C470PS1
advertisement

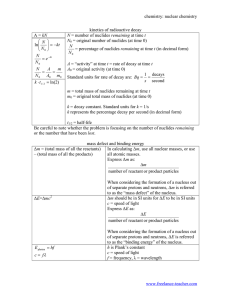
Chemistry 470 – Problem Set #1 Due: Monday Feb. 6, 2012…Thursday Feb. 9 1. Assigned 1/11/12 Using Table of Nuclides (Appendix in either texts or other Nuclear Chemistry texts) or the government website containing the “Nuclear Wallet Cards” ( http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/wallet/ ), find the RA decay modes, and write an equation or equations describing the RA decay(s) of each of the following nuclides. (a) (g) 3 H Tc 97 (b) (h) 8 Li Tc 99 (c) (i) 7 Be (d) Pu 8 B (e) 32 P (f) 60 Co 239 2. The stable isotopes of boron are boron -10 and boron -11. Four RA isotopes with mass numbers 8, 9, 12 and 13 are also known. Explain and predict possible modes of RA decay for these four nuclides. Write appropriate equations. Check against experimental data. 3. Calculate the binding energy (MeV) per nucleon for 24Mg and 27Mg. The atomic masses are: 24Mg=23.9850 and 27Mg=26.9843. 4. A positron and an electron annihilate each other upon collision, producing energy. Write an appropriate equation and calculate the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation produced. 5. Calculate the amount of energy released per gram of hydrogen for the combination of 2 hydrogen atoms. The atomic masses are: 1 2 H=1.00782 and H=2.01410 Write the nuclear equation. Provide the energy Q in units of J per gram of 1H . 6. Using the “Appendix B: Relativistic Relations” in the FKMM text (also posted on Dr. Ng’s website under the “Library of Resources” Hyperlink), calculate (a) the mass (b) the kinetic energy (both in MeV), of an electron traveling at 1.90x108 m/s. 7. Given that the mean binding energy per nucleon of 20Ne is 8.0323 MeV, and that the atomic weight of natural Ne is 20.183 g/mol, calculate the natural abundance of 22Ne assuming that natural Ne consists of only Ne-20 and Ne-22 (mass of 22Ne=21.99138 amu) p+=1.00728 n=1.00867 e-=0.000549