Economic Systems.PPT
1.4 Economic Systems
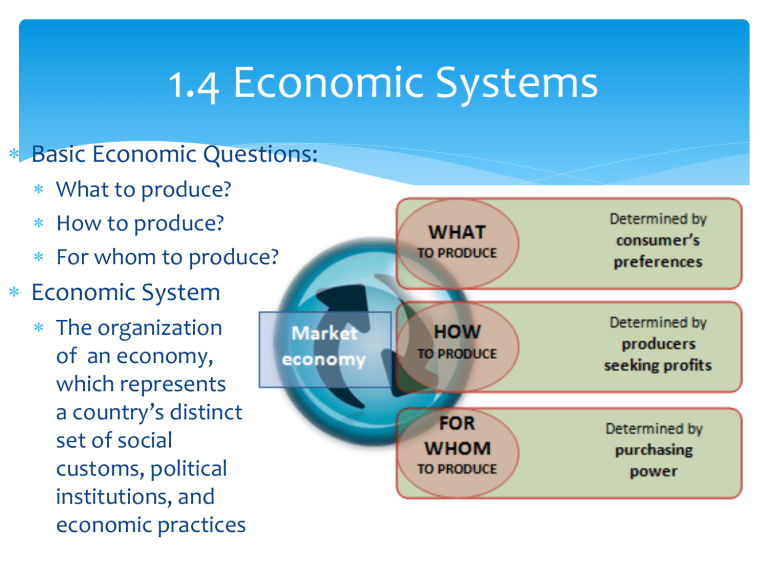
Basic Economic Questions:
What to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
Economic System
The organization of an economy, which represents a country’s distinct set of social customs, political institutions, and economic practices
Traditional Economy
Exactly what it sounds like: everything is based on traditions
i.e. what your dad did you will do
What to produce?
Same as always
How to produce?
Same methods
For whom to produce?
Same customers
Traditional Economy Cont’d
Positives
Very stable and predictable
Negatives
Poor at adaption
Limited Choices
Very Rare
Attacked by increased expectations
Example of a Traditional Economy
Inuit of Northern Canada
For thousands of years, Inuit parents have been teaching their children the survival skills that they need to survive in the severe climate of the Arctic Circle
The children are taught how to fish, hunt, and make traditional tools
If a walrus or bear is caught, hunters divide it evenly into as many pieces as there are heads of families in the hunting party
The hunter most responsible for the successful hunt has first choice, the second-most helpful hunter chooses next, and so on
Market Economy
Everything is based on consumer sovereignty
You decide
What to produce?
Whatever consumers want
How to produce?
Cheapest and most efficient way possible
For whom to produce?
Whoever will buy
Market Economy Cont’d
Positives
Innovation
Flexibility
Efficiency
Negatives
If it isn’t profitable, don’t do it
Cut-throat
Intangibles
Human Costs
Resource Markets
Product Markets
Market Economy Cont’d
Resource Market
Markets in which economic resources are traded
Product Markets
Markets in which consumer products are traded
Resource Markets
Product Markets
Command (Planned) Economy
Opposite to a Market Economy
Command Economy
An economic system based on public ownership and central planning
Rather than production being based on consumer wants, command economies rely on planners to decide what should be produced, how production should be carried out, and how the output should be distributed
Command Economy Cont’d
Positives
Easy on the consumer
Direction of resources to who you feel needs them
Negatives
Hard to predict the future unknowns
Lack of freedom
Mixed Economies
Most countries fall between the extremes of traditional, market and command economies
Modern Mixed Economy
An economic system that combines aspects of a market economy and a command economy
Production decisions are made in both private market and by government
Traditional Mixed Economies
Economic systems in which a traditional sector co-exists with modern sectors
Mixed Economies – USA & China
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XYXD3YsBxU
Definitions
Circular Flows
The circulation of money and the circulation of consumer products and economic resources in the economy
Consumer Sovereignty
The effect of consumer needs and wants on production decisions
Invisible Hand
The tendency for competitive markets to turn self-interested behaviour into socially beneficial activity
Or, stated a different way:
“[t]he invisible hand is essentially a natural phenomenon that guides free markets and capitalism through competition for scarce resources.”
Private, Public & Traditional
Private Sector
The part of an economy in which private markets dominate
Public Sector
The part of an economy in which governments dominate
Traditional Sector
The part of an economy in which custom and traditional production techniques dominate
Economic Goals
Income Equity
Achieved when a country’s total output is distributed fairly
“What is fair”? Is it fair that the salary of a bank executive is hundreds of times higher than the year’s wages of a part-time gardener?
Since value judgment comes into play, satisfying income equity is controversial
Price Stability
Government tries to minimize the country’s rate of inflation (rise in general level of prices)
Purchasing power falls
Peoples incomes don’t necessarily increase
Economic Goals
Full Employment
Government wants to minimize involuntary unemployment
Labour Force: those working and those involuntarily unemployed and actively seeking employment
Unemployment Rate: the percentage of a labour force that is involuntarily unemployed
Viable Balance of Payments
Due to Canada’s dependence on foreign markets, it is important that Canadian imports and exports roughly balance one another
Economic Growth
Outward shift in PPF curve
Helps raise average standard of living in a country
Good for emerging economies trying to eradicate extreme poverty
Economic Goals
Economic Efficiency
Getting the highest benefit from an economy’s scarce resources
Scare economic resources need to be employed in a way that maximizes utility
Environmental Sustainability
While economic activity is carried out, the physical environment should also be sustained without significant harm
Significant changes in the climate recently have been attributed to irreversible damage to the climate via economic activity
Economic Goals
Complementary Goals
Reaching one economic goal makes the other one easier
e.g. Full Employment and Economic Growth
Conflicting Goals
Attaining one goal makes another goal more difficult to achieve
e.g. Price Stability and Full
Employment
These issues are resolved by making priorities, where one goal is achieved at the cost of another







