Chapter 16 Electricity

Integrated Science I
• Electrical conductors – a material that allows electrons to flow easily through it
• Ex) gold, silver, copper, etc.
• Electrical insulators – a material that does not allow electrons to flow easily through it
• Ex) plastic, rubber, wood, etc.
• A complete conducting loop is needed for an electrical circuit to work correctly.
There are 2 types of circuits:
• Parallel – each device is placed in its own separate branch.
• Series – a device placed in a single loop
• An electric circuit is a path in which electrons from a voltage or current source flow
• Voltage or current source could be a battery
• Flow freely in conductors
• Do not flow freely in insulators
• Electric current flows in a closed path called an electric circuit and only flows in one direction
• Household circuits are wired in parallel.
• Why?
• Single power source supplying all lights and appliances with the same voltage
• If one of the lights burns out, current can still flow through the rest of the house
• Christmas tree lights are typically wired in series
• This is why your whole strand goes out
Series Circuit Parallel Circuit
• For protection, household circuits contain:
• Circuit Breakers
• Contains a piece of metal that bends when it gets hot
• Fuses
• Contains a small piece of metal that melts if the current becomes too high
• When it melts, it causes a break in the circuit, stopping the flow of current
• To fix, you must replace the blown fuse with a new one
•
Electric current – is the rate at which positive
charge flows in a circuit
• It measures how fast the electrons are moving in the circuit
• Flows from high to low (think of it like water pressure)
• Measured in amperes (A)
• Equals 1 coulomb of charge per second (C/s)
• A resistor opposes the rate of charge flow in the circuit
• They are not a bad thing!
• Ex) Light bulb, toaster, ANYTHING that takes electricity to run
• Resistance is a measure of "how hard" it is to "push" electricity through a circuit
• Unit of resistance is the ohm ( Ω )
• If we increase the resistance, the voltage goes down
• Because electrons cannot flow as easily
• If we decrease the resistance, the voltage goes up
• Because electrons can flow easily
• Batteries are energy sources and resistors are energy stoppers in circuits
• Electrical Power – the rate at which electrical energy is converted to another form of energy
• SI Unit: Watt (W)
• Term for 1,000 units = kilowatt (kW)
In this example, electrical power is converted to light energy in the light bulb.
The light bulb acts as a resistor
• A chemical reaction that separates positive and negative sides of the battery
• The separation is what causes the electrons to flow in the circuit
• Electrons then transfer energy to other objects and transform electrical energy into other forms:
• Light
• Sound
• Heat
• Current continues to flow, even after the electrons transfer their energy
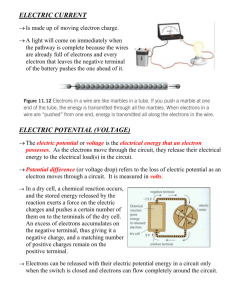
• V = Volt
• Definition: The SI unit of electromotive force, the difference of potential that would drive one ampere of current against one ohm resistance
• Voltage is also known as potential difference
• Measured with a voltage meter
• The voltage difference between the two holes in a wall socket is typically 120 volts
• Q: If electrons are never “used up” in a circuit, why do batteries go dead?
• A: Batteries go dead because the electrons are converted in resistors to other types of energy (light, sound, heat, etc.)
• Q: Do batteries supply all of the electrons in a circuit?
• A: NO! Electrons are in all of the circuit. The battery provides the “push” for the electrons
• Important SI Units:
• Current = amperes (A)
• Voltage = volts (V)
• Resistance = ohms ( Ω )
• Types of Circuits:
• Series = 1 continuous loop
• Parallel = branches
• Power source supplies the electrons in the circuit:
• Resistors then transform electrical energy to sound, light, heat, etc.
• Relationship between current, resistance, and voltage:
• If we increase the voltage, the current goes up
• If we increase the resistance, the current goes down.