Lecture19
advertisement

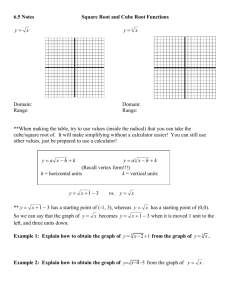
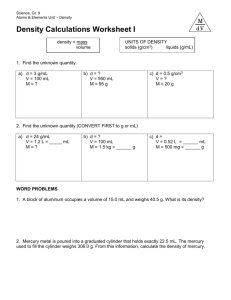
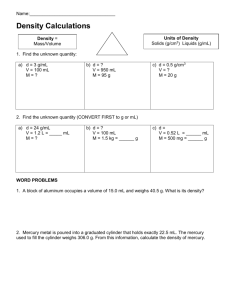
Reading Quiz A cube made of solid wood floats when put into water. This means that •the cube weighs less than an equal volume of water. •the cube weighs the same as an equal volume of water. •the cube weighs more than an equal volume of water. Previous Unit: The Newtonian Revolution What have we learned…. Force, F=ma constant acceleration Third Law torque Gravitational force law g= 9.8 m/s/s Work, energy, power Conservation of energy Conservation of momentum Conservation of angular momentum The New Unit: Fluids and Heat Questions: What are fluids, liquids, gases? What forces do liquids apply to objects? Is the atmosphere a fluid? How do fluids flow? A woman’s high heels sink into the soft ground, but the larger shoes of the much bigger man do not. Pressure = force/area The pressure exerted on the piston extends uniformly throughout the fluid, causing it to push outward with equal force per unit area on the walls and bottom of the cylinder. Pascal’s Principle: Any change in the pressure of a fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions throughout the fluid. A small force F1 applied to a piston with a small area produces a much larger force F2 on the larger piston. This allows a hydraulic jack to lift heavy objects. Torricelli filled a tube with mercury and inverted it into an open container of mercury. Air pressure acting on the mercury in the dish can support a column of mercury 76 cm in height. How much does the atmosphere weigh? The same as 76 cm of mercury. 76cm mercury=1.01x105 pascals Standard atmospheric pressure 32 feet of water or 14.7Lbs/in2 A balloon that was partially inflated near sea level expanded as the experimenters climbed the mountain. Atmospheric pressure changes with altitude. P1V1 = P2V2 Temperature Constant Boyle’s Law The density of a column of air decreases as altitude increases because air expands as pressure decreases. P1V1 = P2V2 Boyle’s Law The atoms in a liquid are closely packed while those in a gas are separated by much larger distances. Gas have a density ~ 1/1000 x liguid density In Boyle’s experiment, adding mercury to the open side of the bent tube caused a decrease in the volume of the trapped air in the closed side. P1V1 = P2V2 Boyle’s Law Archimedes’ Principle: The buoyant force acting on an object fully or partially submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The weight of a column of water is proportional to the volume of the column. The volume V is equal to the area A times the height h. Equilibrium… The pressure acting on the bottom of the suspended metal block is greater than that acting on the top due to the increase of pressure with depth. Lecture Quiz - Question 1: A large metal tank is filled with high pressure of Helium, used to fill Helium balloons. Consider how much the tank weighs when it is full, and when empty. A. The weight is the same full or empty. B. The empty tank weighs less than the full tank. C. The tank weighs less when it is full, because Helium is lighter than air. Lecture - Question 2: One cubic centimeter of Aluminum weighs 2.7 gms (rAl=2.7 gms/cm3). The Al cube is placed in a beaker of water. A. The upward buoyant force on the cube equals the downward force (weight). B. The weight of the displaced water equals the weight of the cube. C. The weight of the cube is reduced in water do to the buoyant force. D. The cube floats, because Aluminum is lighter than water. Lecture - Question 3: A block of wood is added to a beaker of water. It floats. The beaker rests on a scale that reads its weight. A. There is no change in weight, because the buoyant force equals the weight of the water. B. The weight increases by the weight of the block. C. The weight increases by an amount less than the weight of the block.