K.Ohkuma
advertisement

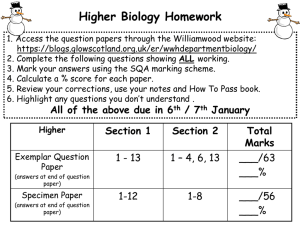
7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections New Physics Search through gg → t t → l X / b X 7/Oct./2005@Shonan Village Kazumasa OHKUMA Based on hep-ph/0508183 PLB593 (2004) 189 & (Fukui Tech.) NPB689 (2004) 108 In collaboration with B.Grzadkowski (Warsaw Univ.) , Z. Hioki (Tokushima Univ.) J.Wudka (UC Riverside) Plan of talk I. Introduction II. Framework III. Optimal-Observable Analysis IV. Summary I. Introduction ★Standard Model is composed by Electro-weak theory and Quantum chromodynamics Highly Successful Model But!! There are some unsolved problems •Many parameters (Couplings, CKM, ‥‥) •Origin of masses •Hierarchy New Physics beyond Standard Model 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-1 How to search for the signal of new physics? One of answers: Top quark physics. Why? Ans. There are some advantageous properties; (1) Heaviest particle observed to date ! ! (i) Sensitive to SSB Higgs (ii) Decay as a free quark ! τ<<10-23[s] Clear information about top quark (2) On top quark sector, C P is negligible in SM ! ! Large CP indicates new physics contribution. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-2 In order to study non-standard effect, we focus on at Photon Collider Interesting option of ILC. Initial CP parity is controllable !! Only CP-even state at ee collider • Couple to CP-odd scalar particles We estimate Statistical Significance of non-Standard Couplings and probe Optimal Beam Polarizations for New Physics Search 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-3 II. Framework ★ Effective Lagrangian approach Model Independent Analysis Complementary relation Model Dependent Analysis Assumption • New fields are not in existence under L scale. • New heavy particles are decoupled. SM Lagrangian is modified by dk quantum effect of new physics. : Energy scale of new physics : SU(3) X SU(2) X U(1) invariant Dim.6 operators : non-standard couplings W.Buchmuller and D.Wyler, NPB268(1986)621 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-4 Top Quark Production Effective Operators for γγ→ t t ttg interaction (Top EDM) ttgg interaction (Contact Interaction) We found relations between EDM operators and Contact interaction operators. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-5 Relations of Operators Bianchi identities and SM classical motion of equations for quark and vector bosons lead us to 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-6 × × × × × × × × × × × : No contribution Need not to consider Contact Interaction. Effective Operators for gg→(H)→t t ggH interaction (Higgs property) Top Decay Effective Operators for t → b W tbW interaction 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-7 Feynman rules for on-shell photos ★ Top Electric Dipole Moment interaction : ag (1) C P-conserving ttg vertex (2) C P-violating ttg vertex ★ Higgs Exchange interaction : ah (1) C P-conserving ggH vertex (2) C P-violating ggH vertex 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-8 ★ Decay Vertex 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-9 Feynman Diagrams for gg → t t S.Y.Choi and Hagiwara PLB359(1995)369, P.Poulos and S.D.Rindani PRD56(1997)6835, etc. B.Grzadkowski and J.F.Gunion, PLB294(1992)316, G.J.Gounaris and G.P.Tsirigoti,PRD56(1997)3030, E.Asakawa, J.Kamoshita, A.Sugamoto and I.Watanabe,EPJC14(2000)335, E.Asakawa, S.Y.Choi,K.Hagiwara and J.S.Lee, PRD62(2000)115005, R.M.Godbole, S.D.Rindani and R.K.Shigh PRD67(2003)095009, etc. In actual experiment, their mixed signals will be observed !! All possible non-standard interactions are taken into account. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-10 III. Optimal Observable Analysis What is Optimal Observable Analysis ? Method for estimating the precision of determination of relevant non-standard couplings. J. F. Gunion, et.al, PRL77 (1996) 5172 How to estimate these precision ? Suppose following distribution: Cross section : final-state phase space : known functions ← Calculable : model-independent coefficients 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-11 Extract C i using appropriate weighting function Extract In general, different choice for the are possible. There is a unique choice which minimizes the resultant statistical uncertainty: DCi. Such function is given by 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-12 Inverse matrix of Mij : Calculable Statistical uncertainty of Ci is given by : Event number : Total cross section Apply to analysis of final-lepton’s energy and angular distribution for . 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-13 Application e.g. Final-lepton’s energy and angular distribution EDM Calculable Higgs Decay 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-14 Matrix Element Mij Inverse where I,J=1,‥,6 correspond to SM, g1,g2, h1, h2 and d, respectively. EX. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-15 Parameters of Photon collider High energy colliding beams of polarized photons are generated by Compton backscattering : Initial electron longitudinal polarization : Degree of circular polarization of initial laser : Degree of linear polarization of initial laser with azimuthal angle 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-16 Probing optimal photon beam polarizations Estimate the uncertainty of couplings Search for the combinations that make varying polarization parameters as minimal, Note 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-17 Unfortunately ! Our results for Xij are very unstable even a tiny fluctuation of Mij changes Xij significantly ! All the couplings cannot be determined at the same time from only . Refrain from determining all the couplings at once. Assumption Some non-standard couplings Ci have been measured in other processes e.g. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-18 Result Under the conditions: , , 5 and 4 parameters analyses lead to unstable solutions. 3 and 2 parameters analysis give stable solutions within 10% ambiguity 3 parameter case : 3 combinations are OK final lepton 1 final bottom 2 2 parameter case : 68 combinations are OK final lepton 39 final bottom 29 Some results are presented hereafter. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-19 Results (3 parameter analysis) Charged-lepton detection (2 of 3) Bottom-quark detection Not so small ! with with : detection efficiency 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-20 Results (2 parameter analysis) There are 68 stable solutions. However All the stable solutions do not give us good statistical precisions. Two statistical uncertainties ( satisfy , ) is minimal for each pair of 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections and 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-21 Results (2 parameter analysis) mH=300 GeV •Final lepton detection 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-22 Results (2 parameter analysis) mH=300 GeV •Final bottom quark detection 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-23 Results (2 parameter analysis) Independent of Higgs mass •Final lepton detection Note There are no combinations which make ag2 small (ag2 < 0.1). 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-24 IV. Summary To study non-standard Effect in top quark . production,we focus on Model independent analysis were performed using effective low-energy Lagrangian. Statistical uncertainties were estimated - CP conserving and violating ttg coupling :ag1,ag2 - CP conserving and violating ggH coupling :ah1,ah2 - anomalous tbW coupling :ad using Optimal Observable method. Probe Optimal beam polarizations for New physics search 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-25 Adjusting beam polarization gives us good statistical precisions: in two parameter analysis - all non-standard couplings (except for ag2) could be determined with accuracy better than 0.1 with a integrated luminosity of 500 fb-1. It is useful to probe the proprieties of Higgs boson couplings. - the statistical uncertainty of large in this analysis. ag2 is still We look for anther processes to determine ag2. 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Page-26 Back up Comparing ee and gg colliders Top quark productions ee collider gg collider It is possible to measure ttg coupling at both colliders. Within the framework of the effective Lagrangian, we can estimate D a g . 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix Note! In the ee ag2 tt l / b X , could not be measured. In gg tt l / b X , ag2 could be measured though it’s not to be measured precisely. B.Grazkowski and Z. Hioki, NP B484 (1997) 17, NP B585 (2000) 3 L. Brzezinski, Grzadkowski and Z. Hioki, Int. J. Mod. Phys. A14 (1999) 1261 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix Comparison of ag1 measurement in ee and gg colliders 1 parameter Optimal Observable analysis ee gg tt tt l X l X 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections ee colliders will give us slightly good precision. 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix Comparing ee and gg colliders ee collider ( e e l / b X ) It seems to be slightly favored to measure ag1. ag2 could not measure in the process. gg collider ( gg tt tt l / b X ) ag2 could be measured in the process. (precision is not good) It seems to be very useful for testing the Higgs coupling. Looking for the processes or observable that make statistical sensitivity small for the measuring ag2 is important ! Circular polarization Asymmetry (-) (-) 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix Linear polarization Asymmetry 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix Results (2 parameter analysis) mH=300 GeV •Final bottom quark detection 7th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections 7/Oct./2005 Shonan Village Appendix