3, VR4, VR5 Page 650: 1-6 Complete each problem AND draw the circuit described in each question (except #6, no drawing necessary) EXIT QUIZ The accompanying circuit diagram represents four resistors connected to a 12-volt source. 1. What is the Req for this circuit? 2. What is the total current in the circuit? 3. What is the voltage across R1?