Document
advertisement

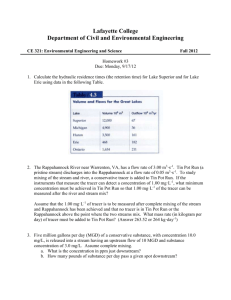
Environmental Modeling Chapter 7: Dissolved Oxygen Sag Curves in Streams Copyright © 2006 by DBS Quote “[Mathematics] The handmaiden of the Sciences” -Eric Temple Bell Concepts • • • • • Introduction Input sources Mathematical Model Sensitivity analysis Limitations Case Study: Any Stream, Anywhere • Every stream has inputs of organic waste – Spreads disease – Consumes DO on decomposition • Ancient communities built near flowing water e.g. NY City, London, W. Europe Meadows et al., 2004 ChemicalCase process:Study: Any Stream, Anywhere MO’s consume DO Physical process: Re-aeration by atmosphere The Problem: D.O. < BOD Sewage treatment begins Introduction • Modeling the effects of release of oxidizable organic matter into a flowing body of water – DO = chemical measurement of dissolved oxygen (mg L-1) – BOD = total DO needed to oxidize organic matter in a water sample = change from initial DO at saturation to amount after 5 days BOD time Wipple and Wipple (1911) Introduction • Standard of living ~ adequate water and wastewater treatment Human Risks • Challenge of preventing rapid spead of disease e.g. typhoid fever (bacteria), hepatitis (viruses), cryptosporidosis (protozoa) • Removed by sand filtration and chlorination/ozonation Aquatic Risks • Aerobic organisms depend on DO • 8-12 mg L-1 • Affected by temperature and salt Inc. salt dec. DO Organic matter is oxidized, stream re-aerates The Streeter-Phelps Equation without trmt: with trmt: End • Review Basic Input Sources • Parameters for S-P equation: – Wastewater: Flow rate, temperature, DO, BOD • BOD measured in lab – DO measured after several days (flat portion of curve) • The following material and model is covered in: CHEM3500/3550 Basic Input Sources Sewage Treatment Plants • Remove turbidity, oxidizable organic matter, and pathogens – Turbidity – settling tanks and filters – Organic matter – trickling filters, activated sludge – Pathogens – filtration, chloination, ozonation ftp://ftp.wiley.com/public/sci_tech_med/pollutant_fate/ Basic Input Sources Sewage Treatment Plants • Prelininary - screening of large materials • Primary - sedimentation - settling tanks • Secondary - biological aeration – trickling filters, activated sludge - metabolizes and flocculates dissolved organics • Tertiary – e.g. P removal http://www.waterencyclopedia.com/Tw-Z/Wastewater-Treatment-and-Management.html Basic Input Sources • Wastewater Treatment Plant Model Movie 1. Wastewater Treatment and Discharge (2000) 2. Wastewater Generation and Collection (2000) 3. Our Urban Environment: Water Quality (2000) End • Review Mathematical Model Take a river: What parameters and processes would be important in developing a model for the oxidation of organic waste? Amount DO consumed our model river: draw in parameters Re-aeration by atmosphere Consumption DO by MO’s Ultimate BODLof mix Stream DO deficit The Streeter-Phelps Equation D = k’BODL [exp(-k’(x/v) – exp(-k2’(x/v))] + D0exp(-k2’(x/v)) k2’ – k’ Consumption by MO’s where: Re-aeration by atmos. O2 D = DO concentration deficit (value below saturation) (mg L-1), k’2= the re-aeration constant (in d-1), BODL= the ultimate BOD (in mg L-1), k’= the BOD rate constant for oxidation (d-1), x = distance downstream from the point source (km), v = average water velocity (km d-1) Do= initial oxygen deficit of mixed stream and wastewater (mg L-1) D is not the remaining DO content but the amount of original DO consumed…must be subtracted from original DO without BOD waste The Streeter-Phelps Equation DO at a given distance below the input: The Streeter-Phelps Equation • k2’ = first-order rate constant for re-aeration • Eact measurements are difficult, get from tables: The Streeter-Phelps Equation • BODL = ultimate BOD or maximum O2 required to oxize the waste sample • Determined from 5 day BOD test or using equation: BODL = BOD5 1 – exp(-k’(x/v)) • Where k’ is obtained from a 20 day BOD experiment • D0 = DO level in the stream upstream from input - initial DO of stream-waste mixture Algae, fungi, protozoa, worms, larger planst die Gray/black, H2S, CH4, NH3 productions, The Streeter-Phelps Equation Zone of Clean Water (Zone 1) Zone of Degradation (Zone 2) Zone of Active Decomposition (Zone 3) Zone of Recovery (Zone 4) Zone of Cleaner Water (Zone 5) Minimum D = critical dissolved oxygen = Dc The Streeter-Phelps Equation tc = 1 k2’ – k’ ln k2’ 1 – D0(k2’-k’) k’ k’ BODL and xc = vtc Critical DO concentration, Dc: Dc = k’ BODL exp(-k’(xc/v)) k 2’ Problem Example Problem: A city discharges 25 million gallons per day of domestic sewage into a stream whose typical rate of flow is 250 cubic feet per second. The velocity of the stream is appoximately 3 miles per hour. The temperature of the sewage is 21 °C, while that of the stream is 15 °C. The 20 °C BOD5 of the sewage is 180 mg/L, while that of the stream is 1.0 mg/L. The sewage contains no DO, but the stream is 90% saturated upstream of the discharge. At 20 °C, k’ is estimated to be 0.34 per day while k2’ is 0.65 per day. 1. Determine Dc and its location. 2. Estimate the 20 °C BOD5 of a sample taken at xc. 3. Plot the curve. 1. Determine DO in stream before discharge (=upstream DO): Saturation conc. at 15 °C = 10.2 mg/L Upstream is 90% saturated = 10.2 mg/L x 0.90 = 9.2 mg/L 2. Determine mixture, T, DO, and BOD using mass balance: Flow rate stream: = 250 ft3/s = 612 x 106 L/d Flow rate sewage: 25 x 106 gallons/d = 94.8 x 106 L/d Temperature of mixture: T = stream input + sewage input – output effect 0 = (stream flow)(stream temp.) + (sewage flow)( sewage temp) – (mix flow)(mix temp) 0 = (612 x 106 L/d)(15 °C) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(20 °C) – (612 x 106 L/d + 94.8 x 106 L/d)Tmix Tmix = (612 x 106 L/d)(15 °C) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(20 °C) = 15.7 °C (612 x 106 L/d +94.8 x 106 L/d) DO in mixture Net change in DO = Stream input + Sewage output – Output 0 = (stream flow)(stream DO) + (sewage flow)(sewage DO) – (mix flow)(mix DO) 0 = (612 x 106 L/d)(9.2 mg/L) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(0.0) - (612 x 106 L/d + 94.8 x 106 L/d)(Domix) DOmix = (612 x 106 L/d)(9.2 mg/L) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(0.0 mg/L) (612 x 106 L/d + 94.8 x 106 L/d) = 7.97 mg/L BOD5 of mixture: Net change in BOD5 = BOD5 = Stream input + Sewage output – Output 0 = (stream flow)(stream BOD5) + (sewage flow)(sewage BOD5) – (mix flow)(mix BOD5) 0 = (612 x 106 L/d)(1.0 mg/L) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(80 mg/L) - (612 x 106 L/d + 94.8 x 106 L/d)(BOD5) BOD5mixture = (612 x 106 L/d)(1.0 mg/L) + (94.8 x 106 L/d)(80 mg/L) = 25.0 mg/L (612 x 106 L/d + 94.8 x 106 L/d) BODL of mixture (at 20 °C) BODL = BOD5 1 – exp(-k’(x/v) = 25.0 mg/L 1 – exp(-0.34/d)(5 d) = 30.6 mg/L 3. Correct rate constants to 15.7 °C k’ = 0.34(1.135)15.7-20 = 0.197 d-1 k2’ = 0.65(1.024)15.7-20 = 0.587 d-1 4. Determine tc and xc: D0 = (initial stream O2 - O2 of mixture) = (9.2 – 7.97) = 1.23 mg O2 L-1 4. Determine tc and xc: tc = 1 k2’ – k’ ln k2’ k’ 1 – D0(k2’-k’) k’ BODL = 2.42 d xc = vtc = 3 mi/h x 24 h/d x 2.42 d = 174.2 mi = 280 km 5. Determine Dc: 5. Determine Dc: V = 3 mi/h = 72 mi/d Dc = k’ BODL exp(-k’(xc/v) k2’ = 0.197 d-1 (30.6 mg/L) exp(-(0.197 d-1)(174.2 mi / 72 mi d-1))) 0.587 d-1 = 6.37 mg L-1 The DO will be depressed 6.37 mg L-1 from saturation. Minimum DO = 9.2 mg L-1 - 6.37 mg L-1 = 2.83 mg L-1 6. Determine BOD5 at critical point, xc: BOD5 = BODL exp(-k’(x/v)) = (30.6 mg L-1) exp(-0.197 d-1)(174.2 mi)/(72 mi d-1) = 19.0 mg L-1 20 °C BOD5 = BOD5 [1 – exp(-k’)(5)] = 19.0 mg L-1 [1 – exp(-0.34 d-1)(5 d)] = 15.5 mg L-1 Easier method • Use Fate!!! • Much easier than by hand End • Review Sensitivity Analysis Limitations • It uses average re-aeration rates of the stream (problem in alternating riffle and pool areas) • Sedimentation is not allowed in the basic model, but can be incorporated with additional experimental data Remediation • Problems are: • Source removal! (install treatment plant) including BOD, NO3-, NH3/NH4+, PO43removal, but you still will have organic rich sediments for some time • Time (flowing aquatic systems can be very resilient) • Notice the difference between the recovery of a biodegradable pollutant versus nonbiodegradable! -Eutrophication -Odors -Low/no D.O. -Aquatic death -Microbes/Pathogens End • Review Further Reading Journals and Reports • Wipple, G.C. and Wipple, M.C. (1911) Solubility of oxygen in sea water. Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 3 pp 362. Books • • • • • • • • Craun, G. (1986) Waterborne Diseases in the United States. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Meadows, D., Randers, J., and Meadows, D. (2004) Limits to Growth: The 30-Year Update. Chelsea Gren Publishing Compnay, White River Junction, VT. Metcalf and Eddy Inc. (1991) Wastewater Engineering, 3rd Ed. McGraw-Hill, New York. Sawyer, C.N. and McCarty, P.L. (1978) Chemistry for Environmental Engineering. McGrawHill, New York. Snoeyink, V.L. and Jenkins, D. (1980) Water Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Ed. (1998) American Waterworks Association, Washington D.C. Streeter, H.W. and Phelps, E.B. (1925) A Study of the Pollution and natural Purification of the Ohio River. United States Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare. Tchobanoglous, G. and Burton, F.L. (1991) Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse. McGraw-Hill, New York.