Teratogens: CNS Destruction
advertisement

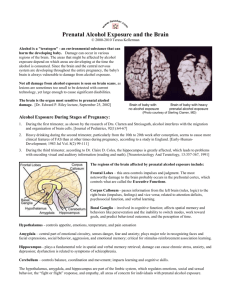
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Persists • Rekindling awareness for the new millennium Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Persists • Research strong in 1970’s-1980’s – Culture insures the problem persists • Fetal damage: body, mind, social issues – Nature insures the problem persists • Topic bridges the gap between science, medical, clinical, social, and practical FAS Problem, Researchers • “Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) now is recognized as the leading known cause of mental retardation in the US, surpassing Down syndrome and spina bifida.” Ann Streissguth, Ph.D Alcohol Affects Placenta • Late-term fetus • Placenta structure and function • Umbilical cord • Alcohol reduces oxygen to fetus • Alcohol reduces AA’s, glucose & vitamins passing thru placenta Migrating Nascent Neurons Teratogen: Alcohol • • • • Maternal blood alcohol concentration Alcohol breakdown (liver) elimination Fetus BAC Alcohol diffusion across placenta – High concentration to low – No liver enzymes to breakdown alcohol – Alcohol diffuses out when mother BAC is lower than fetal BAC “The Mind” FAS Lip-Philtrum Guide Alcohol as a Teratogen • • • • • • • FAS/FAE continuum: who is affected? Agent: Alcohol Dose: light, moderate, heavy, binge Timing: 1st, 2nd, 3rd trimester Genetic/metabolic factors: enzymes Nutritional: vitamins, prenatal care Polydrug use: smoking, others FASD Changes • Cognitive changes – Intelligence – Math weakness • Social changes – Several antisocial behaviors – Prison time • FAS induced static encephalopathy – Several abnormalities FASD Developmental Changes Physical alterations: – Face, less noticeable – Size, smaller than average • Cognitive changes (few alterations) – Math problems persist – Abstract thinking, problem solving same • Social problems same or worse FASD Social Challenges • • • • • • • • • Failure to consider consequences Unresponsive to subtle social cues Lack of friendships Stubbornness or sullenness Low self-esteem Social withdrawal Teasing or bullying Dishonesty Excessive unhappiness FASD School Challenges • • • • • • • Lack of initiative Poor concentration Poor math skills Dependency Impulsivity ADHD symptoms Adverse relationships with teachers FASD Adult Challenges • Delinquent behaviors • Sexual problems – Pregnancy, paternity – STD’s • Not able to find and hold jobs • Drug use and abuse including alcohol • Prison recidivism, est. 1/5 prisoners FAS FAS Statistics • • • • • • Over 10,000 births/day in USA FAS births: 1/700 = 14/day FAE disorders: 1/100 = 100/day Over 90% FAS/FAE develop mental probs Lifetime cost: $5M/FAS person Taxpayers cost: $5M/day, $1.9B/year Alternatives & Solutions • Challenges: – Clinicians have a good understanding of alcohol’s ability to damage CNS – Educators inform themselves & students – Parental involvement = better outcomes – Community assistance • Living/working arrangements • Alternatives to prison Teacher’s Opportunities • More info: NEW K-12 Curriculum Available from NOFAS from CDC education and prevention program • PPT show package about FAS • Resource guide for teachers working with FAS students • Biological Psychology can be useful • Students will make choices • Informed students make better choices Off to a Great Start… Ashley M Lorenz